聊聊java高并發系統之異步非阻塞
在做電商系統時,流量入口如首頁、活動頁、商品詳情頁等系統承載了網站的大部分流量,而這些系統的主要職責包括聚合數據拼裝模板、熱點統計、緩存、下游功能降級開關、托底數據等等。其中聚合數據需要調用其它多個系統服務獲取數據、拼裝數據/模板然后返回給前端,聚合數據來源主要有依賴系統/服務、緩存、數據庫等;而系統之間的調用可以通過如http接口調用(如HttpClient)、SOA服務調用(如dubbo、thrift)等等。
在Java中,如使用Tomcat,一個請求會分配一個線程進行請求處理,該線程負責獲取數據、拼裝數據或模板然后返回給前端;在同步調用獲取數據接口的情況下(等待依賴系統返回數據),整個線程是一直被占用并阻塞的。如果有大量的這種請求,每個請求占用一個線程,但線程一直處于阻塞,降低了系統的吞吐量,這將導致應用的吞吐量下降;我們希望在調用依賴的服務響應比較慢,此時應該讓出線程和CPU來處理下一個請求,當依賴的服務返回了再分配相應的線程來繼續處理。而這應該有更好的解決方案:異步/協程。而Java是不支持協程的(雖然有些Java框架說支持,但還是高層API的封裝),因此在Java中我們還可以使用異步來提升吞吐量。目前java一些開源框架(HttpClient\HttpAsyncClient、dubbo、thrift等等)大部分都支持。
幾種調用方式
同步阻塞調用
即串行調用,響應時間為所有服務的響應時間總和;
半異步(異步Future)
線程池,異步Future,使用場景:并發請求多服務,總耗時為最長響應時間;提升總響應時間,但是阻塞主請求線程,高并發時依然會造成線程數過多,CPU上下文切換;
全異步(Callback)
Callback方式調用,使用場景:不考慮回調時間且只能對結果做簡單處理,如果依賴服務是兩個或兩個以上服務,則不能合并兩個服務的處理結果;不阻塞主請求線程,但使用場景有限。
異步回調鏈式編排
異步回調鏈式編排(JDK8 CompletableFuture),使用場景:其實不是異步調用方式,只是對依賴多服務的Callback調用結果處理做結果編排,來彌補Callback的不足,從而實現全異步鏈式調用。
接下來看看如何設計利用全異步Callback調用和異步回調鏈式編排處理結果來實現全異步系統設計。
同步阻塞調用
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- RpcService rpcService = new RpcService();
- HttpService httpService = new HttpService();
- //耗時10ms
- Map<String, String> result1 = rpcService.getRpcResult();
- //耗時20ms
- Integer result2 = httpService.getHttpResult();
- //總耗時30ms
- }
- static class RpcService {
- Map<String, String> getRpcResult() throws Exception {
- //調用遠程方法(遠程方法耗時約10ms,可以使用Thread.sleep模擬)
- }
- }
- static class HttpService {
- Integer getHttpResult() throws Exception {
- //調用遠程方法(遠程方法耗時約20ms,可以使用Thread.sleep模擬)
- Thread.sleep(20);
- return 0;
- }
- }
- }
半異步(異步Future)
- public class Test {
- final static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- RpcService rpcService = new RpcService();
- HttpService httpService = new HttpService();
- Future<Map<String, String>> future1 = null;
- Future<Integer> future2 = null;
- try {
- future1 = executor.submit(() -> rpcService.getRpcResult());
- future2 = executor.submit(() -> httpService.getHttpResult());
- //耗時10ms
- Map<String, String> result1 = future1.get(300, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- //耗時20ms
- Integer result2 = future2.get(300, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- //總耗時20ms
- } catch (Exception e) {
- if (future1 != null) {
- future1.cancel(true);
- }
- if (future2 != null) {
- future2.cancel(true);
- }
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- static class RpcService {
- Map<String, String> getRpcResult() throws Exception {
- //調用遠程方法(遠程方法耗時約10ms,可以使用Thread.sleep模擬)
- }
- }
- static class HttpService {
- Integer getHttpResult() throws Exception {
- //調用遠程方法(遠程方法耗時約20ms,可以使用Thread.sleep模擬)
- }
- }
- }
全異步(Callback)
- public class AsyncTest {
- public staticHttpAsyncClient httpAsyncClient;
- public static CompletableFuture<String> getHttpData(String url) {
- CompletableFuture asyncFuture = new CompletableFuture();
- HttpPost post = new HttpPost(url);
- HttpAsyncRequestProducer producer = HttpAsyncMethods.create(post);
- AsyncCharConsumer<HttpResponse> consumer = newAsyncCharConsumer<HttpResponse>() {
- HttpResponse response;
- protected HttpResponse buildResult(final HttpContext context) {
- return response;
- }
- …...
- };
- FutureCallback callback = new FutureCallback<HttpResponse>() {
- public void completed(HttpResponse response) {
- asyncFuture.complete(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
- }
- …...
- };
- httpAsyncClient.execute(producer, consumer, callback);
- return asyncFuture;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- AsyncTest.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- Thread.sleep(1000000);
- }
- }
本示例使用HttpAsyncClient演示。
異步回調鏈式編排
CompletableFuture提供了50多個API,可以滿足所需的各種場景的異步處理的編排,在此列舉三個場景:
場景1:三個服務并發異步調用,返回CompletableFuture,不阻塞主線程;
方法test1:
- public static void test1() throws Exception {
- HelloClientDemoTest service = new HelloClientDemoTest();
- /**
- * 場景1 兩個以上服務并發異步調用,返回CompletableFuture,不阻塞主線程
- * 并且兩個服務也是異步非阻塞調用
- */
- CompletableFuture future1 = service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture future2 = service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture future3 =service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- List<CompletableFuture> futureList = Lists.newArrayList(future1,future2, future3);
- CompletableFuture<Void> allDoneFuture =CompletableFuture.allOf(futureList.toArray(newCompletableFuture[futureList.size()]));
- CompletableFuture<String> future4 =allDoneFuture.thenApply(v -> {
- List<Object> result =futureList.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join)
- .collect(Collectors.toList());
- //注意順序
- String result1 = (String)result.get(0);
- String result2 = (String)result.get(1);
- String result3 = (String)result.get(2);
- //處理業務....
- return result1 + result2 + result3;
- }).exceptionally(e -> {
- //e.printStackTrace();
- return "";
- });
- //返回
- }
場景2、兩個服務并發異步調用,返回CompletableFuture,不阻塞主線程;
方法test2:
- public void test2() throws Exception {
- HelloClientDemoTest service = new HelloClientDemoTest();
- /**
- * 場景2 兩個接口并發異步調用,返回CompletableFuture,不阻塞主線程
- * 并且兩個服務也是異步非阻塞調用
- */
- CompletableFuture future1 = service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture future2 =service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture future3 =future1.thenCombine(future2, (f1, f2) -> {
- //處理業務....
- return f1 + "," + f2;
- }).exceptionally(e -> {
- return "";
- });
- //返回
- }
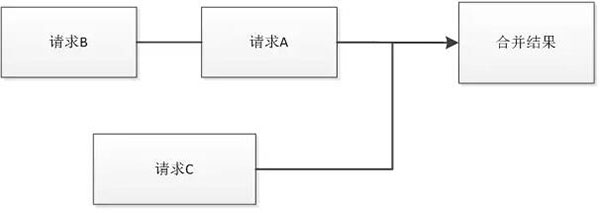
場景3、兩個服務,并發異步調用兩個服務,并且一個服務的結果返回后再次調用另一服務,然后將三個結果后并處理,返回CompletableFuture,整個處理過程中不阻塞任何線程;
方法test3:
- publicvoid test3() throws Exception {
- HelloClientDemoTest service = new HelloClientDemoTest();
- /**
- * 場景3 兩請求依賴調用,然后與另一服務結果組合處理,返回CompletableFuture,不阻塞主線程
- * 并且兩個服務也是異步非阻塞調用
- */
- CompletableFuture future1 = service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture future2 = service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- CompletableFuture<String> future3= future1.thenApply((param) -> {
- CompletableFuture future4 =service.getHttpData("http://www.jd.com");
- return future4;
- });
- CompletableFuture future5 =future2.thenCombine(future3, (f2, f3) -> {
- //....處理業務
- return f2 + "," + f3;
- }).exceptionally(e -> {
- return "";
- });
- //返回future5
- }
全異步Web系統設計
主要技術:servlet3,JDK8 CompletableFuture,支持異步Callback調用的RPC框架。
先看一下處理流程圖:
servlet3:Servlet 接收到請求之后,可能首先需要對請求攜帶的數據進行一些預處理;接著,Servlet 線程將請求轉交給一個異步線程來執行業務處理,線程本身返回至容器。針對業務處理較耗時的情況,這將大大減少服務器資源的占用,并且提高并發處理速度。servlet3可參考商品詳情頁系統的Servlet3異步化實踐,結合其中講解的servlet3整合:
- public void submitFuture(finalHttpServletRequest req, final Callable<CompletableFuture> task) throwsException{
- final String uri = req.getRequestURI();
- final Map<String, String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
- final AsyncContext asyncContext = req.startAsync();
- asyncContext.getRequest().setAttribute("uri", uri);
- asyncContext.getRequest().setAttribute("params", params);
- asyncContext.setTimeout(asyncTimeoutInSeconds * 1000);
- if(asyncListener != null) {
- asyncContext.addListener(asyncListener);
- }
- CompletableFuture future = task.call();
- future.thenAccept(result -> {
- HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse)asyncContext.getResponse();
- try {
- if(result instanceof String) {
- byte[] bytes = new byte[0];
- if (StringUtils.isBlank(result)){
- resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=gbk");
- resp.setContentLength(0);
- } else {
- bytes =result.getBytes("GBK");
- }
- //resp.setBufferSize(bytes.length);
- resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=gbk");
- if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(localIp)) {
- resp.setHeader("t.ser", localIp);
- }
- resp.setContentLength(bytes.length);
- resp.getOutputStream().write(bytes);
- } else {
- write(resp,JSONUtils.toJSON(result));
- }
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); //程序內部錯誤
- try {
- LOG.error("get infoerror, uri : {}, params : {}", uri,JSONUtils.toJSON(params), e);
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- }
- } finally {
- asyncContext.complete();
- }
- }).exceptionally(e -> {
- asyncContext.complete();
- return null;
- });
- }
另外還有Java中協程庫Quasar,可參考《Java的纖程庫 - Quasar》,目前沒有在應用中使用并在測試FiberHttpServlet的時候遇到很多坑,日后把Quasar自如運用后形成日記,希望能結實更多的朋友一起研究,踩坑。
作者:孫偉,目前負責京東商品詳情頁統一服務系統,寫過java,寫過ngx_lua,還寫過storm等,喜歡學習研究新事物。
【本文來自51CTO專欄作者張開濤的微信公眾號(開濤的博客),公眾號id: kaitao-1234567】