Spring Boot 請求路徑可以定義成 /**/** 這種格式嗎?
前兩天松哥和大家分享了 Spring Security 中如何實現權限通配符的功能,里邊用到了一個“邪門歪道” AntPathMatcher,有小伙伴對這個感到陌生,問松哥能不能單獨介紹一下這個玩意,好,安排!
不過 AntPathMatcher 其實在逐漸過時,它的替代品是 PathPattern,我就把這兩個放在一起和大家分享下。
Spring5 也已經出來好久了,里邊有一些新玩法也需要我們去慢慢揭開面紗,其中,系統分析當前請求路徑的方法位于這里:org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping#initLookupPath:
protected String initLookupPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (usesPathPatterns()) {
request.removeAttribute(UrlPathHelper.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
RequestPath requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
String lookupPath = requestPath.pathWithinApplication().value();
return UrlPathHelper.defaultInstance.removeSemicolonContent(lookupPath);
}
else {
return getUrlPathHelper().resolveAndCacheLookupPath(request);
}
}
這個方法就是 Spring5 里邊出來的,以前是沒有這個方法的。在舊的 SpringMVC 中,當我們需要獲取當前請求地址的時候,直接通過如下方式獲取:
String lookupPath = this.getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
但是現在變了,現在獲取當前請求 URL 地址時,方式如下:
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
兩種方式相比,主要是 initLookupPath 方法中多了 usesPathPatterns 選項,這是 Spring5 中的新玩意,所以今天松哥就通過一篇簡單的文章來和大家分享一下 usesPathPatterns 到底是什么,該怎么玩!
這可不是一個小變化哦!特別是如果你在項目中使用了 WebFlux,那么這個東西就顯得尤為重要了!
1. AntPathMatcher
當我們使用 @RequestMapping 注解去標記請求接口的時候(或者使用它的類似方法如 @GetMapping、@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping),我們可以使用一些通配符去匹配 URL 地址,舉個簡單例子,假設我有下面五個接口:
@GetMapping("/hello/**/hello")
public String hello() {
return "/hello/**/hello";
}
@GetMapping("/h?llo")
public String hello2() {
return "/h?llo";
}
@GetMapping("/**/*.html")
public String hello3() {
return "/**/*.html";
}
@GetMapping("/hello/{p1}/{p2}")
public String hello4(@PathVariable String p1, @PathVariable String p2) {
System.out.println("p1 = " + p1);
System.out.println("p2 = " + p2);
return "/hello/{p1}/{p2}";
}
@GetMapping("/{name:[a-z-]+}-{version:\\d\\.\\d\\.\\d}{ext:\\.[a-z]+}")
public void handle(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String version, @PathVariable String ext) {
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("version = " + version);
System.out.println("ext = " + ext);
}
在解釋接口的含義之前,先來說說這幾個通配符的含義:
通配符 | 含義 |
? | 匹配0個或者多個目錄 |
? | 匹配0個或者多個字符 |
? | 匹配任意單個字符 |
了解了通配符的含義,我們再來說說各個接口都能接收哪些請求:
第一個接口,可以接收諸如/hello/123/123/hello、/hello/a/hello? 以及/hello/hello? 這樣的請求,因為中間的** 代表 0 個或者多個目錄。
第二個接口,可以接收諸如/hallo、/hello、/hMllo? 之類的請求,注意它不能接收/haallo? 或者/hllo?,因為? 表示一個字符。
第三個接口可以接收任意以.html? 為后綴的請求,例如/aaa/bb/cc.html、/aa.html? 或者/aa/aa.html。
第四個接口估計大家都比較熟悉,在 RESTful 風格的接口設計中估計大家都用過,它接收的請求格式類似于/hello/aa/bb,其中參數 p1 就對應 aa,參數 p2 對應 bb。
第五個接口則用到了正則,name、version 以及 ext 三個參數格式用正則表達出來,它可以接收諸如/spring-web-3.0.5.jar? 格式的請求,最終的參數 name 就是spring-web?,version 就是3.0.5?,ext 則是.jar。
這是 SpringMVC 中之前就存在的功能,不管你用沒用過,反正它一致存在。
那么是誰支撐了這個功能呢?那就是 AntPathMatcher。
AntPathMatcher 是一個實現了 Ant 風格的路徑匹配器,Ant 風格的路徑規(guī)則實際上就是我們前面給大家介紹的那三種路徑匹配符,很 Easy。這種路徑匹配規(guī)則源自 Apache Ant 項目(https://ant.apache.org),Apache Ant 我們現在其實已經很少會用到了,它的替代品就是大家所熟知的 Maven,如果你有幸維護一些 2010 年之前的老項目的話,有可能會接觸到 Ant。
AntPathMatcher 實際上在 SpringMVC 中有非常廣泛的應用,不僅僅是在 @RequestMapping 中定義接口用到,在其他一些涉及到地址匹配的地方也會用到,例如我們在 SpringMVC 的配置文件中配置靜態(tài)資源過濾時,也是 Ant 風格路徑匹配:
<mvc:resources mapping="/**" location="/"/>
另外像攔截器里的攔截路徑注冊、跨域處理時的路徑匹配等等,都會用到 Ant 風格的路徑匹配符。
整體上來說,AntPathMatcher 是 Spring 中一種比較原始的路徑匹配解決方案,雖然比較簡單,但是它的效率很低,并且在處理 URL 編碼的時候也很不方便。
因此,才有了 Spring5 中的 PathPattern。
2. PathPattern
PathPattern 專為 Web 應用設計,它與之前的 AntPathMatcher 功能大部分比較類似,當然也有一些細微差異,這個松哥后面會說。
如果是 Servlet 應用,目前官方推薦的 URL 匹配解決方案就是 PathPattern(當然你也可以選擇較早的 AntPathMatcher),雖然官方推薦的是 PathPattern,但實際上默認使用的依然是 AntPathMatcher;如果你用的是 WebFlux,PathPattern 就是唯一解決方案了。
注意,PathPattern 是一個非常新鮮的玩藝,目前 Spring 最新版是 5.3.4,在 Spring5.3 之前,我們在 Servlet 應用中,也只能選擇 AntPathMatcher,從 Spring5.3 之后,我們才可以使用 PathPattern 了。
PathPattern 會將 URL 規(guī)則預解析為 PathContainer,它對 URL 地址匹配的處理更加快速,PathPattern 與 AntPathMatcher 的差異主要體現在兩個方面:
第一,PathPattern 只支持結尾部分使用 **?,如果在路徑的中間使用 ** 就會報錯,上文中第一個和第三個接口,在 PathPattern 模式下會報錯,如下:
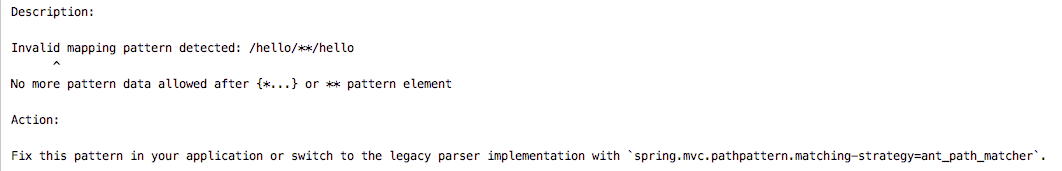
因為在中間或者開始使用 **? 極易造成混亂,因此 PathPattern 只支持在結尾使用 **。
第二,PathPattern 支持使用諸如 {*path} 的方式進行路徑匹配,這種寫法也可以匹配到多層路徑,并且將匹配到的值賦值給 path 變量,例如如下一個接口:
@GetMapping("/javaboy/{*path}")
public void hello6(@PathVariable String path) {
System.out.println("path = " + path);
}
如果請求路徑是 http://localhost:8080/javaboy/aa?,那么參數 path 的值就是 /aa;
如果請求路徑是 http://localhost:8080/javaboy/aa/bb/cc/dd?,那么參數 path 的值就是 /aa/bb/cc/dd;
這個寫法也比較新穎,因為之前的 AntPathMatcher 里邊沒有這個。
3. 如何使用
默認情況下,SpringMVC 中使用的還是 AntPathMatcher,那么如何開啟 PathPattern 呢?很簡單,在 SpringBoot 項目中只需要添加如下配置即可:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setPatternParser(new PathPatternParser());
}
}
添加了這個配置后,在我們文章一開始貼出來的代碼里,就會進入到 if 分支中,進而使用 PathPattern 去解析請求 URL。
4. 小結
今天就和小伙伴們聊這么多,大家可以體驗一把這個東東,不過注意選擇 Spring 的版本哦,一定選擇 5.3 之上的版本!