JavaScript 語法樹與代碼轉化
JavaScript 語法樹與代碼轉化實踐 歸納于筆者的現代 JavaScript 開發:語法基礎與實踐技巧系列文章中。本文引用的參考資料聲明于 JavaScript 學習與實踐資料索引中,特別需要聲明是部分代碼片引用自 Babel Handbook 開源手冊;也歡迎關注前端每周清單系列獲得一手資訊。
JavaScript 語法樹與代碼轉化
瀏覽器的兼容性問題一直是前端項目開發中的難點之一,往往客戶端瀏覽器的升級無法與語法特性的迭代保持一致;因此我們需要使用大量的墊片(Polyfill),以保證現代語法編寫而成的 JavaScript 順利運行在生產環境下的瀏覽器中,從而在可用性與代碼的可維護性之間達成較好的平衡。而以 Babel 為代表的語法轉化工具能夠幫我們自動將 ES6 等現代 JavaScript 代碼轉化為可以運行在舊版本瀏覽器中的 ES5 或其他同等的實現;實際上,Babel 不僅僅是語法解析器,其更是擁有豐富插件的平臺,稍加擴展即可被應用在前端監控埋點、錯誤日志收集等場景中。筆者也利用 Babel 以及 Babylon 為 swagger-decorator 實現了 flowToDecorator 函數,其能夠從 Flow 文件中自動提取出類型信息并為類屬性添加合適的注解。
Babel
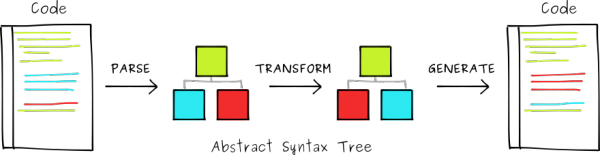
自 Babel 6 之后,核心的 babel-core 僅暴露了部分核心接口,并使用 Babylon 進行語法樹構建,即上圖中的 Parse 與 Generate 步驟;實際的轉化步驟則是由配置的插件(Plugin)完成。而所謂的 Preset 則是一系列插件的合集,譬如 babel-preset-es2015 的源代碼中就定義了一系列的插件:
- return {
- plugins: [
- [transformES2015TemplateLiterals, { loose, spec }],
- transformES2015Literals,
- transformES2015FunctionName,
- [transformES201***rrowFunctions, { spec }],
- transformES2015BlockScopedFunctions,
- [transformES2015Classes, optsLoose],
- transformES2015ObjectSuper,
- ...
- modules === "commonjs" && [transformES2015ModulesCommonJS, optsLoose],
- modules === "systemjs" && [transformES2015ModulesSystemJS, optsLoose],
- modules === "amd" && [transformES2015ModulesAMD, optsLoose],
- modules === "umd" && [transformES2015ModulesUMD, optsLoose],
- [transformRegenerator, { async: false, asyncGenerators: false }]
- ].filter(Boolean) // filter out falsy values
- };
Babel 能夠將輸入的 JavaScript 代碼根據不同的配置將代碼進行適當地轉化,其主要步驟分為解析(Parse)、轉化(Transform)與生成(Generate):
- 在解析步驟中,Babel 分別使用詞法分析(Lexical Analysis)與語法分析(Syntactic Analysis)來將輸入的代碼轉化為抽象語法樹;其中詞法分析步驟會將代碼轉化為令牌流,而語法分析步驟則是將令牌流轉化為語言內置的 AST 表示。
- 在轉化步驟中,Babel 會遍歷上一步生成的令牌流,根據配置對節點進行添加、更新與移除等操作;Babel 本身并沒有進行轉化操作,而是依賴于外置的插件進行實際的轉化。
- ***的代碼生成則是將上一步中經過轉化的抽象語法樹重新生成為代碼,并且同時創建 SourceMap;代碼生成相較于前兩步會簡單很多,其核心思想在于深度優先遍歷抽象語法樹,然后生成對應的代碼字符串。
抽象語法樹
抽象語法樹(Abstract Syntax Tree, AST)的作用在于牢牢抓住程序的脈絡,從而方便編譯過程的后續環節(如代碼生成)對程序進行解讀。AST 就是開發者為語言量身定制的一套模型,基本上語言中的每種結構都與一種 AST 對象相對應。上文提及的解析步驟中的詞法分析步驟會將代碼轉化為所謂的令牌流,譬如對于代碼 n * n,其會被轉化為如下數組:
- [
- { type: { ... }, value: "n", start: 0, end: 1, loc: { ... } },
- { type: { ... }, value: "*", start: 2, end: 3, loc: { ... } },
- { type: { ... }, value: "n", start: 4, end: 5, loc: { ... } },
- ...
- ]
其中每個 type 是一系列描述該令牌屬性的集合:
- {
- type: {
- label: 'name',
- keyword: undefined,
- beforeExpr: false,
- startsExpr: true,
- rightAssociative: false,
- isLoop: false,
- isAssign: false,
- prefix: false,
- postfix: false,
- binop: null,
- updateContext: null
- },
- ...
- }
這里的每一個 type 類似于 AST 中的節點都擁有 start、end、loc 等屬性;在實際應用中,譬如對于 ES6 中的箭頭函數,我們可以通過 babylon 解釋器生成如下的 AST 表示:
- // 源代碼
- (foo, bar) => foo + bar;
- // 簡化的 AST 表示
- {
- "program": {
- "body": [
- {
- "type": "ExpressionStatement",
- "expression": {
- "type": "ArrowFunctionExpression",
- "params": [
- {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "foo"
- },
- {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "bar"
- }
- ],
- "body": {
- "type": "BinaryExpression",
- "left": {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "foo"
- },
- "operator": "+",
- "right": {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "bar"
- }
- }
- }
- }
- ]
- }
- }
我們可以使用 AST Explorer 這個工具進行在線預覽與編輯;在上述的 AST 表示中,顧名思義,ArrowFunctionExpression 就表示該表達式為箭頭函數表達式。該函數擁有 foo 與 bar 這兩個參數,參數所屬的 Identifiers 類型是沒有任何子節點的變量名類型;接下來我們發現加號運算符被表示為了 BinaryExpression 類型,并且其 operator 屬性設置為 +,而左右兩個參數分別掛載于 left 與 right 屬性下。在接下來的轉化步驟中,我們即是需要對這樣的抽象語法樹進行轉換,該步驟主要由 Babel Preset 與 Plugin 控制;Babel 內部提供了 babel-traverse 這個庫來輔助進行 AST 遍歷,該庫還提供了一系列內置的替換與操作接口。而經過轉化之后的 AST 表示如下,在實際開發中我們也常常首先對比轉化前后代碼的 AST 表示的不同,以了解應該進行怎樣的轉化操作:
- // AST shortened for clarity
- {
- "program": {
- "type": "Program",
- "body": [
- {
- "type": "ExpressionStatement",
- "expression": {
- "type": "Literal",
- "value": "use strict"
- }
- },
- {
- "type": "ExpressionStatement",
- "expression": {
- "type": "FunctionExpression",
- "async": false,
- "params": [
- {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "foo"
- },
- {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "bar"
- }
- ],
- "body": {
- "type": "BlockStatement",
- "body": [
- {
- "type": "ReturnStatement",
- "argument": {
- "type": "BinaryExpression",
- "left": {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "foo"
- },
- "operator": "+",
- "right": {
- "type": "Identifier",
- "name": "bar"
- }
- }
- }
- ]
- },
- "parenthesizedExpression": true
- }
- }
- ]
- }
- }
自定義插件
Babel 支持以觀察者(Visitor)模式定義插件,我們可以在 visitor 中預設想要觀察的 Babel 結點類型,然后進行操作;譬如我們需要將下述箭頭函數源代碼轉化為 ES5 中的函數定義:
- // Source Code
- const func = (foo, bar) => foo + bar;
- // Transformed Code
- "use strict";
- const _func = function(_foo, _bar) {
- return _foo + _bar;
- };
在上一節中我們對比過轉化前后兩個函數語法樹的差異,這里我們就開始定義轉化插件。首先每個插件都是以 babel 對象為輸入參數,返回某個包含 visitor 的對象的函數。***我們需要調用 babel-core 提供的 transform 函數來注冊插件,并且指定需要轉化的源代碼或者源代碼文件:
- // plugin.js 文件,定義插件
- import type NodePath from "babel-traverse";
- export default function(babel) {
- const { types: t } = babel;
- return {
- name: "ast-transform", // not required
- visitor: {
- Identifier(path) {
- path.node.name = `_${path.node.name}`;
- },
- ArrowFunctionExpression(path: NodePath<BabelNodeArrowFunctionExpression>, state: Object) {
- // In some conversion cases, it may have already been converted to a function while this callback
- // was queued up.
- if (!path.isArrowFunctionExpression()) return;
- path.arrowFunctionToExpression({
- // While other utils may be fine inserting other arrows to make more transforms possible,
- // the arrow transform itself absolutely cannot insert new arrow functions.
- allowInsertArrow: false,
- specCompliant: !!state.opts.spec
- });
- }
- }
- };
- }
- // babel.js 使用插件
- var babel = require('babel-core');
- var plugin= require('./plugin');
- var out = babel.transform(src, {
- plugins: [plugin]
- });
常用轉化操作
遍歷
- 獲取子節點路徑
我們可以通過 path.node.{property} 的方式來訪問 AST 中節點屬性:
- // the BinaryExpression AST node has properties: `left`, `right`, `operator`
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- path.node.left;
- path.node.right;
- path.node.operator;
- }
我們也可以使用某個路徑對象的 get 方法,通過傳入子路徑的字符串表示來訪問某個屬性:
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- path.get('left');
- }
- Program(path) {
- path.get('body.0');
- }
- 判斷某個節點是否為指定類型
1.內置的 type 對象提供了許多可以直接用來判斷節點類型的工具函數:
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- if (t.isIdentifier(path.node.left)) {
- // ...
- }
- }
或者同時以淺比較來查看節點屬性:
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- if (t.isIdentifier(path.node.left, { name: "n" })) {
- // ...
- }
- }
- // 等價于
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- if (
- path.node.left != null &&
- path.node.left.type === "Identifier" &&
- path.node.left.name === "n"
- ) {
- // ...
- }
- }
- 判斷某個路徑對應的節點是否為指定類型
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- if (path.get('left').isIdentifier({ name: "n" })) {
- // ...
- }
- }
獲取指定路徑的父節點有時候我們需要從某個指定節點開始向上遍歷獲取某個父節點,此時我們可以通過傳入檢測的回調來判斷:
- path.findParent((path) => path.isObjectExpression());
- // 獲取最近的函數聲明節點
- path.getFunctionParent();
- 獲取兄弟路徑如果某個路徑存在于 Function 或者 Program 中的類似列表的結構中,那么其可能會包含兄弟路徑:
- // 源代碼
- var a = 1; // pathA, path.key = 0
- var b = 2; // pathB, path.key = 1
- var c = 3; // pathC, path.key = 2
- // 插件定義
- export default function({ types: t }) {
- return {
- visitor: {
- VariableDeclaration(path) {
- // if the current path is pathA
- path.inList // true
- path.listKey // "body"
- path.key // 0
- path.getSibling(0) // pathA
- path.getSibling(path.key + 1) // pathB
- path.container // [pathA, pathB, pathC]
- }
- }
- };
- }
- 停止遍歷部分情況下插件需要停止遍歷,我們此時只需要在插件中添加 return 表達式:
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- if (path.node.operator !== '**') return;
- }
我們也可以指定忽略遍歷某個子路徑:
- outerPath.traverse({
- Function(innerPath) {
- innerPath.skip(); // if checking the children is irrelevant
- },
- ReferencedIdentifier(innerPath, state) {
- state.iife = true;
- innerPath.stop(); // if you want to save some state and then stop traversal, or deopt
- }
- });
操作
- 替換節點
- // 插件定義
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- path.replaceWith(
- t.binaryExpression("**", path.node.left, t.numberLiteral(2))
- );
- }
- // 代碼結果
- function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- + return n ** 2;
- }
- 將某個節點替換為多個節點
- // 插件定義
- ReturnStatement(path) {
- path.replaceWithMultiple([
- t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("Is this the real life?")),
- t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("Is this just fantasy?")),
- t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("(Enjoy singing the rest of the song in your head)")),
- ]);
- }
- // 代碼結果
- function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- + "Is this the real life?";
- + "Is this just fantasy?";
- + "(Enjoy singing the rest of the song in your head)";
- }
- 將某個節點替換為源代碼字符串
- // 插件定義
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- path.replaceWithSourceString(`function add(a, b) {
- return a + b;
- }`);
- }
- // 代碼結果
- - function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- + function add(a, b) {
- + return a + b;
- }
- 插入兄弟節點
- // 插件定義
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- path.insertBefore(t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("Because I'm easy come, easy go.")));
- path.insertAfter(t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("A little high, little low.")));
- }
- // 代碼結果
- + "Because I'm easy come, easy go.";
- function square(n) {
- return n * n;
- }
- + "A little high, little low.";
- 移除某個節點
- // 插件定義
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- path.remove();
- }
- // 代碼結果
- - function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- - }
- 替換節點
- // 插件定義
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- path.parentPath.replaceWith(
- t.expressionStatement(t.stringLiteral("Anyway the wind blows, doesn't really matter to me, to me."))
- );
- }
- // 代碼結果
- function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- + "Anyway the wind blows, doesn't really matter to me, to me.";
- }
- 移除某個父節點
- // 插件定義
- BinaryExpression(path) {
- path.parentPath.remove();
- }
- // 代碼結果
- function square(n) {
- - return n * n;
- }
作用域
- 判斷某個局部變量是否被綁定:
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- if (path.scope.hasBinding("n")) {
- // ...
- }
- }
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- if (path.scope.hasOwnBinding("n")) {
- // ...
- }
- }
- 創建 UID
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- path.scope.generateUidIdentifier("uid");
- // Node { type: "Identifier", name: "_uid" }
- path.scope.generateUidIdentifier("uid");
- // Node { type: "Identifier", name: "_uid2" }
- }
- 將某個變量聲明提取到副作用中
- // 插件定義
- FunctionDeclaration(path) {
- const id = path.scope.generateUidIdentifierBasedOnNode(path.node.id);
- path.remove();
- path.scope.parent.push({ id, init: path.node });
- }
- // 代碼結果
- - function square(n) {
- + var _square = function square(n) {
- return n * n;
- - }
- + };
【本文是51CTO專欄作者“張梓雄 ”的原創文章,如需轉載請通過51CTO與作者聯系】