實現異步編程,這個工具類你得掌握!
本文轉載自微信公眾號「月伴飛魚」,作者日常加油站。轉載本文請聯系月伴飛魚公眾號。
前言
最近看公司代碼,多線程編程用的比較多,其中有對CompletableFuture的使用,所以想寫篇文章總結下
在日常的Java8項目開發中,CompletableFuture是很強大的并行開發工具,其語法貼近java8的語法風格,與stream一起使用也能大大增加代碼的簡潔性
大家可以多應用到工作中,提升接口性能,優化代碼
基本介紹
CompletableFuture是Java 8新增的一個類,用于異步編程,繼承了Future和CompletionStage
這個Future主要具備對請求結果獨立處理的功能,CompletionStage用于實現流式處理,實現異步請求的各個階段組合或鏈式處理,因此completableFuture能實現整個異步調用接口的扁平化和流式處理,解決原有Future處理一系列鏈式異步請求時的復雜編碼
Future的局限性
1、Future 的結果在非阻塞的情況下,不能執行更進一步的操作
我們知道,使用Future時只能通過isDone()方法判斷任務是否完成,或者通過get()方法阻塞線程等待結果返回,它不能非阻塞的情況下,執行更進一步的操作。
2、不能組合多個Future的結果
假設你有多個Future異步任務,你希望最快的任務執行完時,或者所有任務都執行完后,進行一些其他操作
3、多個Future不能組成鏈式調用
當異步任務之間有依賴關系時,Future不能將一個任務的結果傳給另一個異步任務,多個Future無法創建鏈式的工作流。
4、沒有異常處理
現在使用CompletableFuture能幫助我們完成上面的事情,讓我們編寫更強大、更優雅的異步程序
基本使用
創建異步任務
通常可以使用下面幾個CompletableFuture的靜態方法創建一個異步任務
- public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable); //創建無返回值的異步任務
- public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor); //無返回值,可指定線程池(默認使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool)
- public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier); //創建有返回值的異步任務
- public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor); //有返回值,可指定線程池
使用示例:
- Executor executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
- CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
- //do something
- }, executor);
- int poiId = 111;
- CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- PoiDTO poi = poiService.loadById(poiId);
- return poi.getName();
- });
- // Block and get the result of the Future
- String poiName = future.get();
使用回調方法
通過future.get()方法獲取異步任務的結果,還是會阻塞的等待任務完成
CompletableFuture提供了幾個回調方法,可以不阻塞主線程,在異步任務完成后自動執行回調方法中的代碼
- public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable runnable); //無參數、無返回值
- public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action); //接受參數,無返回值
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn); //接受參數T,有返回值U
使用示例:
- CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
- .thenRun(() -> System.out.println("do other things. 比如異步打印日志或發送消息"));
- //如果只想在一個CompletableFuture任務執行完后,進行一些后續的處理,不需要返回值,那么可以用thenRun回調方法來完成。
- //如果主線程不依賴thenRun中的代碼執行完成,也不需要使用get()方法阻塞主線程。
- CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
- .thenAccept((s) -> System.out.println(s + " world"));
- //輸出:Hello world
- //回調方法希望使用異步任務的結果,并不需要返回值,那么可以使用thenAccept方法
- CompletableFuture<Boolean> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- PoiDTO poi = poiService.loadById(poiId);
- return poi.getMainCategory();
- }).thenApply((s) -> isMainPoi(s)); // boolean isMainPoi(int poiId);
- future.get();
- //希望將異步任務的結果做進一步處理,并需要返回值,則使用thenApply方法。
- //如果主線程要獲取回調方法的返回,還是要用get()方法阻塞得到
組合兩個異步任務
- //thenCompose方法中的異步任務依賴調用該方法的異步任務
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
- //用于兩個獨立的異步任務都完成的時候
- public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
- BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
使用示例:
- CompletableFuture<List<Integer>> poiFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
- () -> poiService.queryPoiIds(cityId, poiId)
- );
- //第二個任務是返回CompletableFuture的異步方法
- CompletableFuture<List<DealGroupDTO>> getDeal(List<Integer> poiIds){
- return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> poiService.queryPoiIds(poiIds));
- }
- //thenCompose
- CompletableFuture<List<DealGroupDTO>> resultFuture = poiFuture.thenCompose(poiIds -> getDeal(poiIds));
- resultFuture.get();
thenCompose和thenApply的功能類似,兩者區別在于thenCompose接受一個返回CompletableFuture的Function,當想從回調方法返回的CompletableFuture中直接獲取結果U時,就用thenCompose
如果使用thenApply,返回結果resultFuture的類型是CompletableFuture>>,而不是CompletableFuture>
- CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello")
- .thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "world"), (s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);
- //future.get()
組合多個CompletableFuture
當需要多個異步任務都完成時,再進行后續處理,可以使用allOf方法
- CompletableFuture<Void> poiIDTOFuture = CompletableFuture
- .supplyAsync(() -> poiService.loadPoi(poiId))
- .thenAccept(poi -> {
- model.setModelTitle(poi.getShopName());
- //do more thing
- });
- CompletableFuture<Void> productFuture = CompletableFuture
- .supplyAsync(() -> productService.findAllByPoiIdOrderByUpdateTimeDesc(poiId))
- .thenAccept(list -> {
- model.setDefaultCount(list.size());
- model.setMoreDesc("more");
- });
- //future3等更多異步任務,這里就不一一寫出來了
- CompletableFuture.allOf(poiIDTOFuture, productFuture, future3, ...).join(); //allOf組合所有異步任務,并使用join獲取結果
該方法挺適合C端的業務,比如通過poiId異步的從多個服務拿門店信息,然后組裝成自己需要的模型,最后所有門店信息都填充完后返回
這里使用了join方法獲取結果,它和get方法一樣阻塞的等待任務完成
多個異步任務有任意一個完成時就返回結果,可以使用anyOf方法
- CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- throw new IllegalStateException(e);
- }
- return "Result of Future 1";
- });
- CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- throw new IllegalStateException(e);
- }
- return "Result of Future 2";
- });
- CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- throw new IllegalStateException(e);
- return "Result of Future 3";
- });
- CompletableFuture<Object> anyOfFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2, future3);
- System.out.println(anyOfFuture.get()); // Result of Future 2
異常處理
- Integer age = -1;
- CompletableFuture<Void> maturityFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- if(age < 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Age can not be negative");
- }
- if(age > 18) {
- return "Adult";
- } else {
- return "Child";
- }
- }).exceptionally(ex -> {
- System.out.println("Oops! We have an exception - " + ex.getMessage());
- return "Unknown!";
- }).thenAccept(s -> System.out.print(s));
- //Unkown!
exceptionally方法可以處理異步任務的異常,在出現異常時,給異步任務鏈一個從錯誤中恢復的機會,可以在這里記錄異常或返回一個默認值
使用handler方法也可以處理異常,并且無論是否發生異常它都會被調用
- Integer age = -1;
- CompletableFuture<String> maturityFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- if(age < 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Age can not be negative");
- }
- if(age > 18) {
- return "Adult";
- } else {
- return "Child";
- }
- }).handle((res, ex) -> {
- if(ex != null) {
- System.out.println("Oops! We have an exception - " + ex.getMessage());
- return "Unknown!";
- }
- return res;
- });
分片處理
分片和并行處理:分片借助stream實現,然后通過CompletableFuture實現并行執行,最后做數據聚合(其實也是stream的方法)
CompletableFuture并不提供單獨的分片api,但可以借助stream的分片聚合功能實現
舉個例子:
- //請求商品數量過多時,做分批異步處理
- List<List<Long>> skuBaseIdsList = ListUtils.partition(skuIdList, 10);//分片
- //并行
- List<CompletableFuture<List<SkuSales>>> futureList = Lists.newArrayList();
- for (List<Long> skuId : skuBaseIdsList) {
- CompletableFuture<List<SkuSales>> tmpFuture = getSkuSales(skuId);
- futureList.add(tmpFuture);
- }
- //聚合
- futureList.stream().map(CompletalbleFuture::join).collent(Collectors.toList());
舉個例子
帶大家領略下CompletableFuture異步編程的優勢
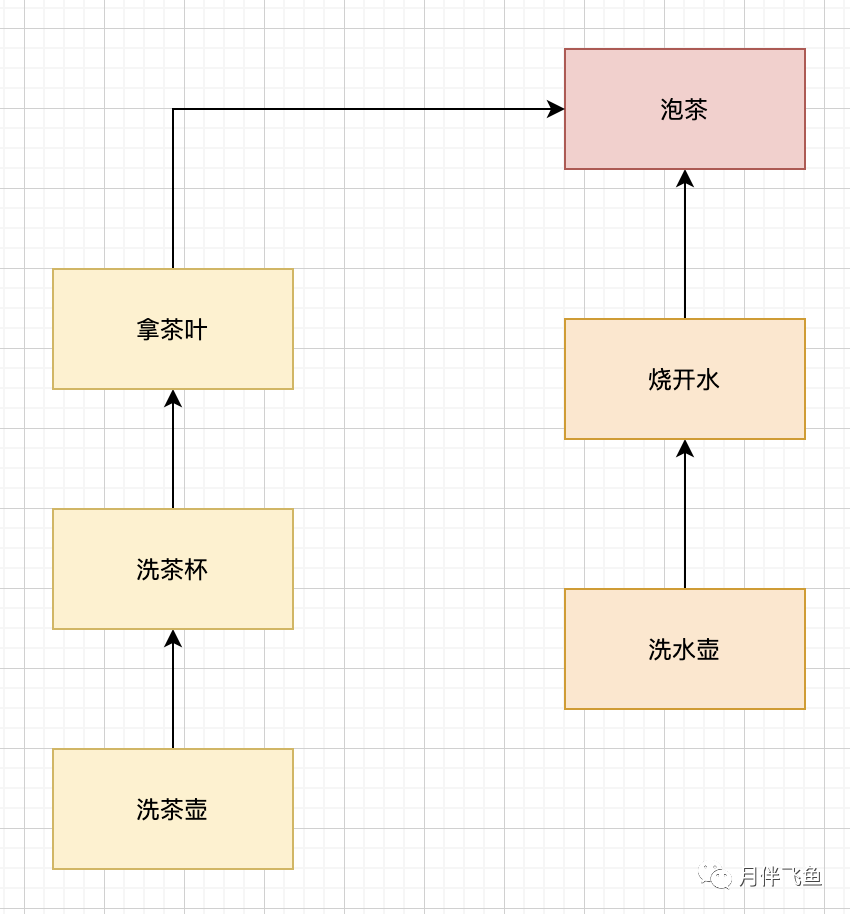
這里我們用CompletableFuture實現水泡茶程序
首先還是需要先完成分工方案,在下面的程序中,我們分了3個任務:
- 任務1負責洗水壺、燒開水
- 任務2負責洗茶壺、洗茶杯和拿茶葉
- 任務3負責泡茶。其中任務3要等待任務1和任務2都完成后才能開始
下面是代碼實現,你先略過runAsync()、supplyAsync()、thenCombine()這些不太熟悉的方法,從大局上看,你會發現:
- 無需手工維護線程,沒有繁瑣的手工維護線程的工作,給任務分配線程的工作也不需要我們關注;
- 語義更清晰,例如 f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, ()->{}) 能夠清晰地表述任務3要等待任務1和任務2都完成后才能開始;
- 代碼更簡練并且專注于業務邏輯,幾乎所有代碼都是業務邏輯相關的
- //任務1:洗水壺->燒開水
- CompletableFuture f1 =
- CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
- System.out.println("T1:洗水壺...");
- sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- System.out.println("T1:燒開水...");
- sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- });
- //任務2:洗茶壺->洗茶杯->拿茶葉
- CompletableFuture f2 =
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
- System.out.println("T2:洗茶壺...");
- sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
- sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- System.out.println("T2:拿茶葉...");
- sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
- return "龍井";
- });
- //任務3:任務1和任務2完成后執行:泡茶
- CompletableFuture f3 =
- f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf)->{
- System.out.println("T1:拿到茶葉:" + tf);
- System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
- return "上茶:" + tf;
- });
- //等待任務3執行結果
- System.out.println(f3.join());
- void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u) {
- try {
- u.sleep(t);
- }catch(InterruptedException e){}
- }
注意事項
1.CompletableFuture默認線程池是否滿足使用
前面提到創建CompletableFuture異步任務的靜態方法runAsync和supplyAsync等,可以指定使用的線程池,不指定則用CompletableFuture的默認線程池
- private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
- ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
可以看到,CompletableFuture默認線程池是調用ForkJoinPool的commonPool()方法創建,這個默認線程池的核心線程數量根據CPU核數而定,公式為Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() - 1,以4核雙槽CPU為例,核心線程數量就是4*2-1=7個
這樣的設置滿足CPU密集型的應用,但對于業務都是IO密集型的應用來說,是有風險的,當qps較高時,線程數量可能就設的太少了,會導致線上故障
所以可以根據業務情況自定義線程池使用
2.get設置超時時間不能串行get,不然會導致接口延時線程數量*超時時間