玩轉Matplotlib的十個高級技巧
Matplotlib是Python中流行的數(shù)據(jù)可視化庫,僅使用簡單的幾行代碼就可以生成圖表。但是默認的方法是生成的圖表很簡單,如果想增強數(shù)據(jù)演示的影響和清晰度,可以試試本文總結的10個高級技巧,這些技巧可以將可視化提升到一個新的水平:

1、rcParams
rcParams字典。它包含了用于創(chuàng)建圖形的默認樣式的所有Matplotlib設置。你可以直接從matplotlib命名空間導入它:
from matplotlib import rcParams
>>> rcParams
...
'axes.grid': False,
'axes.grid.axis': 'both',
'axes.grid.which': 'major',
'axes.labelcolor': 'black',
'axes.labelpad': 4.0,
'axes.labelsize': 'medium',
'axes.labelweight': 'normal',
'axes.linewidth': 0.8,
...
rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 8, 6
rcParams['legend.fontsize'] = "large"
rcParams['xtick.major.size'] = 4
rcParams['xtick.minor.size'] = 1這時所有的Matplotlib設置,如果你想修改任何的Matplotlib參數(shù),直接修改這個字典就可以了,你甚至可以將他序列化到本地,然后在其他項目中直接加載,這樣你的每一個Matplotlib實例使用的都是相同的配置了。
還可以調用PyPlot的rcdefaults函數(shù),它會將所有參數(shù)重置成默認值。
plt.rcdefaults()2、get_* functions
在底層,Matplotlib是完全面向對象的。
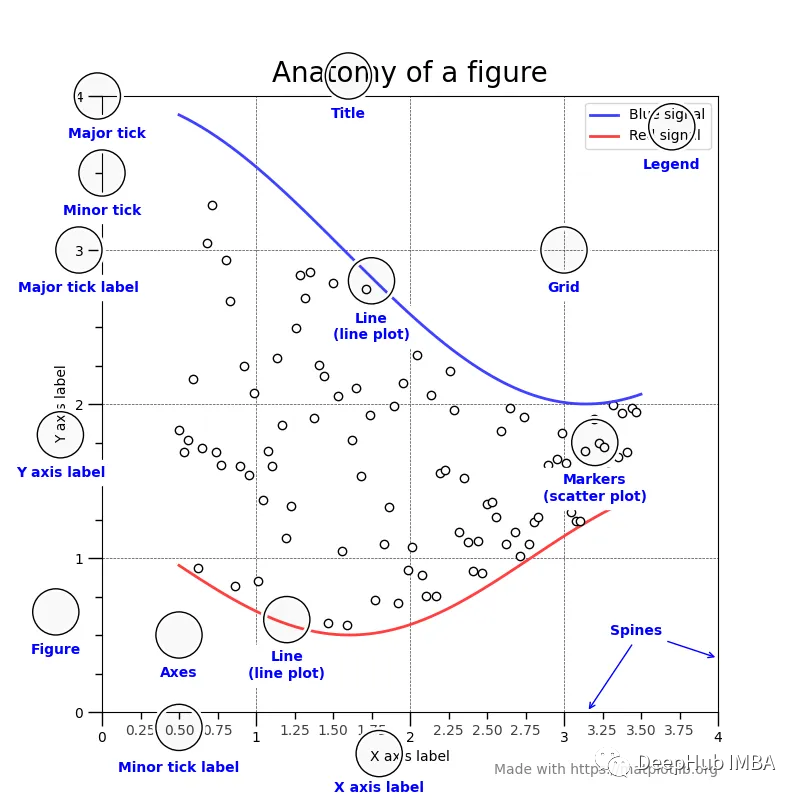 圖片
圖片
上圖中看到的每個單獨的組件都是作為一個單獨的類實現(xiàn)的。它們都繼承自基類Matplotlib Artist。
但是類太多,并且每個類的參數(shù)都不一樣這會給使用帶來很大的不方便,所以Matplotlib定制了有許多以get_前綴開頭的函數(shù),可以直接創(chuàng)建圖形中的組件。下面是一個例子:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
>>> [func for func in dir(ax) if func.startswith("get")]
['get_adjustable',
'get_label',
'get_legend',
'get_legend_handles_labels',
'get_lines',
'get_navigate',
'get_title',
'get_transform',
'get_xmajorticklabels',
'get_xminorticklabels',
'get_xscale',
'get_xticklabels',
'get_zorder']假設我們想自定義一個圖形的坐標:
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # Create a figure and an axes.
l1 = ax.plot(x, x, label="linear")
l2 = ax.plot(x, x ** 2, label="quadratic")
l3 = ax.plot(x, x ** 3, label="cubic")
ax.set_title("Simple Plot")
plt.show()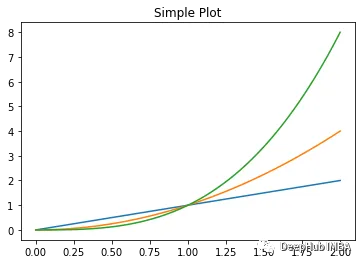 ??????
??????
這很簡單,只需在axes對象上調用get_xticklabels,就可以得到Matplotlib Text實例的列表:
>>> ax.get_xticklabels()
[Text(0, 0, 'Ideal'),
Text(1, 0, 'Premium'),
Text(2, 0, 'Very Good'),
Text(3, 0, 'Good'),
Text(4, 0, 'Fair')]還可以使用get_xticklines調整刻度線,或者使用get_xticks調整刻度的位置。
已經(jīng)獲得了對象,下面就可以進行調整了
3、get / setp
調用plt.getp函數(shù),可以查看它當前具有的參數(shù)。例如,假設我們想要樣式化下面圖的l2:
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # Create a figure and an axes.
l1 = ax.plot(x, x, label="linear")
l2 = ax.plot(x, x ** 2, label="quadratic")
l3 = ax.plot(x, x ** 3, label="cubic")
ax.set_title("Simple Plot")
plt.show()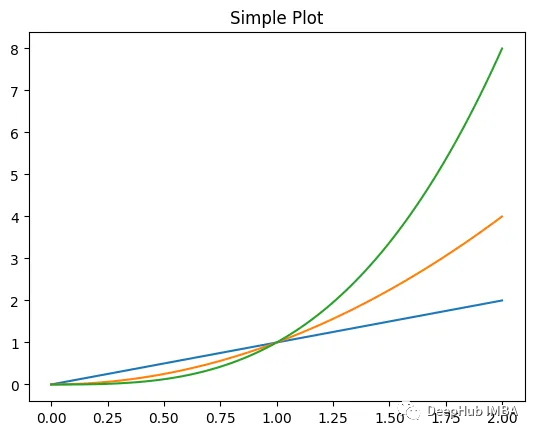 圖片
圖片
這個方法返回了圖表的所有屬性
>>> plt.getp(l2)
...
drawstyle or ds = default
figure = Figure(640x480)
linestyle or ls = -
linewidth or lw = 1.5
marker = None
markeredgecolor or mec = #ff7f0e
markeredgewidth or mew = 1.0
markerfacecolor or mfc = #ff7f0e
markerfacecoloralt or mfcalt = none
zorder = 2
...而plt.setp可以更改屬性在沒有任何參數(shù)的對象上調用this會打印出該對象可以接受的屬性值:
>>> plt.setp(l2)
...
linestyle or ls: {'-', '--', '-.', ':', '', (offset, on-off-seq), ...}
linewidth or lw: float
sketch_params: (scale: float, length: float, randomness: float)
snap: bool or None
zorder: float
...要打印單個屬性的可能值,可以將屬性的名稱作為字符串輸入setp:
>>> plt.setp(l2, "linestyle")
linestyle: {'-', '--', '-.', ':', '', (offset, on-off-seq), ...}修改屬性的方法如下:
>>> plt.setp(l2, linestyle="-.", lw=5, color="red", alpha=0.5)
[None, None, None, None]要查看更改后的當前圖形,只需在圖形對象上調用get_figure:
fig.get_figure()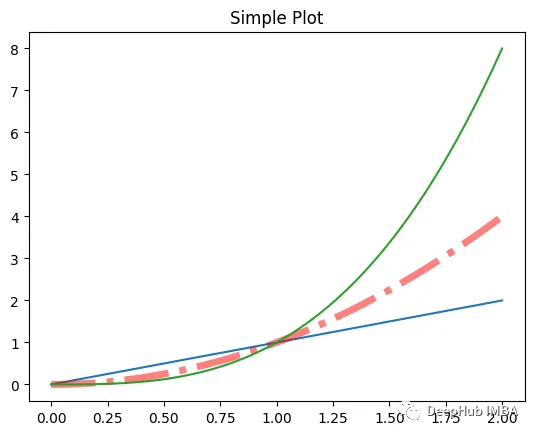 ??????
??????
第二行的樣式已經(jīng)變了
4、Legends
Legends可以方便的告訴我們圖中每個組件的含義,默認是這樣顯示的:
x = np.linspace(0, 2, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots() # Create a figure and an axes.
l1 = ax.plot(x, x, label="linear")
l2 = ax.plot(x, x ** 2, label="quadratic")
l3 = ax.plot(x, x ** 3, label="cubic")
ax.set_title("Simple Plot")
ax.legend()
plt.show()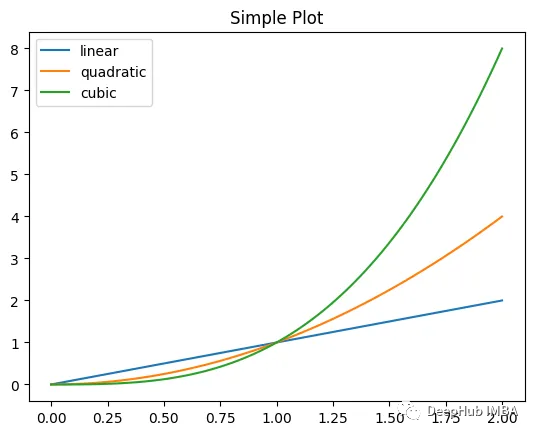 圖片
圖片
我們可以調整他的參數(shù),例如:
圖例的位置、字體屬性、大小,顏色,樣式、圖例中的列數(shù),等等
可以在創(chuàng)建前設置,也可以在創(chuàng)建后使用get_legend提取,并使用getp、setp函數(shù)。
5、cycler
你有沒有想過Matplotlib是如何自己改變顏色或循環(huán)不同風格的?
在底層,Matplotlib使用名為Cyclers的Python內置對象:
from cycler import cycler
c1 = cycler(arg1=[1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> c1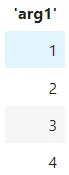 ??????
??????
這個循環(huán)函數(shù)接受任何鍵值參數(shù)并創(chuàng)建一個字典列表:
c2 = cycler(arg2=list("rgba"))
for i in c2:
print(i)
------------------------------
{'arg2': 'r'}
{'arg2': 'g'}
{'arg2': 'b'}
{'arg2': 'a'}還可以將多個循環(huán)器與“plus”和“multiply”操作符組合起來,這樣可以獲得索引到索引或窮舉的參數(shù)組合:
for i in c1 + c2:
print(i)
--------------------------------
{'arg1': 1, 'arg2': 'r'}
{'arg1': 2, 'arg2': 'g'}
{'arg1': 3, 'arg2': 'b'}
{'arg1': 4, 'arg2': 'a'}將這個自定義循環(huán)器并將其傳遞給Matplotlib,就可以定制樣式。下面,我們創(chuàng)建四種不同的線條樣式,允許Matplotlib循環(huán)使用不同的線條顏色,樣式和大小:
line_prop_cycler = (
cycler(color=list("rgcy"))
+ cycler(ls=["-", "--", "-.", ":"])
+ cycler(lw=[3, 6, 9, 12])
)可以使用axes對象的set_prop_cycle函數(shù)將這個自定義循環(huán)器傳遞給繪圖:
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 50)
offsets = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 4, endpoint=False)
yy = np.transpose([np.sin(x + phi) for phi in offsets])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
ax.set_prop_cycle(line_prop_cycler) # Set propcycle before plotting
ax.plot(x, yy)
plt.show();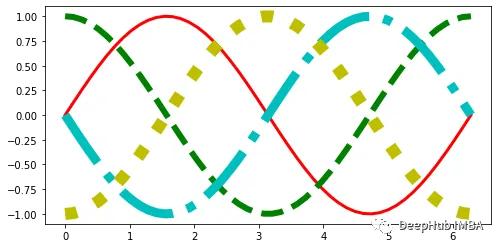 圖片
圖片
rcParams字典中默認設置如下:
rcParams["axes.prop_cycle"] 圖片
圖片
我們可以直接修改
6、tick_params
軸刻度應該準確地傳達數(shù)據(jù)點及其單位的最小值和最大值,并顯示幾個關鍵的檢查點,以便在不同的繪圖部分之間進行比較。
大多數(shù)tick屬性可以使用axes對象的tick_params函數(shù)來控制。以下是文檔中的例子:
>>> ax.tick_params()
Parameters
----------
axis : {'x', 'y', 'both'}, default: 'both'
The axis to which the parameters are applied.
which : {'major', 'minor', 'both'}, default: 'major'
The group of ticks to which the parameters are applied.
reset : bool, default: False
Whether to reset the ticks to defaults before updating them.
Other Parameters
----------------
direction : {'in', 'out', 'inout'}
Puts ticks inside the axes, outside the axes, or both.
length : float
Tick length in points.
width : float
Tick width in points.
color : color
Tick color.首先應該指定的兩個參數(shù)是axis和which。這些參數(shù)將應用于X或Y軸刻度,以及最小和最大刻度。
大多數(shù)時候,在Matplotlib中不會看到小刻度。如果需要可以使用axes對象上的minortics_on函數(shù):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 2))
>>> ax.minorticks_on()
7、Tickers
如果不像自定義tick參數(shù)(因為很麻煩)。可以使用許多內置的Matplotlib的“主題”集合(稱為tickers)。
from matplotlib import ticker
dir(ticker)
['AutoLocator',
'AutoMinorLocator',
'EngFormatter',
'FixedFormatter',
'FixedLocator',
'FormatStrFormatter',
'Formatter',
'FuncFormatter',
'IndexFormatter',
'IndexLocator',
'Integral',
'LinearLocator',
]在ticker模塊下有許多這樣的子模塊。一般情況下標題中帶有Locator的控件控制刻度的位置。而Formatters 則表示標簽的樣式。選擇好后可以使用下面的方式進行設置:
from matplotlib.ticker import EngFormatter
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(EngFormatter())使用axes對象的xaxis或yaxis屬性,調用set_major(minor)_formatter(locator)函數(shù),并傳入類名。
8、grid
自定義網(wǎng)格線可以突出數(shù)據(jù)范圍。在Matplotlib中,可以使用軸線對象的網(wǎng)格函數(shù)創(chuàng)建和自定義網(wǎng)格。下面是一個垂直網(wǎng)格的例子:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.grid(axis="x", linestyle=":", lw=3, color="r")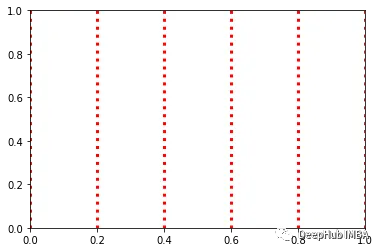
9、bar_label
條形圖在數(shù)據(jù)分析中很常見。它們最重要的地方就是每個條的高度,條形標簽可以突出每個條的顯示。
bar_label函數(shù)接受一個BarContainer對象作為參數(shù),并自動標注每個bar的高度。
下面是Seaborn的一個簡單的計數(shù)圖:
import seaborn as sns
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
ax = sns.countplot(diamonds["cut"])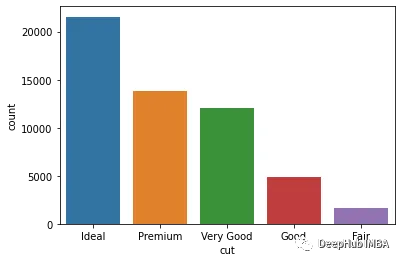
每次使用Seaborn或ax.bar等函數(shù)創(chuàng)建barplot時,BarContainer對象都會被添加到圖中。可以使用axes對象的containers屬性來檢索這個容器對象:
ax.containers
[<BarContainer object of 5 artists>]在上面的列表中有一個BarContainer對象有5個bar。我們只需在創(chuàng)建了plot之后將這個對象傳遞給bar_label:
ax = sns.countplot(diamonds["cut"])
ax.bar_label(ax.containers[0], padding=1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 25000)
plt.show();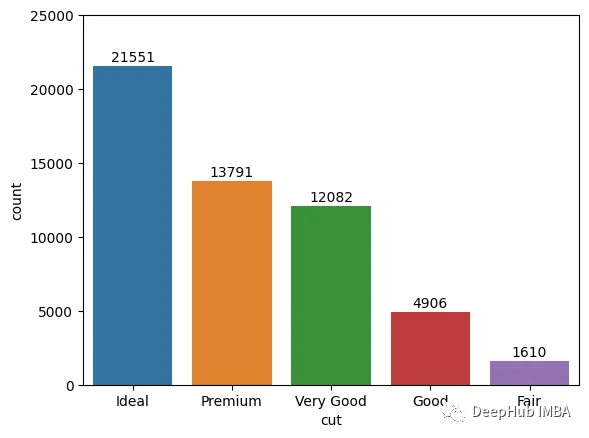
10、zorder
當有很多圖的時候,顯示順序是非常重要的。你需要確保在畫布上以適當?shù)捻樞蚶L制每個圖形,就需要zorder參數(shù)。
下面,我們用不同的zorders創(chuàng)建了三行:
x = np.linspace(0, 7.5, 100)
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="zorder=2", zorder=2) # bottom
plt.plot(x, np.sin(x + 0.5), label="zorder=3", zorder=3)
plt.axhline(0, label="zorder=2.5", color="lightgrey", zorder=2.5)
plt.title("Custom order of elements")
l = plt.legend(loc="upper right")
l.set_zorder(2.5) # legend between blue and orange line
plt.show()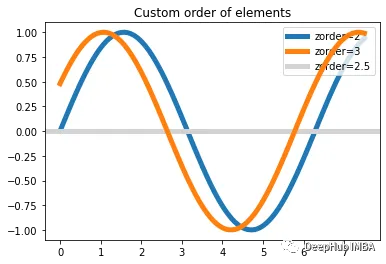
可以看到zorder越大,就會在最上方顯示,覆蓋掉小的組件。
總結
Matplotlib在2023年6月的下載量超過3000萬,幾乎是其最大競爭對手Plotly的4倍。Matplotlib的成功不僅僅在于它的簡單(只需要幾行代碼就能生成簡單的圖形),還在于他的功能強大,但是要使用這些強大的功能就需要使用他的高級功能,但是這些高級功能往往需要比較復雜的配置或者參數(shù),需要我們?yōu)g覽官方的文檔。所以才出現(xiàn)了seaborn,他將Matplotlib進行了整合不僅簡單而且好看。
但是有時我們需要更深入的定制功能,seaborn也許還達不到我們的目標,我們只能自己定義的參數(shù),本文總結的是個高級技巧可以輕松的幫你完整自定義Matplotlib的任務。




































