如何從0構建區塊鏈之三
在前2集中,我們使用Go和Javascript構建了兩個基本DEMO,傳送門:
Javascript:區塊鏈研究實驗室 | 如何從0構建區塊鏈(二)
現在讓我們使用Python來構建另一個分類帳DEMO,這是增長最快且最受歡迎的編程語言之一。
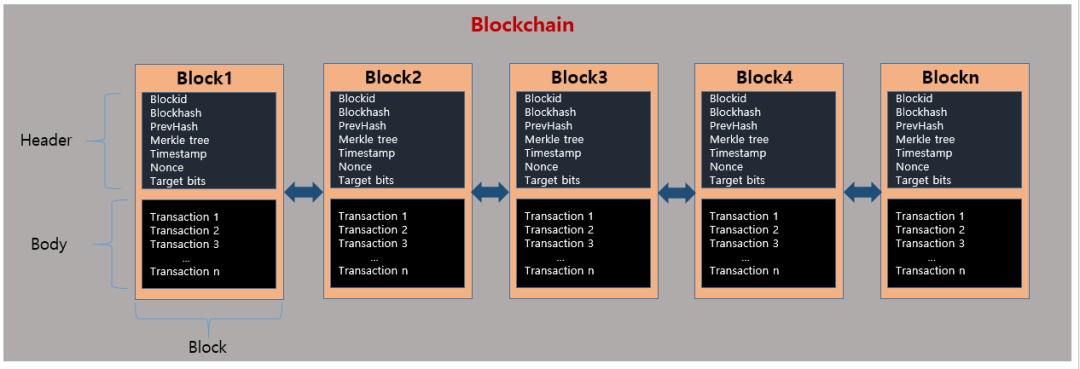
回顧一下,一個區塊鏈是一個區塊鏈,每個區塊包含圖1中列出的一些信息。由于我們正在構建一個分類帳DEMO,因此讓我們遠離將來將涉及的復雜術語和機制。我將使用注釋符號(#)來解釋每一行代碼,記住#之后的所有內容都是注釋。
我們開始吧!
讓我們先導入兩個重要的庫:
- # Start
- import datetime as d # import the datetime library for our block timestamp and rename it as d for simplicity while typing
- import hashlib as h # import the library for hashing our block data and rename it as h for simplicity while typing
這兩個庫用于對生成的每個塊進行哈希處理和加時間戳。
創建一個名為Block的類:
- class Block: # create a class called Block
- def __init__(self,index,timestamp,data ,prevhash): # declare an initial method that defines a block, a block contains the following information
- self.index = index # a block contains an ID
- self.timestamp =timestamp # a block contains a timestamp
- self.data = data # a block contains some transactions
- self.prevhash =prevhash # a block contains a hash of the previous block
- self.hash =self.hashblock() # a block contains a hash, the hash is obtained by hashing all the data contained in the block
此類具有一個包含所有塊信息的初始方法,但是沒有任何方法返回塊哈希,因此讓我們繼續在Block類下創建它。
- def hashblock (self): # define a method for data encryption, this method will retain a hash of the block
- block_encryption=h.sha256() # We need a sha256 function to hash the content of the block, so let's declare it here
- block_encryption.update(str(self.index)+str(self.timestamp)+str(self.data)+str(self.prevhash)) # to encrypt the data in the block, We need just to sum everything and apply the hash function on it
- return block_encryption.hexdigest() # let's return that hash result
部署區塊鏈時,它只有一個區塊,即有史以來的第一個區塊,第一個區塊稱為創世區塊,以下所有區塊將被添加到第一個區塊之上,因此讓我們創建一個靜態方法,該方法將返回起源塊。
- @staticmethod # declaring a static method for the genesis block
- def genesisblock(): # this method is for generating the first block named genesis block
- return Block(0,d.datetime.now(),"genesis block transaction"," ") # return the genesis block
每個塊之后是下一個塊,下一個塊是鏈上最近添加的塊,我們必須聲明另一個靜態方法來返回每個新塊,讓我們創建它。
- @staticmethod# let's declare another static method to get the next block
- def newblock(lastblock): # get the next block, the block that comes after the previous block (prevblock+1)
- index = lastblock.index+1 # the id of this block will be equals to the previous block + 1, which is logic
- timestamp = d.datetime.now() # The timestamp of the next block
- hashblock = lastblock.hash # the hash of this block
- data = "Transaction " +str(index) # The data or transactions containing in that block
- return Block(index,timestamp,data,hashblock)# return the entire block
制作區塊并創建新的區塊方法,現在我們需要初始化區塊鏈以接收所有傳入的區塊。
- blockchain = [Block.genesisblock()] # now it's time to initialize our blockchain with a genesis block in it
- prevblock = blockchain[0] # the previous block is the genesis block itself since there is no block that comes before it at the indice 0
鏈上只有創世塊,讓我們向分類賬中添加更多塊并進行打印。
- for i in range (0,5): # the loop starts from here, we will print 5 blocks, this number can be increased if needed
- addblock = Block.newblock(prevblock) # the block to be added to our chain
- blockchain.append(addblock) # we add that block to our chain of blocks
- prevblock =addblock #now the previous block becomes the last block so we can add another one if needed
- print"Block ID #{} ".format(addblock.index) # show the block id
- print"Timestamp:{}".format(addblock.timestamp)# show the block timestamp
- print"Hash of the block:{}".format(addblock.hash)# show the hash of the added block
- print"Previous Block Hash:{}".format(addblock.prevhash)# show the previous block hash
- print"data:{}\n".format(addblock.data)# show the transactions or data contained in that block
- # end
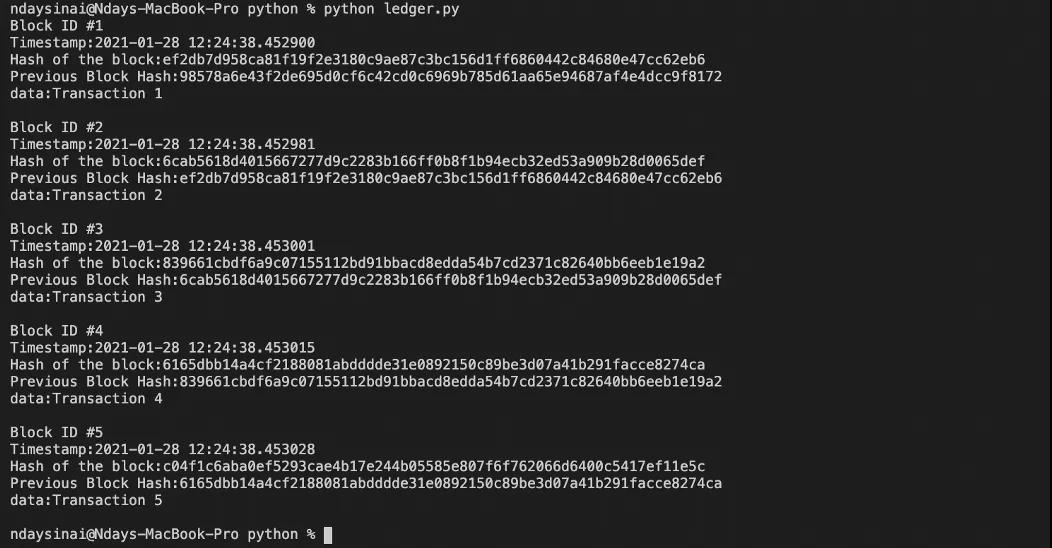
結果如下:
編號為1的區塊具有創世區塊的哈希值,該哈希值未在我們的區塊鏈中顯示,由我們決定是否顯示創世區塊,讓我向您展示如何打印其內容。在之前for loop,添加以下行:
- # let's print the genesis block information
- print"Block ID :{} ".format(prevblock.index)
- print"Timestamp:{}".format(prevblock.timestamp)
- print"Hash of the block:{}".format(prevblock.hash)
- print"Previous Block Hash:{}".format(prevblock.prevhash)
- print"data:{}\n".format(prevblock.data)
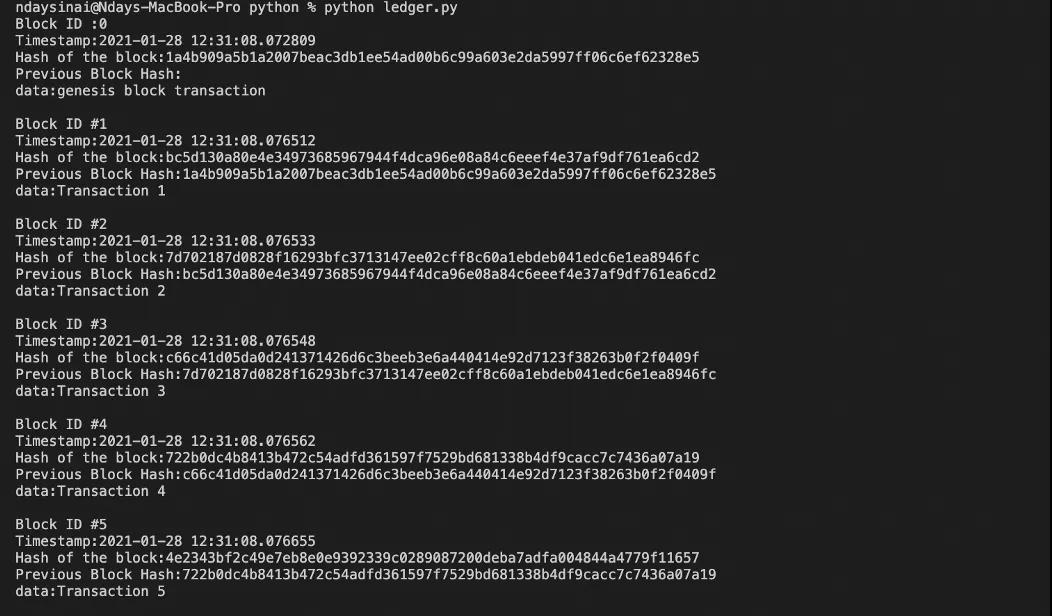
這是最終結果:
現在,創始塊在分類帳中變得可見。
恭喜你!您剛剛使用Python創建了另一個區塊鏈DEMO。
保持關注下一個高級概念??。
整個代碼:
- # Start
- import datetime as d # import the datetime library for our block timestamp and rename it as d for simplicity while typing
- import hashlib as h # import the library for hashing our block data and rename it as h for simplicity while typing
- class Block: # create a Block class
- def __init__(self,index,timestamp,data ,prevhash): # declare an initial method that defines a block, a block contains the following information
- self.index = index # a block contains an ID
- self.timestamp =timestamp # a block contains a timestamp
- self.data = data # a block contains some transactions
- self.prevhash =prevhash # a block contains a hash of the previous block
- self.hash =self.hashblock() # a block contains a hash, the hash is obtained by hashing all the data contained in the block
- def hashblock (self): # define a method for data encryption, this method will retain a hash of the block
- block_encryption=h.sha256() # We need a sha256 function to hash the content of the block, so let's declare it here
- block_encryption.update(str(self.index)+str(self.timestamp)+str(self.data)+str(self.prevhash)) # to encrypt the data in the block, We need just to sum everything and apply the hash function on it
- return block_encryption.hexdigest() # let's return that hash result
- @staticmethod # declaring a static method for the genesis block
- def genesisblock(): # delcare a function for generating the first block named genesis
- return Block(0,d.datetime.now(),"genesis block transaction"," ") # return the genesis block
- @staticmethod# let's declare another static method to get the next block
- def newblock(lastblock): # get the next block, the block that comes after the previous block (prevblock+1)
- index = lastblock.index+1 # the id of this block will be equals to the previous block + 1, which is logic
- timestamp = d.datetime.now() # The timestamp of the next block
- hashblock = lastblock.hash # the hash of this block
- data = "Transaction " +str(index) # The data or transactions containing in that block
- return Block(index,timestamp,data,hashblock)# return the entire block
- blockchain = [Block.genesisblock()] # now it's time to initialize our blockchain with a genesis block in it
- prevblock = blockchain[0] # the previous block is the genesis block itself since there is no block that comes before it at the indice 0
- # let's print the genesis block information
- print"Block ID :{} ".format(prevblock.index)
- print"Timestamp:{}".format(prevblock.timestamp)
- print"Hash of the block:{}".format(prevblock.hash)
- print"Previous Block Hash:{}".format(prevblock.prevhash)
- print"data:{}\n".format(prevblock.data)
- for i in range (0,5): # the loop starts from here, we will need only 5 blocks in our ledger for now, this number can be increased
- addblock = Block.newblock(prevblock) # the block to be added to our chain
- blockchain.append(addblock) # we add that block to our chain of blocks
- prevblock =addblock #now the previous block becomes the last block so we can add another one if needed
- print"Block ID #{} ".format(addblock.index) # show the block id
- print"Timestamp:{}".format(addblock.timestamp)# show the block timestamp
- print"Hash of the block:{}".format(addblock.hash)# show the hash of the added block
- print"Previous Block Hash:{}".format(addblock.prevhash)# show the previous block hash
- print"data:{}\n".format(addblock.data)# show the transactions or data contained in that block
- # end