PostMessage 還能這樣玩
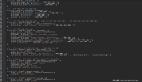
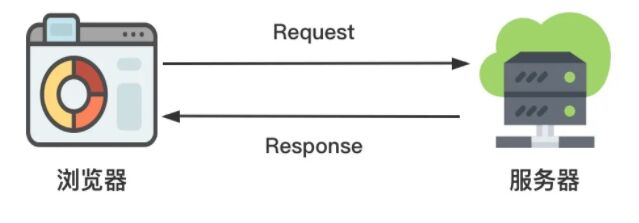
在日常工作中,消息通信是一個很常見的場景。比如大家熟悉 B/S 結構,在該結構下,瀏覽器與服務器之間是基于 HTTP 協議進行消息通信:
然而除了 HTTP 協議之外,在一些對數據實時性要求較高的場景下,我們會使用 WebSocket 協議來完成消息通信:

對于這兩種場景,相信大家都不會陌生。接下來,阿寶哥將介紹消息通信的另外一種場景,即父頁面與 iframe 加載的子頁面之間,如何進行消息通信。
為什么會突然寫這個話題呢?其實是因為在近期項目中,阿寶哥需要實現父頁面與 iframe 加載的子頁面之間的消息通信。另外,剛好近期阿寶哥在寫 源碼分析 專題,所以就到 Github 上搜索 🔍 了一番,然后找到了一個不錯的項目 —— Postmate。
在閱讀完 Postmate 源碼之后,阿寶哥覺得該項目的一些設計思想挺值得借鑒的,所以就寫了這篇文章來跟大家分享一下。閱讀完本文之后,你將學到以下知識:
- 消息系統中握手的作用及如何實現握手;
- 消息模型的設計及如何實現消息驗證來保證通信安全;
- postMessage 的使用及如何利用它實現父子頁面的消息通信;
- 消息通信 API 的設計與實現。
好的,廢話不多說,我們先來簡單介紹一下 Postmate。
一、Postmate 簡介
Postmate 是一個強大,簡單,基于 Promise 的 postMessage 庫。它允許父頁面以最小的成本與跨域的子 iframe 進行通信。該庫擁有以下特性:
- 基于 Promise 的 API,可實現優雅而簡單的通信;
- 使用 消息驗證 來保護雙向 父 <-> 子 消息通信的安全;
- 子對象公開父對象可以訪問的可檢索的模型對象;
- 子對象可派發父對象已監聽的事件;
- 父對象可以調用子對象中的函數;
- 零依賴。如果需要可以為 Promise API 提供自定義 polyfill 或抽象;
- 輕量,大小約 1.6 KB(minified & gzipped)。
接下來阿寶哥將從如何進行握手、如何實現雙向消息通信和如何斷開連接,這三個方面來分析一下 Postmate 這個庫。另外,在此期間還會穿插介紹 Postmate 項目中一些好的設計思路。
二、如何進行握手
TCP 建立連接的時候,需要進行三次握手。同樣,當父頁面與子頁面通信的時候,Postmate 也是通過 “握手” 來確保雙方能正常通信。因為 Postmate 通信的基礎是基于 postMessage,所以在介紹如何握手之前,我們先來簡單了解一下 postMessage API。
2.1 postMessage 簡介
對于兩個不同頁面的腳本,只有當執行它們的頁面位于具有相同的協議、端口號以及主機時,這兩個腳本才能相互通信。window.postMessage() 方法提供了一種受控機制來規避此限制,只要正確的使用,這種方法就很安全。
2.1.1 postMessage() 語法
- otherWindow.postMessage(message, targetOrigin, [transfer]);
- otherWindow:其他窗口的一個引用,比如 iframe 的 contentWindow 屬性、執行 window.open 返回的窗口對象等。
- message:將要發送到其他 window 的數據,它將會被結構化克隆算法序列化。
- targetOrigin:通過窗口的 origin 屬性來指定哪些窗口能接收到消息事件,其值可以是字符串 "*"(表示無限制)或者一個 URI。
- transfer(可選):是一串和 message 同時傳遞的 Transferable 對象。這些對象的所有權將被轉移給消息的接收方,而發送一方將不再保有所有權。
發送方通過 postMessage API 來發送消息,而接收方可以通過監聽 message 事件,來添加消息處理回調函數,具體使用方式如下:
- window.addEventListener("message", receiveMessage, false);
- function receiveMessage(event) {
- let origin = event.origin || event.originalEvent.origin;
- if (origin !== "http://semlinker.com") return;
- }
2.2 Postmate 握手的實現
在電信和微處理器系統中,術語握手(Handshake,亦稱為交握)具有以下含義:
- 在數據通信中,由硬件或軟件管理的事件序列,在進行信息交換之前,需要對操作模式的狀態互相達成協定。
- 在接收站和發送站之間建立通信參數的過程。
對于通信系統來說,握手是在通信電路建立之后,信息傳輸開始之前。握手用于達成參數,如信息傳輸率,字母表,奇偶校驗, 中斷過程,和其他協議特性。
而對于 Postmate 這個庫來說,握手是為了確保父頁面與 iframe 子頁面之間可以正常的通信,對應的握手流程如下所示:

在 Postmate 中,握手消息是由父頁面發起的,在父頁面中要發起握手信息,首先需要創建 Postmate 對象:
- const postmate = new Postmate({
- container: document.getElementById('some-div'), // iframe的容器
- url: 'http://child.com/page.html', // 包含postmate.js的iframe子頁面地址
- name: 'my-iframe-name' // 用于設置iframe元素的name屬性
- });
在以上代碼中,我們通過調用 Postmate 構造函數來創建 postmate 對象,在 Postmate 構造函數內部含有兩個主要步驟:設置 Postmate 對象的內部屬性和發送握手消息:

以上流程圖對應的代碼相對比較簡單,這里阿寶哥就不貼詳細的代碼了。感興趣的小伙伴可以閱讀 src/postmate.js 文件中的相關內容。為了能夠響應父頁面的握手信息,我們需要在子頁面中創建一個 Model 對象:
- const model = new Postmate.Model({
- // Expose your model to the Parent. Property values may be functions, promises, or regular values
- height: () => document.height || document.body.offsetHeight
- });
其中 Postmate.Model 構造函數的定義如下:
- // src/postmate.js
- Postmate.Model = class Model {
- constructor(model) {
- this.child = window;
- this.model = model;
- this.parent = this.child.parent;
- return this.sendHandshakeReply();
- }
- }
在 Model 構造函數中,我們可以很清楚地看到調用 sendHandshakeReply 這個方法,這里我們只看核心的代碼:

現在我們來總結一下父頁面和子頁面之間的握手流程:當子頁面加載完成后,父頁面會通過 postMessage API 向子頁面發送 handshake 握手消息。在子頁面接收到 handshake握手消息之后,同樣也會使用 postMessage API 往父頁面回復 handshake-reply 消息。
另外,需要注意的是,為了保證子頁面能收到 handshake 握手消息,在 sendHandshake方法內部會啟動一個定時器來執行發送操作:
- // src/postmate.js
- class Postmate {
- sendHandshake(url) {
- return new Postmate.Promise((resolve, reject) => {
- const loaded = () => {
- doSend();
- responseInterval = setInterval(doSend, 500);
- };
- if (this.frame.attachEvent) {
- this.frame.attachEvent("onload", loaded);
- } else {
- this.frame.addEventListener("load", loaded);
- }
- this.frame.src = url;
- });
- }
- }
當然為了避免發送過多無效的握手信息,在 doSend 方法內部會限制最大的握手次數:
- const doSend = () => {
- attempt++;
- this.child.postMessage(
- {
- postmate: "handshake",
- type: messageType,
- model: this.model,
- },
- childOrigin
- );
- // const maxHandshakeRequests = 5;
- if (attempt === maxHandshakeRequests) {
- clearInterval(responseInterval);
- }
- };
在主應用和子應用雙方完成握手之后,就可以進行雙向消息通信了,下面我們來了解一下如何實現雙向消息通信。
三、如何實現雙向消息通信
在調用 Postmate 和 Postmate.Model 構造函數之后,會返回一個 Promise 對象。而當 Promise 對象的狀態從 pending 變為 resolved 之后,就會分別返回 ParentAPI 和 ChildAPI 對象:
Postmate
- // src/postmate.js
- class Postmate {
- constructor({
- container = typeof container !== "undefined" ? container : document.body,
- model, url, name, classListArray = [],
- }) {
- // 省略設置 Postmate 對象的內部屬性
- return this.sendHandshake(url);
- }
- sendHandshake(url) {
- // 省略部分代碼
- return new Postmate.Promise((resolve, reject) => {
- const reply = (e) => {
- if (!sanitize(e, childOrigin)) return false;
- if (e.data.postmate === "handshake-reply") {
- return resolve(new ParentAPI(this));
- }
- return reject("Failed handshake");
- };
- });
- }
- }
ParentAPI
- class ParentAPI{
- +get(property: any) // 獲取子頁面中Model對象上的property屬性上的值
- +call(property: any, data: any) // 調用子頁面中Model對象上的方法
- +on(eventName: any, callback: any) // 監聽子頁面派發的事件
- +destroy() // 移除事件監聽并刪除iframe
- }
Postmate.Model
- // src/postmate.js
- Postmate.Model = class Model {
- constructor(model) {
- this.child = window;
- this.model = model;
- this.parent = this.child.parent;
- return this.sendHandshakeReply();
- }
- sendHandshakeReply() {
- // 省略部分代碼
- return new Postmate.Promise((resolve, reject) => {
- const shake = (e) => {
- if (e.data.postmate === "handshake") {
- this.child.removeEventListener("message", shake, false);
- return resolve(new ChildAPI(this));
- }
- return reject("Handshake Reply Failed");
- };
- this.child.addEventListener("message", shake, false);
- });
- }
- };
ChildAPI
- class ChildAPI{
- +emit(name: any, data: any)
- }
3.1 子頁面 -> 父頁面
3.1.1 子頁面發送消息
- const model = new Postmate.Model({
- // Expose your model to the Parent. Property values may be functions, promises, or regular values
- height: () => document.height || document.body.offsetHeight
- });
- model.then(childAPI => {
- childAPI.emit('some-event', 'Hello, World!');
- });
在以上代碼中,子頁面可以通過 ChildAPI 對象提供的 emit 方法來發送消息,該方法的定義如下:
- export class ChildAPI {
- emit(name, data) {
- this.parent.postMessage(
- {
- postmate: "emit",
- type: messageType,
- value: {
- name,
- data,
- },
- },
- this.parentOrigin
- );
- }
- }
3.1.2 父頁面監聽消息
- const postmate = new Postmate({
- container: document.getElementById('some-div'), // iframe的容器
- url: 'http://child.com/page.html', // 包含postmate.js的iframe子頁面地址
- name: 'my-iframe-name' // 用于設置iframe元素的name屬性
- });
- postmate.then(parentAPI => {
- parentAPI.on('some-event', data => console.log(data)); // Logs "Hello, World!"
- });
在以上代碼中,父頁面可以通過 ParentAPI 對象提供的 on 方法來注冊事件處理器,該方法的定義如下:
- export class ParentAPI {
- constructor(info) {
- this.parent = info.parent;
- this.frame = info.frame;
- this.child = info.child;
- this.events = {};
- this.listener = (e) => {
- if (!sanitize(e, this.childOrigin)) return false;
- // 省略部分代碼
- if (e.data.postmate === "emit") {
- if (name in this.events) {
- this.events[name].forEach((callback) => {
- callback.call(this, data);
- });
- }
- }
- };
- this.parent.addEventListener("message", this.listener, false);
- }
- on(eventName, callback) {
- if (!this.events[eventName]) {
- this.events[eventName] = [];
- }
- this.events[eventName].push(callback);
- }
- }
3.2 消息驗證
為了保證通信的安全,在消息處理時,Postmate 會對消息進行驗證,對應的驗證邏輯被封裝到 sanitize 方法中:
- const sanitize = (message, allowedOrigin) => {
- if (typeof allowedOrigin === "string" && message.origin !== allowedOrigin)
- return false;
- if (!message.data) return false;
- if (typeof message.data === "object" && !("postmate" in message.data))
- return false;
- if (message.data.type !== messageType) return false;
- if (!messageTypes[message.data.postmate]) return false;
- return true;
- };
對應的驗證規則如下:
- 驗證消息的來源是否合法;
- 驗證是否含有消息體;
- 驗證消息體中是否含有 postmate 屬性;
- 驗證消息的類型是否為 "application/x-postmate-v1+json";
- 驗證消息體中的 postmate 對應的消息類型是否合法;
以下是 Postmate 支持的消息類型:
- const messageTypes = {
- handshake: 1,
- "handshake-reply": 1,
- call: 1,
- emit: 1,
- reply: 1,
- request: 1,
- };
其實要實現消息驗證的提前,我們還需要定義標準的消息體模型:
- {
- postmate: "emit", // 必填:"request" | "call" 等等
- type: messageType, // 必填:"application/x-postmate-v1+json"
- // 自定義屬性
- }
了解完子頁面如何與父頁面進行通信及如何進行消息驗證之后,下面我們來看一下父頁面如何與子頁面進行消息通信。
3.3 父頁面 -> 子頁面
3.3.1 調用子頁面模型對象上的方法

在頁面中,通過 ParentAPI 對象提供的 call 方法,我們就可以調用子頁面模型對象上的方法:
- export class ParentAPI {
- call(property, data) {
- this.child.postMessage(
- {
- postmate: "call",
- type: messageType,
- property,
- data,
- },
- this.childOrigin
- );
- }
- }
在 ChildAPI 對象中,會對 call 消息類型進行對應的處理,相應的處理邏輯如下所示:
- export class ChildAPI {
- constructor(info) {
- // 省略部分代碼
- this.child.addEventListener("message", (e) => {
- if (!sanitize(e, this.parentOrigin)) return;
- const { property, uid, data } = e.data;
- // 響應父頁面發送的call消息類型,用于調用Model對象上的對應方法
- if (e.data.postmate === "call") {
- if (
- property in this.model &&
- typeof this.model[property] === "function"
- ) {
- this.model[property](data);
- }
- return;
- }
- });
- }
- }
通過以上代碼我們可知,call 消息只能用來調用子頁面 Model 對象上的方法并不能獲取方法調用的返回值。然而在一些場景下,我們是需要獲取方法調用的返回值,接下來我們來看一下 ParentAPI 是如何實現這個功能。
3.3.2 調用子頁面模型對象上的方法并獲取返回值

若需要獲取調用后的返回值,我們需要調用 ParentAPI 對象上提供的 get 方法:
- export class ParentAPI {
- get(property) {
- return new Postmate.Promise((resolve) => {
- // 從響應中獲取數據并移除監聽
- const uid = generateNewMessageId();
- const transact = (e) => {
- if (e.data.uid === uid && e.data.postmate === "reply") {
- this.parent.removeEventListener("message", transact, false);
- resolve(e.data.value);
- }
- };
- // 監聽來自子頁面的響應消息
- this.parent.addEventListener("message", transact, false);
- // 向子頁面發送請求
- this.child.postMessage(
- {
- postmate: "request",
- type: messageType,
- property,
- uid,
- },
- this.childOrigin
- );
- });
- }
- }
對于父頁面發送的 request 消息,在子頁面中會通過 resolveValue 方法來獲取返回結果,然后通過 postMessage 來返回結果:
- // src/postmate.js
- export class ChildAPI {
- constructor(info) {
- this.child.addEventListener("message", (e) => {
- if (!sanitize(e, this.parentOrigin)) return;
- const { property, uid, data } = e.data;
- // 響應父頁面發送的request消息
- resolveValue(this.model, property).then((value) =>
- e.source.postMessage(
- {
- property,
- postmate: "reply",
- type: messageType,
- uid,
- value,
- },
- e.origin
- )
- );
- });
- }
- }
以上代碼中的 resolveValue 方法實現也很簡單:
- const resolveValue = (model, property) => {
- const unwrappedContext =
- typeof model[property] === "function" ? model[property]() : model[property];
- return Postmate.Promise.resolve(unwrappedContext);
- };
此時,我們已經介紹了 Postmate 如何進行握手及如何實現雙向消息通信,最后我們來介紹一下如何斷開連接。
四、如何斷開連接
當父頁面與子頁面完成消息通信之后,我們需要斷開連接。這時我們可以調用 ParentAPI對象上的 destroy 方法來斷開連接。
- // src/postmate.js
- export class ParentAPI {
- destroy() {
- window.removeEventListener("message", this.listener, false);
- this.frame.parentNode.removeChild(this.frame);
- }
- }
本文阿寶哥以 Postmate 這個庫為例,介紹了如何基于 postMessage 來實現父頁面和 iframe 子頁面之間優雅的消息通信。如果你還意猶未盡的話,可以閱讀阿寶哥之前寫的與通信相關的文章:如何優雅的實現消息通信? 和 你不知道的 WebSocket。
五、參考資源
- MDN - postMessage
- Github - postmate【編輯推薦】