對(duì)比 HashMap,HashTable,TreeMap區(qū)別?很多人不知道
本文轉(zhuǎn)載自微信公眾號(hào)「程序員漫畫(huà)編程」,作者程序職場(chǎng) 。轉(zhuǎn)載本文請(qǐng)聯(lián)系程序員漫畫(huà)編程公眾號(hào)。
01概念
HashMap
HashMap實(shí)現(xiàn)了Map接口,繼承AbstractMap,它是基于哈希表的 Map 接口的實(shí)現(xiàn)。
HashMap是引用數(shù)據(jù)類型。
Hashtable
Hashtable:是Map接口的另外一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)類,和HashMap用法類似,同時(shí)也有區(qū)別。
treeMap
TreeMap:基于紅黑樹(shù)(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap實(shí)現(xiàn)。該映射根據(jù)其鍵的自然順序進(jìn)行排序,或者根據(jù)創(chuàng)建映射時(shí)提供的Comparator進(jìn)行排序,具體取決于使用的構(gòu)造方法。
02區(qū)別
1. HashTable的方法是同步的,HashMap未經(jīng)同步,所以在多線程場(chǎng)合要手動(dòng)同步HashMap這個(gè)區(qū)別就像Vector和ArrayList一樣。
2. HashTable不允許null值,key和value都不可以,HashMap允許null值,key和value都可以。
3. HashTable有一個(gè)contains(Object value)功能和containsValue(Object value)功能一樣。
4. HashTable使用Enumeration,HashMap使用Iterator。
5. HashTable中hash數(shù)組默認(rèn)大小是11,增加的方式是 old*2+1。HashMap中hash數(shù)組的默認(rèn)大小是16,而且一定是2的指數(shù)。
6. 哈希值的使用不同,HashTable直接使用對(duì)象的hashCode。
7,這三個(gè)都對(duì)Map接口進(jìn)行了實(shí)現(xiàn)
03安全性
1.HashMap是不安全的線程,他允許Key值出現(xiàn)一次null Value值出現(xiàn)無(wú)數(shù)次的Null
2.Hashtable是安全的線程,他不僅實(shí)現(xiàn)了Map接口也實(shí)現(xiàn)了Dictionary接口,他的key值與Value值都不允許出現(xiàn)Null
3.treeMap 非線程安全 可以進(jìn)行排序的,默認(rèn)按照鍵的自然順序進(jìn)行升序排序,若要進(jìn)行降序排序則需要在構(gòu)造集合時(shí)候傳遞一個(gè)比較器。
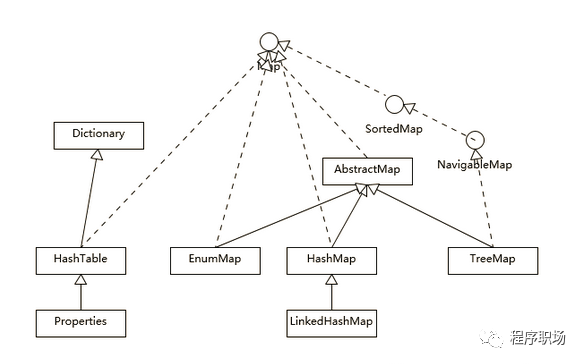
04關(guān)系圖
05實(shí)例應(yīng)用
- class HashMaps
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Map map=new HashMap();
- map.put(“a”, “aaa”);
- map.put(“b”, “bbb”);
- map.put(“c”, “ccc”);
- map.put(“d”, “ddd”);
- Iterator iterator = map.keySet().iterator();
- while (iterator.hasNext()) {
- Object key = iterator.next();
- System.out.println(“map.get(key) is :”+map.get(key));
- }
- Hashtable tab=new Hashtable();
- tab.put(“a”, “aaa”);
- tab.put(“b”, “bbb”);
- tab.put(“c”, “ccc”);
- tab.put(“d”, “ddd”);
- Iterator iterator_1 = tab.keySet().iterator();
- while (iterator_1.hasNext()) {
- Object key = iterator_1.next();
- System.out.println(“tab.get(key) is :”+tab.get(key));
- }
- TreeMap tmp=new TreeMap();
- tmp.put(“a”, “aaa”);
- tmp.put(“b”, “bbb”);
- tmp.put(“c”, “ccc”);
- tmp.put(“d”, “ddd”);
- Iterator iterator_2 = tmp.keySet().iterator();
- while (iterator_2.hasNext()) {
- Object key = iterator_2.next();
- System.out.println(“tmp.get(key) is :”+tmp.get(key));
- }
- }
- }