深入Vue2.0底層思想–模板渲染
初衷
在使用vue2.0的過程,有時看API很難理解vue作者的思想,這促使我想要去深入了解vue底層的思想,了解完底層的一些思想,才能更好的用活框架,雖然網上已經有很多源碼解析的文檔,但我覺得只有自己動手了,才能更加深印象。
vue2.0和1.0模板渲染的區別
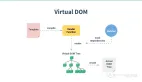
Vue 2.0 中模板渲染與 Vue 1.0 完全不同,1.0 中采用的 DocumentFragment (想了解可以觀看這篇文章),而 2.0 中借鑒 React 的 Virtual DOM。基于 Virtual DOM,2.0 還可以支持服務端渲染(SSR),也支持 JSX 語法。
知識普及
在開始閱讀源碼之前,先了解一些相關的知識:AST 數據結構,VNode 數據結構,createElement 的問題,render函數。
AST 數據結構
AST 的全稱是 Abstract Syntax Tree(抽象語法樹),是源代碼的抽象語法結構的樹狀表現形式,計算機學科中編譯原理的概念。而vue就是將模板代碼映射為AST數據結構,進行語法解析。
我們看一下 Vue 2.0 源碼中 AST 數據結構 的定義:
- declare type ASTNode = ASTElement | ASTText | ASTExpression
- declare type ASTElement = { // 有關元素的一些定義
- type: 1;
- tag: string;
- attrsList: Array{ name: string; value: string }>;
- attrsMap: { [key: string]: string | null };
- parent: ASTElement | void;
- children: ArrayASTNode>;
- //......
- }
- declare type ASTExpression = {
- type: 2;
- expression: string;
- text: string;
- static?: boolean;
- }
- declare type ASTText = {
- type: 3;
- text: string;
- static?: boolean;
- }
我們看到 ASTNode 有三種形式:ASTElement,ASTText,ASTExpression。用屬性 type 區分。
VNode數據結構
下面是 Vue 2.0 源碼中 VNode 數據結構 的定義 (帶注釋的跟下面介紹的內容有關):
- constructor {
- this.tag = tag //元素標簽
- this.data = data //屬性
- this.children = children //子元素列表
- this.text = text
- this.elm = elm //對應的真實 DOM 元素
- this.ns = undefined
- this.context = context
- this.functionalContext = undefined
- this.key = data && data.key
- this.componentOptions = componentOptions
- this.componentInstance = undefined
- this.parent = undefined
- this.raw = false
- this.isStatic = false //是否被標記為靜態節點
- this.isRootInsert = true
- this.isComment = false
- this.isCloned = false
- this.isOnce = false
- }
真實DOM存在什么問題,為什么要用虛擬DOM
我們為什么不直接使用原生 DOM 元素,而是使用真實 DOM 元素的簡化版 VNode,最大的原因就是 document.createElement 這個方法創建的真實 DOM 元素會帶來性能上的損失。我們來看一個 document.createElement 方法的例子
- let div = document.createElement('div');
- for(let k in div) {
- console.log(k);
- }
打開 console 運行一下上面的代碼,會發現打印出來的屬性多達 228 個,而這些屬性有 90% 多對我們來說都是無用的。VNode 就是簡化版的真實 DOM 元素,關聯著真實的dom,比如屬性elm,只包括我們需要的屬性,并新增了一些在 diff 過程中需要使用的屬性,例如 isStatic。
render函數
這個函數是通過編譯模板文件得到的,其運行結果是 VNode。render 函數 與 JSX 類似,Vue 2.0 中除了 Template 也支持 JSX 的寫法。大家可以使用 Vue.compile(template)方法編譯下面這段模板。
- div id="app">
- header>
- h1>I am a template!/h1>
- /header>
- p v-if="message">
- {{ message }}
- /p>
- p v-else>
- No message.
- /p>
- /div>
方法會返回一個對象,對象中有 render 和 staticRenderFns 兩個值。看一下生成的 render函數
- (function() {
- with(this){
- return _c('div',{ //創建一個 div 元素
- attrs:{"id":"app"} //div 添加屬性 id
- },[
- _m(0), //靜態節點 header,此處對應 staticRenderFns 數組索引為 0 的 render 函數
- _v(" "), //空的文本節點
- (message) //三元表達式,判斷 message 是否存在
- //如果存在,創建 p 元素,元素里面有文本,值為 toString(message)
- ?_c('p',[_v("\n "+_s(message)+"\n ")])
- //如果不存在,創建 p 元素,元素里面有文本,值為 No message.
- :_c('p',[_v("\n No message.\n ")])
- ]
- )
- }
- })
要看懂上面的 render函數,只需要了解 _c,_m,_v,_s 這幾個函數的定義,其中 _c 是 createElement(創建元素),_m 是 renderStatic(渲染靜態節點),_v 是 createTextVNode(創建文本dom),_s 是 toString (轉換為字符串)
除了 render 函數,還有一個 staticRenderFns 數組,這個數組中的函數與 VDOM 中的 diff 算法優化相關,我們會在編譯階段給后面不會發生變化的 VNode 節點打上 static 為 true 的標簽,那些被標記為靜態節點的 VNode 就會單獨生成 staticRenderFns 函數
- (function() { //上面 render 函數 中的 _m(0) 會調用這個方法
- with(this){
- return _c('header',[_c('h1',[_v("I'm a template!")])])
- }
- })
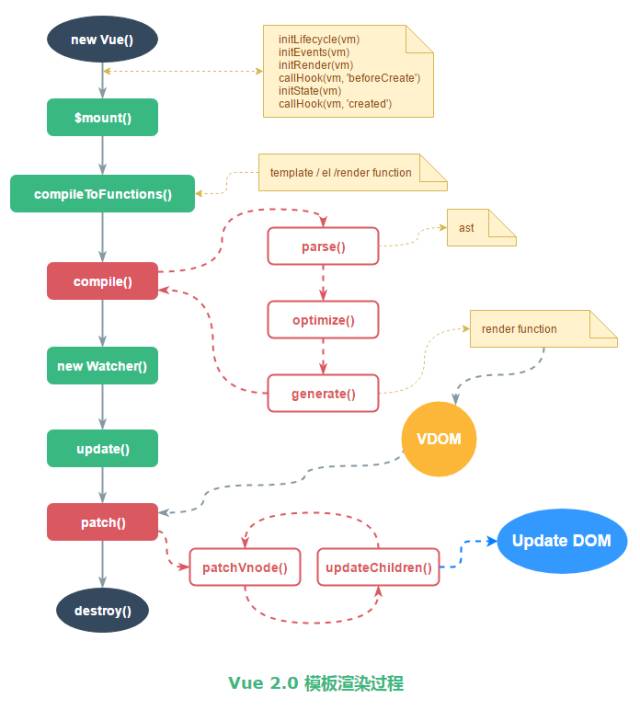
模板渲染過程(重要的函數介紹)
了解完一些基礎知識后,接下來我們講解下模板的渲染過程
$mount 函數,主要是獲取 template,然后進入 compileToFunctions 函數。
compileToFunctions 函數,主要將 template 編譯成 render 函數。首先讀緩存,沒有緩存就調用 compile 方法拿到 render 函數 的字符串形式,再通過 new Function 的方式生成 render 函數。
- // 有緩存的話就直接在緩存里面拿
- const key = options && options.delimiters
- ? String(options.delimiters) + template
- : template
- if (cache[key]) {
- return cache[key]
- }
- const res = {}
- const compiled = compile(template, options) // compile 后面會詳細講
- res.render = makeFunction(compiled.render) //通過 new Function 的方式生成 render 函數并緩存
- const l = compiled.staticRenderFns.length
- res.staticRenderFns = new Array(l)
- for (let i = 0; i l; i++) {
- res.staticRenderFns[i] = makeFunction(compiled.staticRenderFns[i])
- }
- ......
- }
- return (cache[key] = res) // 記錄至緩存中
compile 函數就是將 template 編譯成 render 函數的字符串形式,后面一小節我們會詳細講到。
完成render方法的生成后,會進入 _mount 中進行DOM更新。該方法的核心邏輯如下:
- // 觸發 beforeMount 生命周期鉤子
- callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
- // 重點:新建一個 Watcher 并賦值給 vm._watcher
- vm._watcher = new Watcher(vm, function updateComponent () {
- vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
- }, noop)
- hydrating = false
- // manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
- // mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
- if (vm.$vnode == null) {
- vm._isMounted = true
- callHook(vm, 'mounted')
- }
- return vm
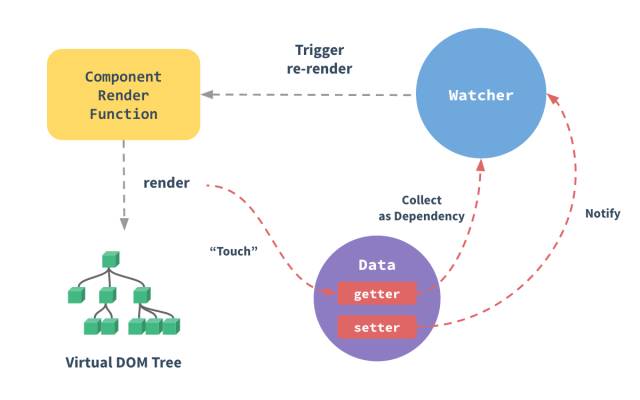
首先會new一個watcher對象(主要是將模板與數據建立聯系),在watcher對象創建后,會運行傳入的方法 vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) 。其中的vm._render()主要作用就是運行前面compiler生成的render方法,并返回一個vNode對象。vm.update() 則會對比新的 vdom 和當前 vdom,并把差異的部分渲染到真正的 DOM 樹上。
推薦個圖,響應式工程流程
(想深入了解watcher的背后實現原理的,可以觀看這篇文章 Vue2.0 源碼閱讀:響應式原理)
compile
上文中提到 compile 函數就是將 template 編譯成 render 函數 的字符串形式。
- export function compile (
- template: string,
- options: CompilerOptions
- ): CompiledResult {
- const AST = parse(template.trim(), options) //1. parse
- optimize(AST, options) //2.optimize
- const code = generate(AST, options) //3.generate
- return {
- AST,
- render: code.render,
- staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
- }
- }
這個函數主要有三個步驟組成:parse,optimize 和 generate,分別輸出一個包含 AST,staticRenderFns 的對象和 render函數 的字符串。
parse 函數,主要功能是將 template字符串解析成 AST。前面定義了ASTElement的數據結構,parse 函數就是將template里的結構(指令,屬性,標簽等)轉換為AST形式存進ASTElement中,最后解析生成AST。
optimize 函數(src/compiler/optimizer.js)主要功能就是標記靜態節點,為后面 patch 過程中對比新舊 VNode 樹形結構做優化。被標記為 static 的節點在后面的 diff 算法中會被直接忽略,不做詳細的比較。
generate 函數(src/compiler/codegen/index.js)主要功能就是根據 AST 結構拼接生成 render 函數的字符串。
- const code = AST ? genElement(AST) : '_c("div")'
- staticRenderFns = prevStaticRenderFns
- onceCount = prevOnceCount
- return {
- render: `with(this){return ${code}}`, //最外層包一個 with(this) 之后返回
- staticRenderFns: currentStaticRenderFns
- }
其中 genElement 函數(src/compiler/codegen/index.js)是會根據 AST 的屬性調用不同的方法生成字符串返回。
- function genElement (el: ASTElement): string {
- if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
- return genStatic(el)
- } else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
- return genOnce(el)
- } else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
- return genFor(el)
- } else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
- return genIf(el)
- } else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget) {
- return genChildren(el) || 'void 0'
- } else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
- }
- return code
- }
- }
以上就是 compile 函數中三個核心步驟的介紹,compile 之后我們得到了 render 函數 的字符串形式,后面通過 new Function 得到真正的渲染函數。數據發現變化后,會執行 Watcher 中的 _update 函數(src/core/instance/lifecycle.js),_update 函數會執行這個渲染函數,輸出一個新的 VNode 樹形結構的數據。然后在調用 patch 函數,拿這個新的 VNode 與舊的 VNode 進行對比,只有發生了變化的節點才會被更新到真實 DOM 樹上。
patch
patch.js 就是新舊 VNode 對比的 diff 函數,主要是為了優化dom,通過算法使操作dom的行為降到最低,diff 算法來源于 snabbdom,是 VDOM 思想的核心。snabbdom 的算法為了 DOM 操作跨層級增刪節點較少的這一目標進行優化,它只會在同層級進行, 不會跨層級比較。
想更加深入VNode diff算法原理的,可以觀看(解析vue2.0的diff算法)
總結
- compile 函數主要是將 template 轉換為 AST,優化 AST,再將 AST 轉換為 render函數;
- render函數 與數據通過 Watcher 產生關聯;
- 在數據發生變化時調用 patch 函數,執行此 render 函數,生成新 VNode,與舊 VNode 進行 diff,最終更新 DOM 樹。