裝飾器的美妙之處在于它們非常易于應用,為你的代碼提供了許多額外的功能。在本文中,我將介紹 5 個方便的裝飾器,你可以輕松地將它們應用于調試代碼時遇到的實際問題。
本文的目的是為你提供一些現成的裝飾器,并啟發你想出一些方便的通用裝飾器。
在我們開始之前:你知道你也可以讓裝飾器跟蹤狀態嗎?示例:計算調用函數的次數,以便你可以對其進行速率限制。請務必閱讀: 以了解裝飾器的工作原理、如何應用它們以及何時使用裝飾器。
在本文中,我將通過以下5裝飾器來探索裝飾器。
- 計時你的功能
- 性能檢查
- 中繼器
- 在執行之前詢問你是否確定
- 將你的功能包裝在 try-catch 中
1、定時器
讓我們從簡單的開始;我們將從一個裝飾器開始,它打印出我們的函數運行所花費的時間。這是代碼:
from functools import wraps
import time
def timer(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.perf_counter()
# Call the actual function
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
duration = time.perf_counter() - start
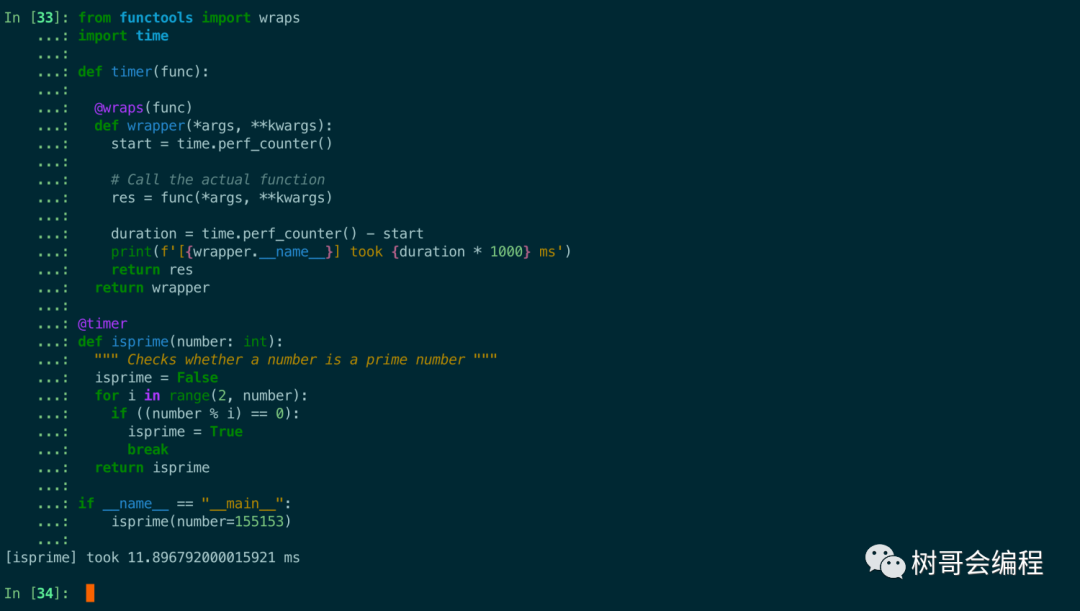
print(f'[{wrapper.__name__}] took {duration * 1000} ms')
return res
return wrapper
請注意,我們的裝飾器本身是用@wraps(func) 包裹的。這是為了確保我們傳遞我們的包裝函數。如果我們不這樣做wrapper.__name__,只會打印 'wrapper' 而不是我們實際裝飾的函數。我將在計算素數的函數上使用這個裝飾器:
from functools import wraps
import time
def timer(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.perf_counter()
# Call the actual function
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
duration = time.perf_counter() - start
print(f'[{wrapper.__name__}] took {duration * 1000} ms')
return res
return wrapper
@timer
def isprime(number: int):
""" Checks whether a number is a prime number """
isprime = False
for i in range(2, number):
if ((number % i) == 0):
isprime = True
break
return isprime
if __name__ == "__main__":
isprime(number=155153)
現在我們調用函數看看輸出:
2、性能檢查
定時我們的功能很有用,但我們想要更多信息。除了持續時間之外,下面這個裝飾器還提供有關函數的信息,包括名稱和文檔字符串,以及內存使用情況等性能信息:
from functools import wraps
import time
def performance_check(func):
"""Measure performance of a function"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
tracemalloc.start()
start_time = time.perf_counter()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
duration = time.perf_counter() - start_time
current, peak = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()
tracemalloc.stop()
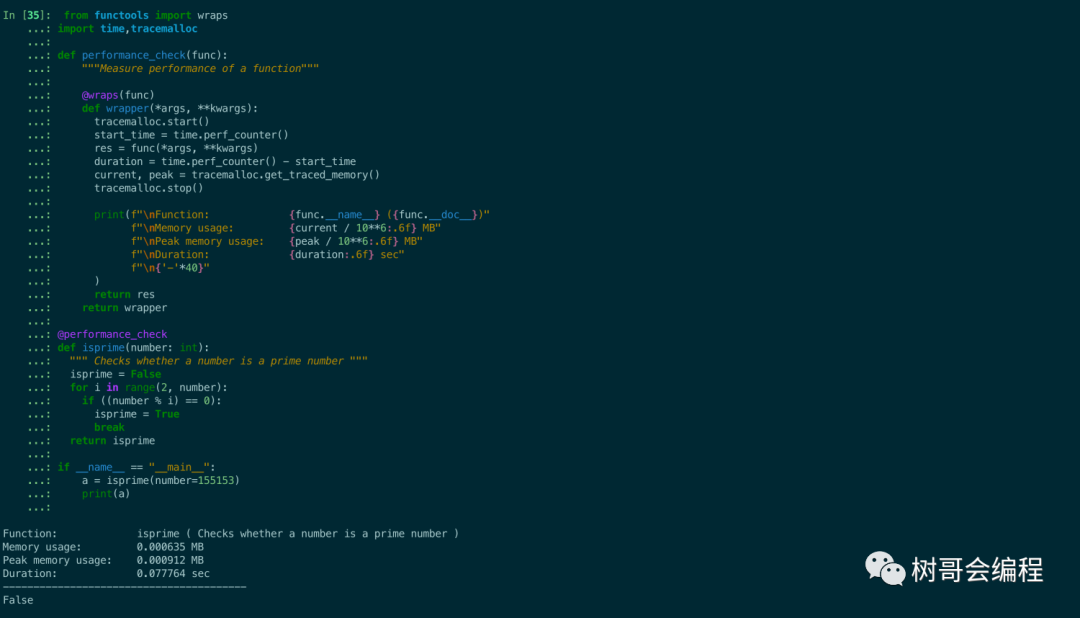
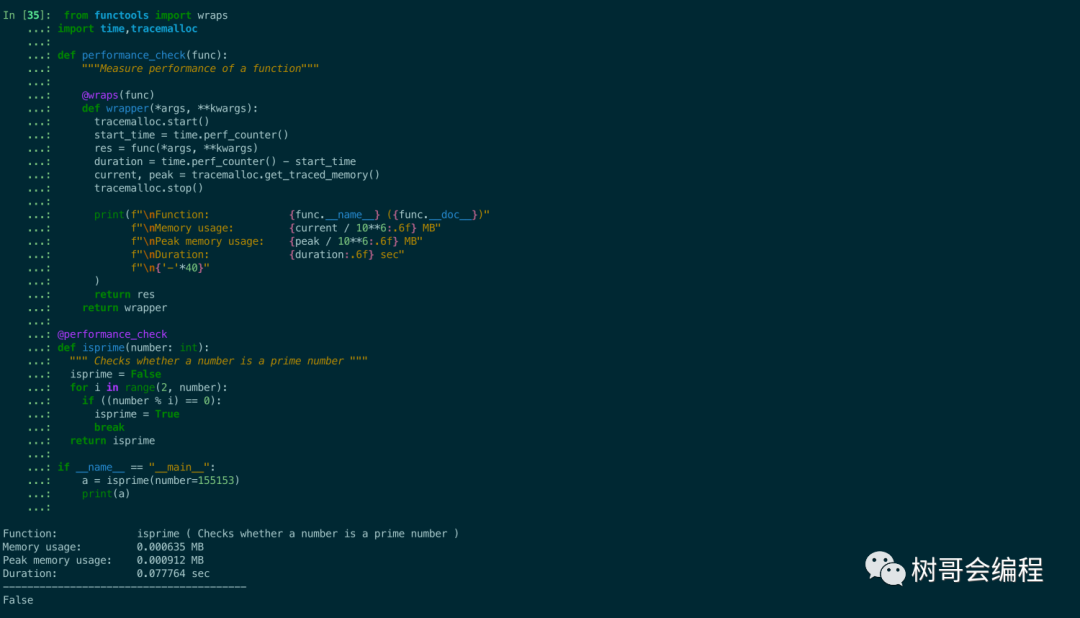
print(f"\nFunction: {func.__name__} ({func.__doc__})"
f"\nMemory usage: {current / 10**6:.6f} MB"
f"\nPeak memory usage: {peak / 10**6:.6f} MB"
f"\nDuration: {duration:.6f} sec"
f"\n{'-'*40}"
)
return res
return wrapper
我們還是用計算素數的函數上使用這個裝飾器:
from functools import wraps
import time,tracemalloc
def performance_check(func):
"""Measure performance of a function"""
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
tracemalloc.start()
start_time = time.perf_counter()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
duration = time.perf_counter() - start_time
current, peak = tracemalloc.get_traced_memory()
tracemalloc.stop()
print(f"\nFunction: {func.__name__} ({func.__doc__})"
f"\nMemory usage: {current / 10**6:.6f} MB"
f"\nPeak memory usage: {peak / 10**6:.6f} MB"
f"\nDuration: {duration:.6f} sec"
f"\n{'-'*40}"
)
return res
return wrapper
@performance_check
def isprime(number: int):
""" Checks whether a number is a prime number """
isprime = False
for i in range(2, number):
if ((number % i) == 0):
isprime = True
break
return isprime
if __name__ == "__main__":
a = isprime(number=155153)
print(a)
我們調用素數函數來看看輸出:
3、中繼器
此裝飾器在調用時重復某個功能。這可以方便測試性能或壓力測試,例如
def repeater(iterations:int=1):
""" Repeats the decorated function [iterations] times """
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
res = None
for i in range(iterations):
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
return res
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper
我們使用一個打印hello的函數來測試一下,讓它執行兩次。
def repeater(iterations:int=1):
""" Repeats the decorated function [iterations] times """
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
res = None
for i in range(iterations):
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
return res
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper
@repeater(iteratinotallow=2)
def sayhello():
print("hello")
現在調用 sayhello() 將產生以下輸出,這個裝飾器可以很好地用于執行幾次,例如測量函數的性能。
4、在執行函數之前提示你是否繼續執行
這個裝飾器可以添加到需要很長時間才能完成或具有重大后果(如刪除數據)的函數中。一旦你調用該函數,裝飾器就會確保你在調用之前確認你要執行該函數。否則它只會返回而不調用該函數。
def prompt_sure(prompt_text:str):
""" Shows prompt asking you whether you want to continue. Exits on anything but y(es) """
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if (input(prompt_text).lower() != 'y'):
return
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper
我們依然使用sayhello函數來演示該裝飾器的功能
def prompt_sure(prompt_text:str):
""" Shows prompt asking you whether you want to continue. Exits on anything but y(es) """
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if (input(prompt_text).lower() != 'y'):
return
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper
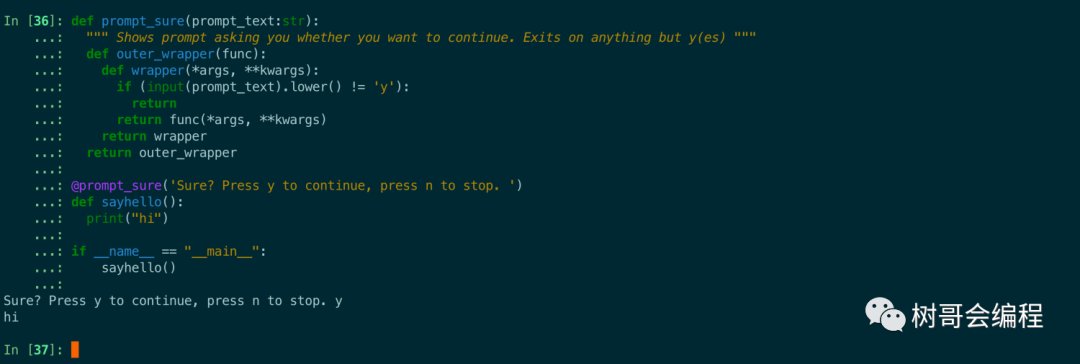
@prompt_sure('Sure? Press y to continue, press n to stop. ')
def sayhello():
print("hi")
if __name__ == "__main__":
sayhello()
我們能夠在裝飾器上設置提示消息。當我們調用sayhello()時,會看到Sure? Press y to continue, press n to stop.如果輸入 'y' 那么我們將執行sayhello(),任何其他輸入(包括沒有輸入將阻止sayhello()執行)。
5、裝飾器中的 TryCatch
這使用裝飾器將您的函數包裝在 try-except-block 中。優點是,只需一行 Python 代碼,您的整個函數就可以免受異常的影響。這是代碼的樣子:
def trycatch(func):
""" Wraps the decorated function in a try-catch. If function fails print out the exception. """
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
return res
except Exception as e:
print(f"Exception in {func.__name__}: {e}")
return wrapper
我們將在下面的函數中使用這個裝飾器
def trycatch(func):
""" Wraps the decorated function in a try-catch. If function fails print out the exception. """
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
return res
except Exception as e:
print(f"Exception in {func.__name__}: {e}")
return wrapper
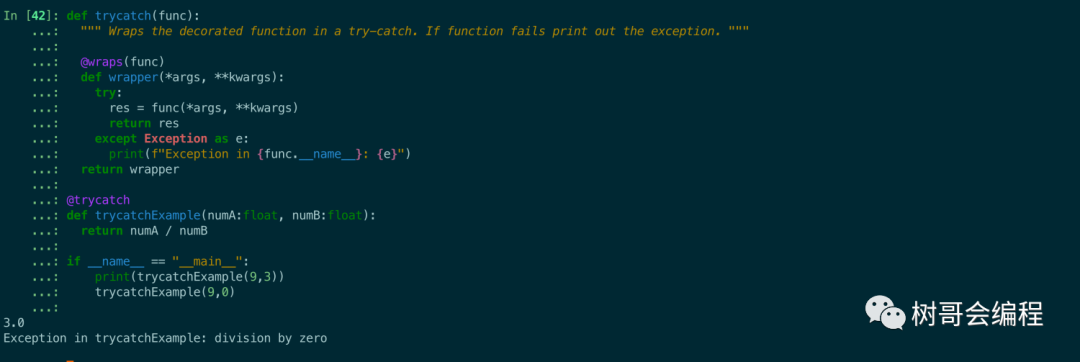
@trycatch
def trycatchExample(numA:float, numB:float):
return numA / numB
if __name__ == "__main__":
trycatchExample(9.3)
trycatchExample(9,0)
現在,當我們調用trycatchExample(9, 3)函數時返回3.0。如果我們調用trycatchExample(9, 0)(除以 0),它會正確返回以下內容Exception in trycatchExample: division by zero
我建議僅將此裝飾器用于調試代碼,并更準確地捕獲函數中的錯誤。
結論
通過這篇文章,我希望能夠提供更多關于裝飾器帶來的優勢的信息。如果我啟發了你,請分享你自己的一些方便的裝飾器。
本文轉載自微信公眾號「樹哥會編程」,可以通過以下二維碼關注。轉載本文請聯系樹哥會編程公眾號。















































