六個優雅的Linux命令行技巧
- 一些非常有用的命令能讓命令行的生活更滿足
使用 Linux 命令工作可以獲得許多樂趣,但是如果您使用一些命令,它們可以減少您的工作或以有趣的方式顯示信息時,您將獲得更多的樂趣。在今天的文章中,我們將介紹六個命令,它們可能會使你用在命令行上的時間更加值當。
watch
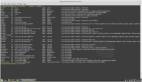
watch 命令會重復運行您給出的任何命令,并顯示輸出。默認情況下,它每兩秒運行一次命令。命令的每次運行都將覆蓋上一次運行時顯示的內容,因此您始終可以看到***的數據。
您可能會在等待某人登錄時使用它。在這種情況下,您可以使用 watch who 命令或者 watch -n 15 who 命令使每 15 秒運行一次,而不是兩秒一次。另外終端窗口的右上角會顯示日期和時間。
- $ watch -n 5 who
- Every 5.0s: who stinkbug: Wed Aug 23 14:52:15 2017
- shs pts/0 2017-08-23 14:45 (192.168.0.11)
- zoe pts/1 2017-08-23 08:15 (192.168.0.19)
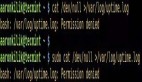
您也可以使用它來查看日志文件。如果您顯示的數據沒有任何變化,則只有窗口角落里的日期和時間會發生變化。
- $ watch tail /var/log/syslog
- Every 2.0s: tail /var/log/syslog stinkbug: Wed Aug 23 15:16:37 2017
- Aug 23 14:45:01 stinkbug CRON[7214]: (root) CMD (command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/nu
- ll && debian-sa1 1 1)
- Aug 23 14:45:17 stinkbug systemd[1]: Started Session 179 of user shs.
- Aug 23 14:55:01 stinkbug CRON[7577]: (root) CMD (command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/nu
- ll && debian-sa1 1 1)
- Aug 23 15:05:01 stinkbug CRON[7582]: (root) CMD (command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/nu
- ll && debian-sa1 1 1)
- Aug 23 15:08:48 stinkbug systemd[1]: Starting Cleanup of Temporary Directories...
- Aug 23 15:08:48 stinkbug systemd-tmpfiles[7584]: [/usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/var.conf:1
- 4] Duplicate line for path "/var/log", ignoring.
- Aug 23 15:08:48 stinkbug systemd[1]: Started Cleanup of Temporary Directories.
- Aug 23 15:13:41 stinkbug systemd[1]: Started Session 182 of user shs.
- Aug 23 15:14:29 stinkbug systemd[1]: Started Session 183 of user shs.
- Aug 23 15:15:01 stinkbug CRON[7828]: (root) CMD (command -v debian-sa1 > /dev/nu
- ll && debian-sa1 1 1)
這里的輸出和使用命令 tail -f /var/log/syslog 的輸出相似。
look
這個命令的名字 look 可能會讓我們以為它和 watch 做類似的事情,但其實是不同的。look 命令用于搜索以某個特定字符串開頭的單詞。
- $ look ecl
- eclectic
- eclectic's
- eclectically
- eclecticism
- eclecticism's
- eclectics
- eclipse
- eclipse's
- eclipsed
- eclipses
- eclipsing
- ecliptic
- ecliptic's
look 命令通常有助于單詞的拼寫,它使用 /usr/share/dict/words 文件,除非你使用如下的命令指定了文件名:
- $ look esac .bashrc
- esac
- esac
- esac
在這種情況下,它的作用就像跟在一個 awk 命令后面的 grep ,只打印匹配行上的***個單詞。
man -k
man -k 命令列出包含指定單詞的手冊頁。它的工作基本上和 apropos 命令一樣。
- $ man -k logrotate
- dh_installlogrotate (1) - install logrotate config files
- logrotate (8) - rotates, compresses, and mails system logs
- logrotate.conf (5) - rotates, compresses, and mails system logs
help
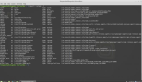
當你完全絕望的時候,您可能會試圖使用此命令,help 命令實際上是顯示一個 shell 內置命令的列表。最令人驚訝的是它有相當多的參數變量。你可能會看到這樣的東西,然后開始想知道這些內置功能可以為你做些什么:
- $ help
- GNU bash, version 4.4.7(1)-release (i686-pc-linux-gnu)
- These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help' to see this list.
- Type `help name' to find out more about the function `name'.
- Use `info bash' to find out more about the shell in general.
- Use `man -k' or `info' to find out more about commands not in this list.
- A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
- job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
- (( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
- . filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec ...] or jobs >
- : kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
- [ arg... ] let arg [arg ...]
- [[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] ...
- alias [-p] [name[=value] ... ] logout [n]
- bg [job_spec ...] mapfile [-d delim] [-n count] [-O or>
- bind [-lpsvPSVX] [-m keymap] [-f file> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
- break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
- builtin [shell-builtin [arg ...]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
- caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
- case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]...)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
- cd [-L|[-P [-e]] [-@]] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
- command [-pVv] command [arg ...] readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] ...] o>
- compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] [> return [n]
- complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS ... ;] do COMM>
- compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option->
- continue [n] shift [n]
- coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname ...]
- declare [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] [name[=v> source filename [arguments]
- dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
- disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec ... | pid > test [expr]
- echo [-neE] [arg ...] time [-p] pipeline
- enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
- eval [arg ...] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec ...]
- exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
- exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name ...]
- export [-fn] [name[=value] ...] or ex> typeset [-aAfFgilnrtux] [-p] name[=v>
- false ulimit [-SHabcdefiklmnpqrstuvxPT] [l>
- fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
- fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name ...]
- for NAME [in WORDS ... ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [-n] [name ...]
- for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
- function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables - Names and meanings of so>
- getopts optstring name [arg] wait [-n] [id ...]
- hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
- help [-dms] [pattern ...] { COMMANDS ; }
stat -c
stat 命令用于顯示文件的大小、所有者、用戶組、索引節點號、權限、修改和訪問時間等重要的統計信息。這是一個非常有用的命令,可以顯示比 ls -l 更多的細節。
- $ stat .bashrc
- File: .bashrc
- Size: 4048 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
- Device: 806h/2054d Inode: 421481 Links: 1
- Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 1000/ shs) Gid: ( 1000/ shs)
- Access: 2017-08-23 15:13:41.781809933 -0400
- Modify: 2017-06-21 17:37:11.875157790 -0400
- Change: 2017-06-21 17:37:11.899157791 -0400
- Birth: -
使用 -c 選項,您可以指定要查看的字段。例如,如果您只想查看一個文件或一系列文件的文件名和訪問權限,則可以這樣做:
- $ stat -c '%n %a' .bashrc
- .bashrc 644
在此命令中, %n 表示每個文件的名稱,而 %a 表示訪問權限。%u 表示數字類型的 UID,而 %U 表示用戶名。
- $ stat -c '%n %a' bin/*
- bin/loop 700
- bin/move2nohup 700
- bin/nohup.out 600
- bin/show_release 700
- $ stat -c '%n %a %U' bin/*
- bin/loop 700 shs
- bin/move2nohup 700 shs
- bin/nohup.out 600 root
- bin/show_release 700 shs
TAB
如果你沒有使用過 tab 鍵來補全文件名,你真的錯過了一個非常有用的命令行技巧。tab 鍵提供文件名補全功能(包括使用 cd 時的目錄)。它在出現歧義之前盡可能多的填充文件名(多個文件以相同的字母開頭。如果您有一個名為 bigplans 的文件,另一個名為 bigplans2017 的文件會發生歧義,你將聽到一個聲音,然后需要決定是按下回車鍵還是輸入 2 之后再按下 tab 鍵選擇第二個文件。