
Beautiful Soup4是一個 Python 庫,用于從 HTML 和 XML 文件中提取數據。它是一個工具箱,通過解析文檔為用戶提供需要抓取的數據,Beautiful Soup自動將輸入文檔轉換為Unicode編碼,輸出文檔轉換為utf-8編碼。你不需要考慮編碼方式,除非文檔沒有指定一個編碼方式,這時,Beautiful Soup就不能自動識別編碼方式了。
BeautifulSoup安裝
使用pip來安裝BeautifulSoup。
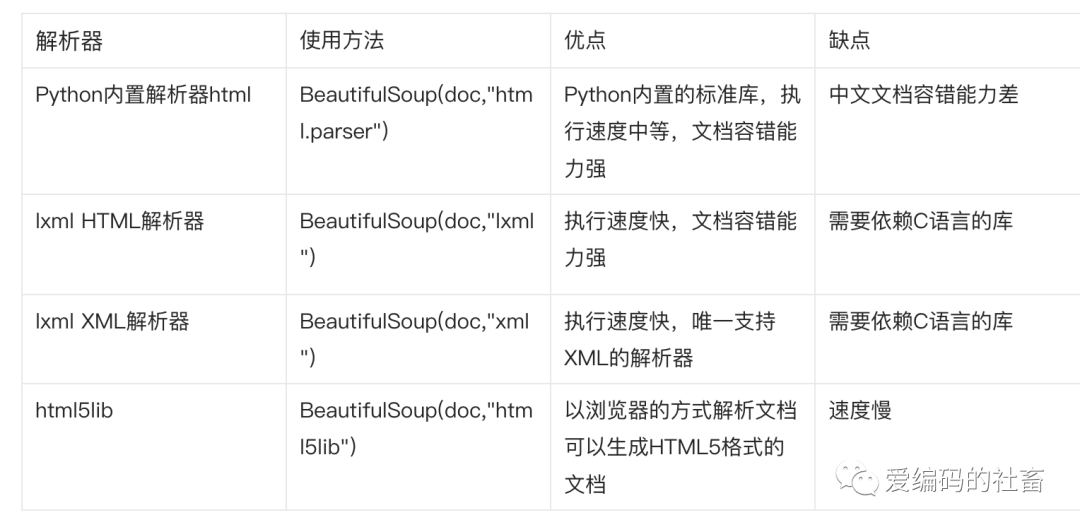
另外要安裝解析器,下列表格列出一些常用的解析器。
使用BeautifulSoup及四大對象
1、創建BeautifulSoup對象
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
print(soup.prettify()) // 格式化輸出
print(soup.get_text()) // 獲取網頁所有的文字內容
2、BeautifulSoup四大對象
Beautiful Soup 將復雜 HTML 文檔轉換成一個復雜的樹形結構,每個節點都是 Python 對象,所有對象可以歸納為 4 種。
- Tag:HTML中的標簽,簡單來說就是html標簽。
- NavigableString:簡單來說就是標簽里面的內容,它的類型是一個NavigableString,翻譯過來叫可以遍歷的字符串。
- BeautifulSoup:BeautifulSoup對象表示的是一個文檔的全部內容,大部分時候,可以把它當作Tag對象,是一個特殊的Tag,我們可以分別獲取它的類型、名稱、以及屬性
- Comment:一個特殊類型的NavigableString對象,其實輸出的內容不包括注釋符號
Tag對象示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
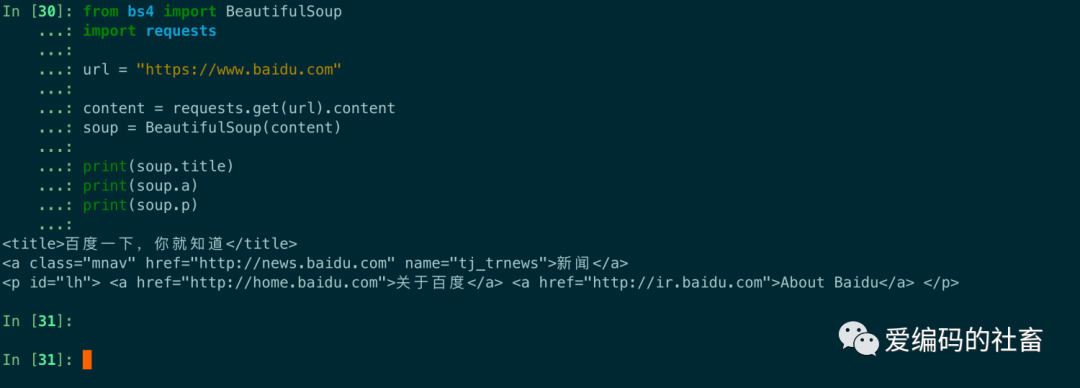
print(soup.title)
print(soup.a)
print(soup.p)
運行輸出如下圖所示,但是發現好像這個網頁不止一個a標簽跟p標簽,是因為它查找的是在所有內容中的第一個符合要求的標簽,要想得到所有符合要求的標簽,后面會介紹find_all函數。
在Tag對象中有兩個重要的屬性,name和attrs。
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
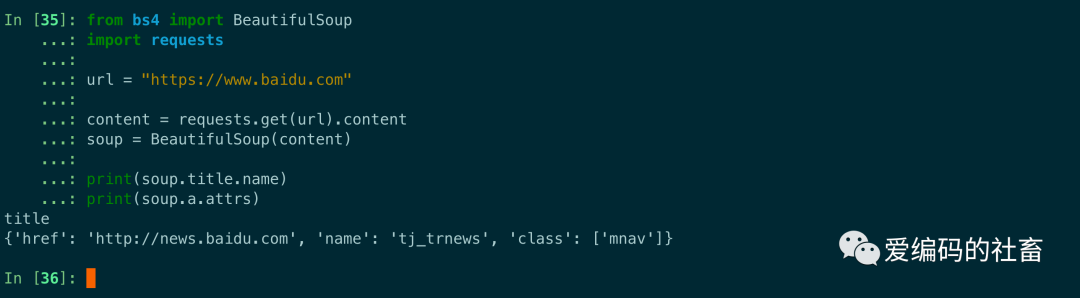
print(soup.a.attrs)
運行輸出如下圖所示,name輸出的是標簽的本身,attrs輸出的是一個字典的類型,如果我們需要得到某個標簽的某個屬性可以使用字典一些方法去獲取比如get方法,print(soup.p.get("class"))或者直接使用print(soup.p["class"])。
NavigableString代碼示例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
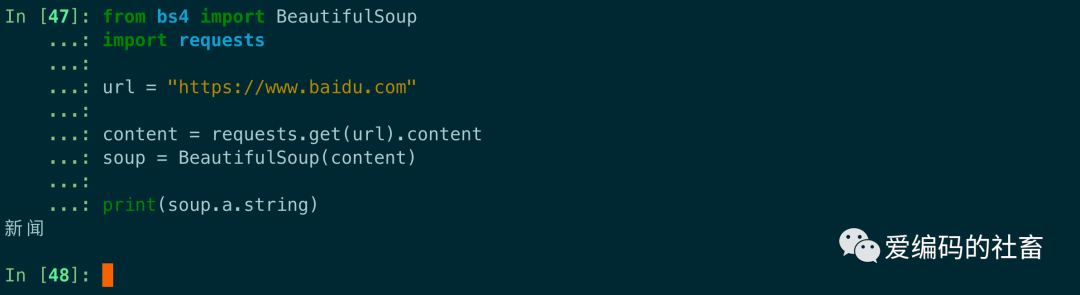
print(soup.a.string)
運行輸出如下圖,可以NavigableString類型的string方法輕松獲取到了標簽里面的內容。
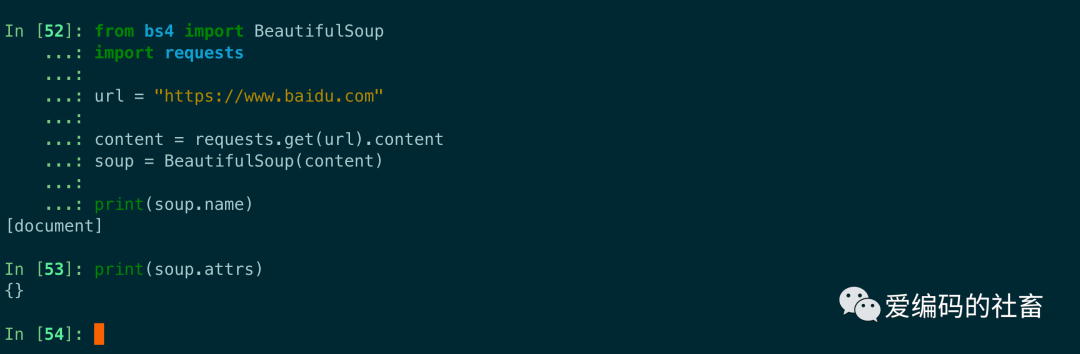
BeautifulSoup代碼示例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
print(soup.name)
print(soup.attrs)
運行輸出如下圖所示:
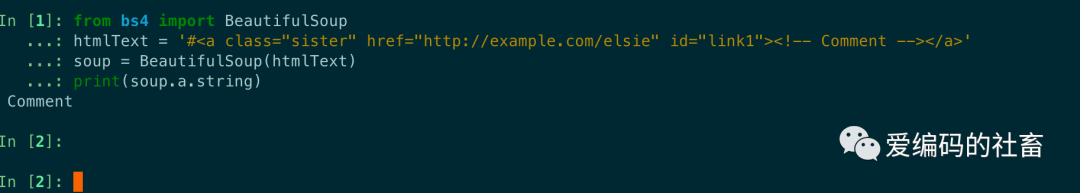
Comment代碼示例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
htmlText = '#<a class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Comment --></a>'
soup = BeautifulSoup(htmlText)
print(soup.a.string)
運行輸出如下,a 標簽里的內容實際上是注釋,但是如果利用 .string方法來輸出它的內容,發現它已經把注釋符號去掉了,所以這可能會給帶來不必要的麻煩。
文檔樹遍歷
tag里面的content屬性可以將tag的子節點以列表的形式返回。通過遍歷content.返回的列表來獲取每一個子節點或者直接使用tag的children方法來獲取。
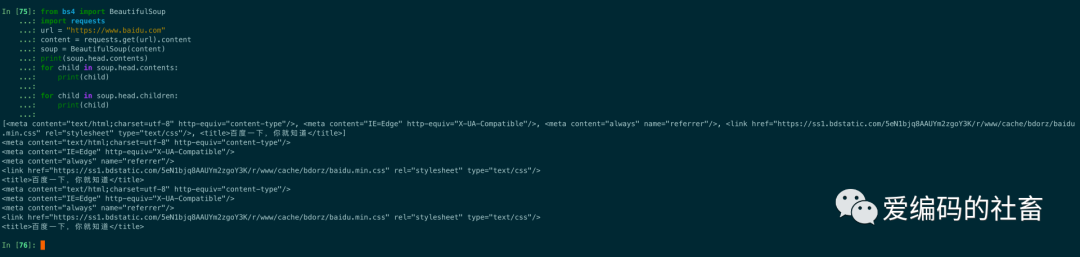
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
print(soup.head.contents)
for child in soup.head.contents:
print(child)
for child in soup.head.children:
print(child)
運行輸出結果如下圖所示:
tag里面的.descendants 屬性可以對所有tag的子孫節點進行遞歸循環,和 children類似,我們也需要遍歷獲取其中的內容。
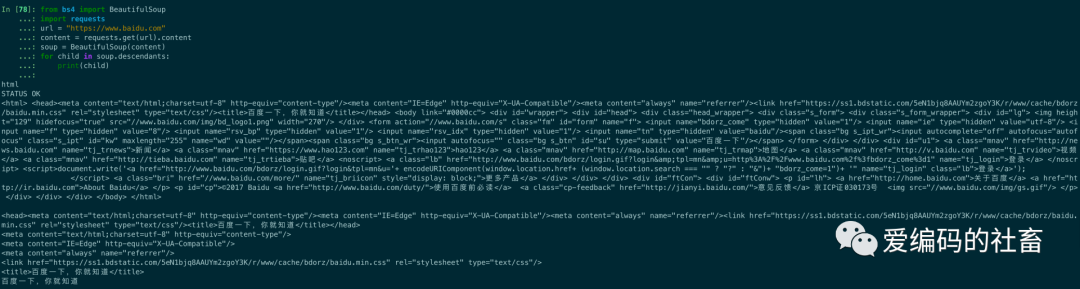
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
for child in soup.descendants:
print(child)
運行結果輸出如下圖所示:
使用.string方法來獲取內容,如果一個標簽里面沒有標簽了,那么 .string 就會返回標簽里面的內容。如果標簽里面只有唯一的一個標簽了,那么 .string 也會返回最里面的內容,如果標簽里面沒有內容則返回None。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
print(soup.a.string)
print(soup.title.string)
運行結果輸出如下圖所示:

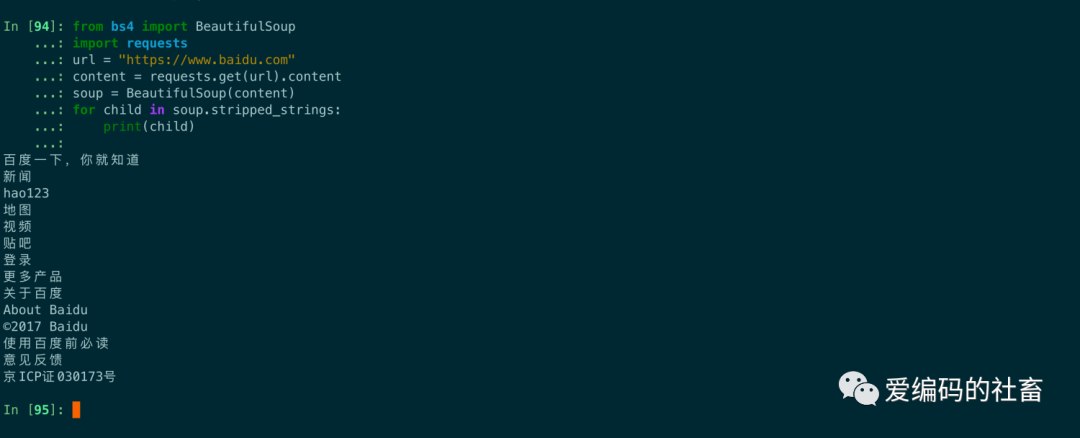
使用strippend_strings 屬性來獲取多個內容還可以出除多余的空白字符,需要使用遍歷來獲取。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content)
for child in soup.stripped_strings:
print(child)
運行結果輸出如下圖所示:
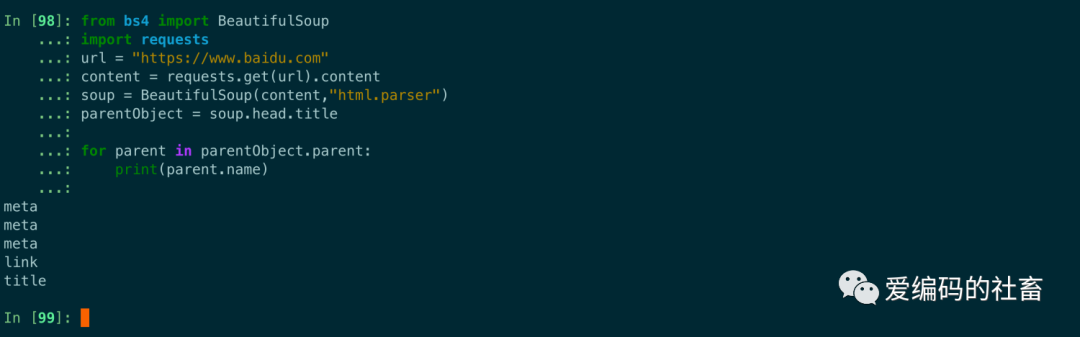
通過元素的 .parents 屬性可以遞歸得到元素的所有父輩節點。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"html.parser")
parentObject = soup.head.title
for parent in parentObject.parent:
print(parent.name)
運行結果輸出如下圖所示:
還有一些節點就不舉例,跟其它獲取節點一樣也是需要遍歷,而且使用的場景不同,兄弟節點使用.next_siblings或者.previous_sibling方法,前后節點使用.next_element或者.previous_element方法。
搜索文檔樹
find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,\kwargs)**,find_all()方法用于搜索當前tag的所有tag子節點,并判斷是否符合過濾條件。
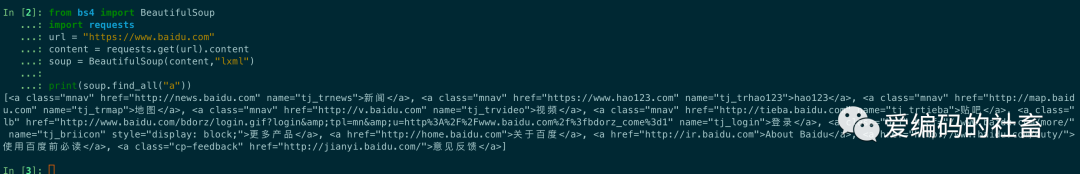
最簡單的過濾器是字符串,在搜索方法中傳入一個字符串參數,beautifulsoup會查找與字符串完整匹配的內容,下面的例子用于查找文檔中的所有a標簽
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all("a"))
運行結果如下圖所示:
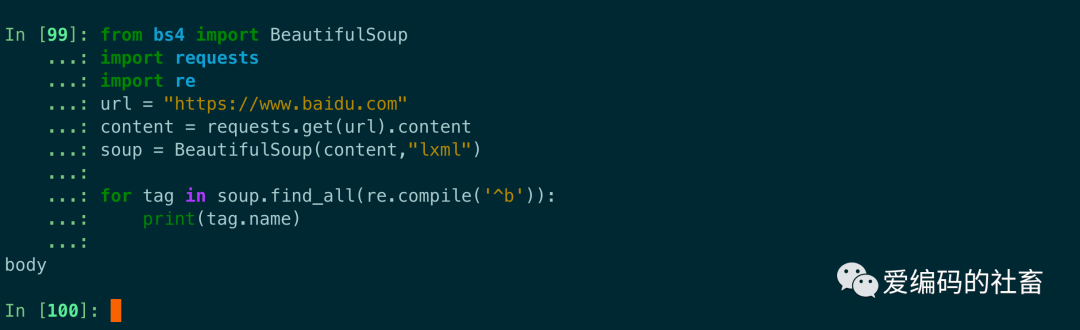
如果傳入正則表達式作為參數,beautiful soup會通過正則表達式的match()來匹配內容,下面例子中找出所有以b開頭的標簽,這表示b開頭標簽都應該被找到。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import re
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
for tag in soup.find_all(re.compile('^b')):
print(tag.name)
運行結果如下圖所示:
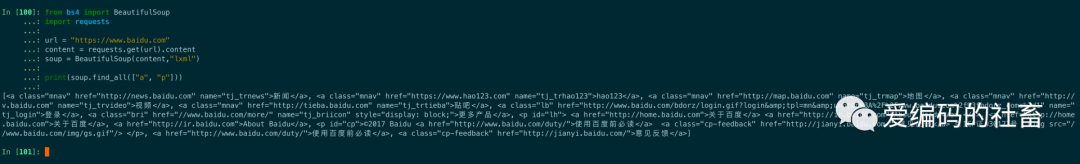
如果傳入列表參數,Beautiful Soup會將與列表中任一元素匹配的內容返回.下面代碼找到文檔中所有標簽和標簽。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all(["a", "p"]))
運行結果如下圖所示:
true 可以匹配任何值,下面代碼查找到所有的tag,但是不會返回字符串節點。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
for tag in soup.find_all(True):
print(tag.name)
運行結果如下圖所示:

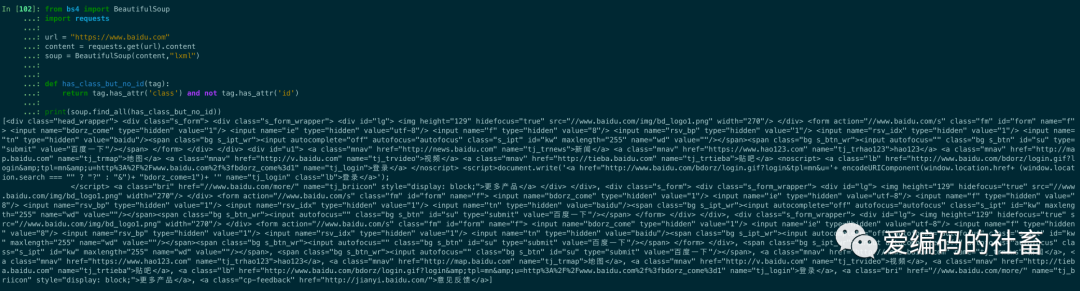
如果沒有合適過濾器,那么還可以定義一個函數,函數只接受一個元素參數,如果這個方法返回 True 表示當前元素匹配并且被找到,如果不是則返回 False。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
print(soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id))
輸出結果如下圖所示:
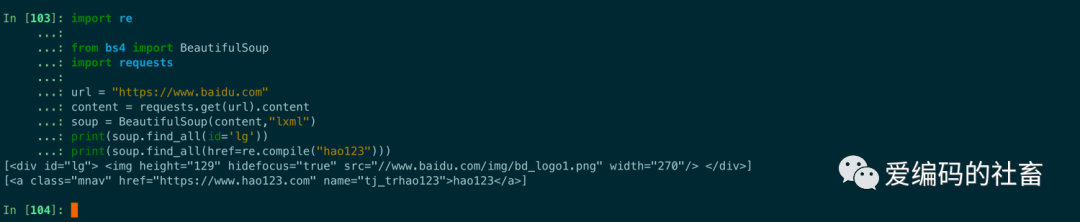
注意:如果一個指定名字的參數不是搜索內置的參數名,搜索時會把該參數當作指定名字tag的屬性來搜索,如果包含一個名字為id的參數,Beautifulsoup會搜索每個tag的'id'值。
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.find_all(id='lg'))
print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile("hao123")))
運行結果如下圖所示:
find(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs ), 它與 find_all() 方法唯一的區別是 find_all() 方法的返回結果是值包含一個元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回結果。?
CSS選擇器
在使用BeautifulSoup中常用的有5中css選擇器方法,用到的方法是 soup.select(),返回類型是列表。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.select("title"))
運行結果如下圖所示:

from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
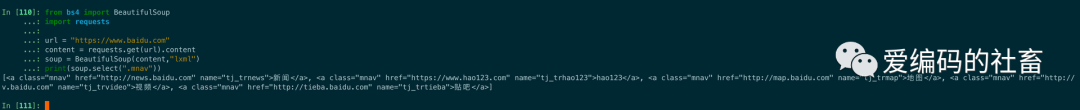
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.select(".mnav"))
運行結果如下圖所示:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.select("#lg"))
運行結果如下圖所示:
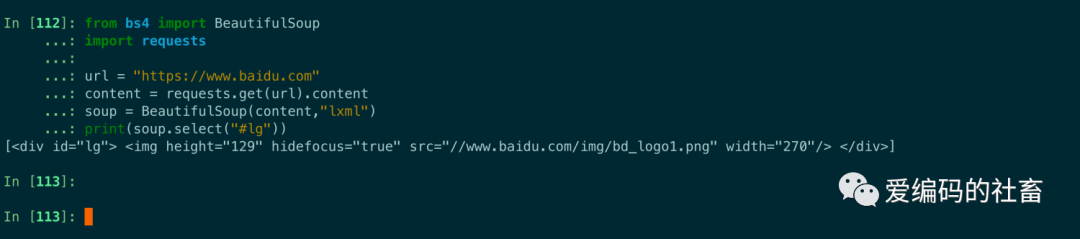
組合查找有點類似前端CSS選擇器中的組合選擇器,組合查找還可以使用子代選擇器。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
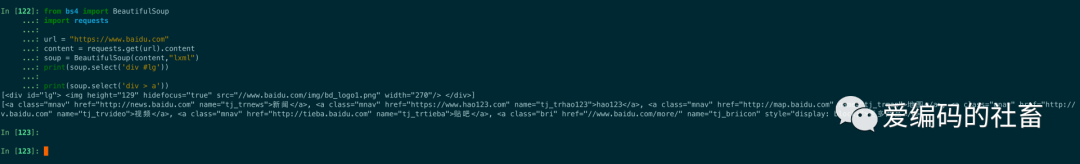
print(soup.select('div #lg'))
print(soup.select('div > a'))
運行結果如下圖所示:
使用屬性需要用中括號括起來,注意屬性和標簽屬于同一節點,所以中間不能加空格,否則會無法匹配到。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.select('a[class="mnav"]'))
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
content = requests.get(url).content
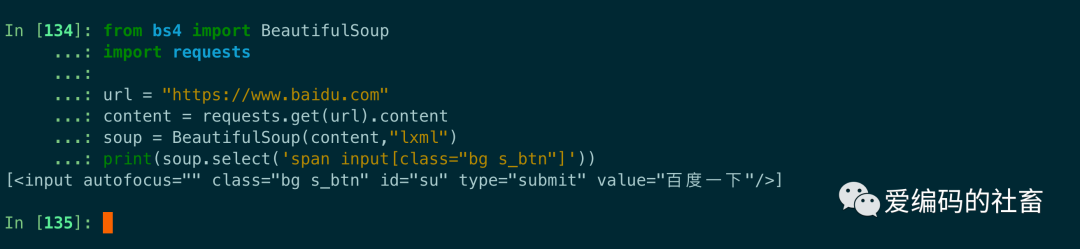
soup = BeautifulSoup(content,"lxml")
print(soup.select('span input[class="bg s_btn"]'))
運行結果如下圖所示:
修改文檔樹
Beautiful Soup的強項是文檔樹的搜索,但同時也可以方便的修改文檔樹
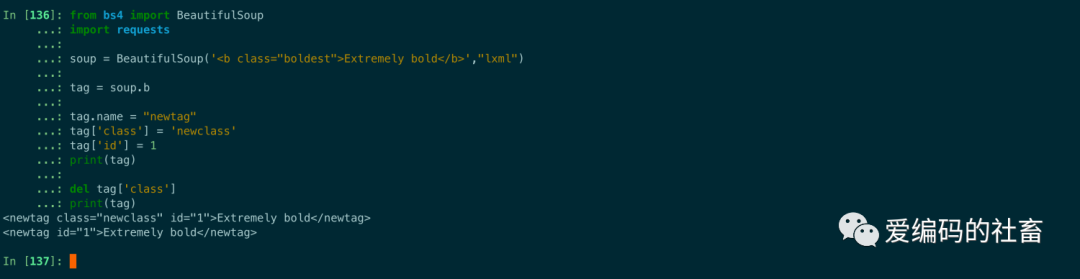
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
soup = BeautifulSoup('<b class="boldest">Extremely bold</b>',"lxml")
tag = soup.b
tag.name = "newtag"
tag['class'] = 'newclass'
tag['id'] = 1
print(tag)
del tag['class']
print(tag)
運行結果如下圖所示:
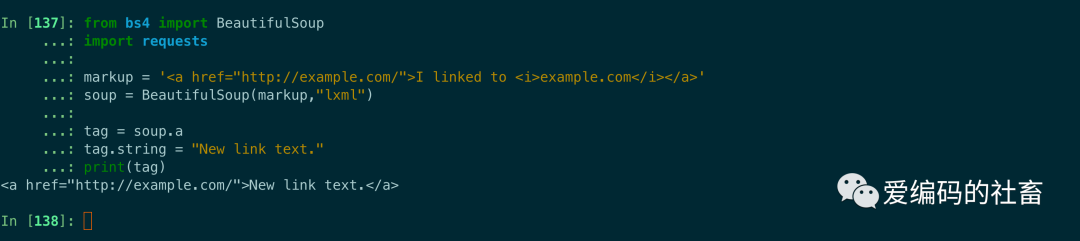
給tag的 .string 屬性賦值,就相當于用當前的內容替代了原來的內容,如果當前的tag包含了其它tag,那么給它的 .string 屬性賦值會覆蓋掉原有的所有內容包括子tag。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
markup = '<a >I linked to <i>example.com</i></a>'
soup = BeautifulSoup(markup,"lxml")
tag = soup.a
tag.string = "New link text."
print(tag)
運行結果如下圖所示:
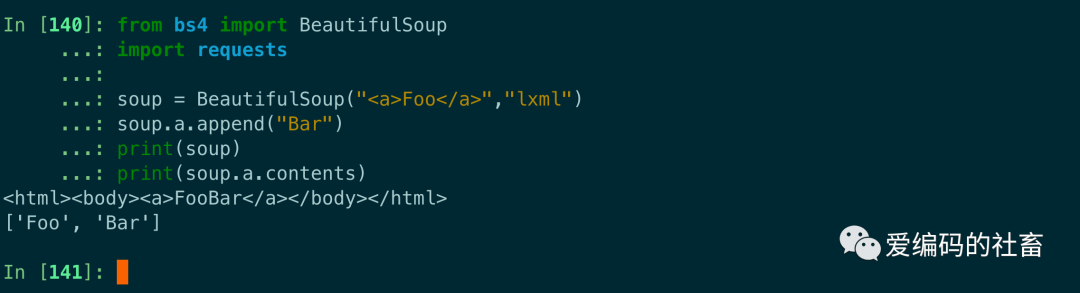
Tag.append() 方法可以在tag中添加內容。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
soup = BeautifulSoup("<a>Foo</a>","lxml")
soup.a.append("Bar")
print(soup)
print(soup.a.contents)
運行結果如下圖所示:
總結
本篇內容比較多,把 Beautiful Soup 的方法進行了大部分整理和總結,但是還不夠完整只是列出一些常用的,如果需要完整的可以查看Beautiful Soup 官網的文檔,希望對大家有幫助,掌握了 Beautiful Soup,一定會給你在數據爬取帶來方便。
本文轉載自微信公眾號「愛編碼的社畜」,可以通過以下二維碼關注。轉載本文請聯系愛編碼的社畜公眾號。








































































