Spring Boot防重復提交優化策略
啥是防抖
 圖片
圖片
所謂防抖,一是防用戶手抖,二是防網絡抖動。在Web系統中,表單提交是一個非常常見的功能,如果不加控制,容易因為用戶的誤操作或網絡延遲導致同一請求被發送多次,進而生成重復的數據記錄。要針對用戶的誤操作,前端通常會實現按鈕的loading狀態,阻止用戶進行多次點擊。而對于網絡波動造成的請求重發問題,僅靠前端是不行的。為此,后端也應實施相應的防抖邏輯,確保在網絡波動的情況下不會接收并處理同一請求多次。
一個理想的防抖組件或機制,我覺得應該具備以下特點:
- 邏輯正確,也就是不能誤判;
- 響應迅速,不能太慢;
- 易于集成,邏輯與業務解耦;
- 良好的用戶反饋機制,比如提示“您點擊的太快了”
思路解析
哪一類接口需要防抖?
接口防抖也不是每個接口都需要加,一般需要加防抖的接口有這幾類:
- 用戶輸入類接口:比如搜索框輸入、表單輸入等,用戶輸入往往會頻繁觸發接口請求,但是每次觸發并不一定需要立即發送請求,可以等待用戶完成輸入一段時間后再發送請求。
- 按鈕點擊類接口:比如提交表單、保存設置等,用戶可能會頻繁點擊按鈕,但是每次點擊并不一定需要立即發送請求,可以等待用戶停止點擊一段時間后再發送請求。
- 滾動加載類接口:比如下拉刷新、上拉加載更多等,用戶可能在滾動過程中頻繁觸發接口請求,但是每次觸發并不一定需要立即發送請求,可以等待用戶停止滾動一段時間后再發送請求。
如何確定接口是重復的?
防抖也即防重復提交,那么如何確定兩次接口就是重復的呢?首先,我們需要給這兩次接口的調用加一個時間間隔,大于這個時間間隔的一定不是重復提交;其次,兩次請求提交的參數比對,不一定要全部參數,選擇標識性強的參數即可;最后,如果想做的更好一點,還可以加一個請求地址的對比。
分布式部署下如何做接口防抖?
有兩個方案:
使用共享緩存
流程圖如下:
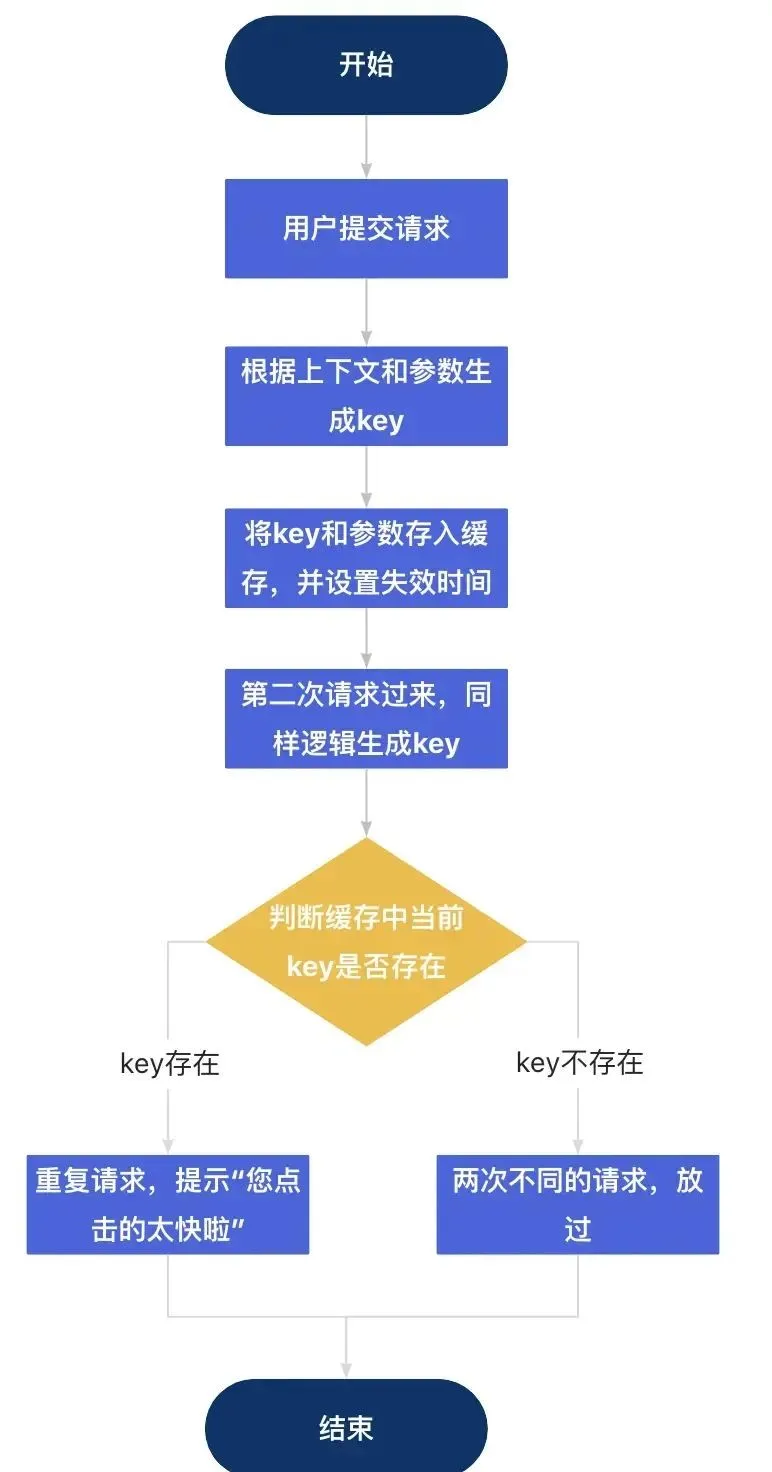 圖片
圖片
使用分布式鎖
流程圖如下:
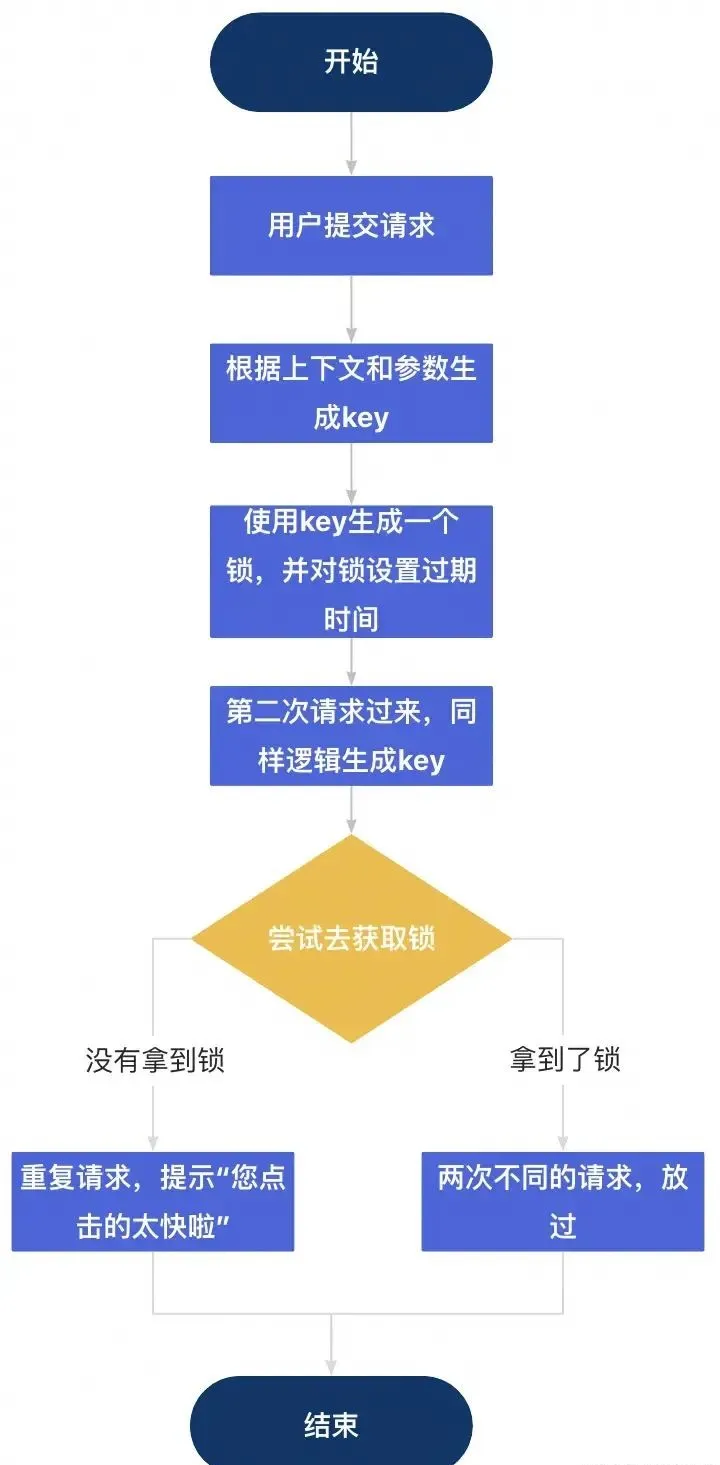 圖片
圖片
常見的分布式組件有Redis、Zookeeper等,但結合實際業務來看,一般都會選擇Redis,因為Redis一般都是Web系統必備的組件,不需要額外搭建。
具體實現
現在有一個保存用戶的接口
@PostMapping("/add")
@RequiresPermissions(value = "add")
@Log(methodDesc = "添加用戶")
public ResponseEntity<String> add(@RequestBody AddReq addReq) {
return userService.add(addReq);
}import java.util.List;
import lombok.Data;
@Datapublic class AddReq {
/** * 用戶名稱 */ private String userName;
/** * 用戶手機號 */ private String userPhone;
/** * 角色ID列表 */ private List<Long> roleIdList;}目前數據庫表中沒有對userPhone字段做UK索引,這就會導致每調用一次add就會創建一個用戶,即使userPhone相同。
請求鎖
根據上面的要求,我定了一個注解@RequestLock,使用方式很簡單,把這個注解打在接口方法上即可。
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @description 請求防抖鎖,用于防止前端重復提交導致的錯誤
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface RequestLock {
/**
* redis鎖前綴
*
* @return 默認為空,但不可為空
*/
String prefix() default "";
/**
* redis鎖過期時間
*
* @return 默認2秒
*/
int expire() default 2;
/**
* redis鎖過期時間單位
*
* @return 默認單位為秒
*/
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.SECONDS;
/**
* redis key分隔符
*
* @return 分隔符
*/
String delimiter() default "&";
}@RequestLock注解定義了幾個基礎的屬性,redis鎖前綴、redis鎖時間、redis鎖時間單位、key分隔符。其中前面三個參數比較好理解,都是一個鎖的基本信息。key分隔符是用來將多個參數合并在一起的,比如userName是張三,userPhone是123456,那么完整的key就是"張三&123456",最后再加上redis鎖前綴,就組成了一個唯一key。
唯一key生成
這里有些同學可能就要說了,直接拿參數來生成key不就行了嗎?額,不是不行,但我想問一個問題:如果這個接口是文章發布的接口,你也打算把內容當做key嗎?要知道,Redis的效率跟key的大小息息相關。所以,我的建議是選取合適的字段作為key就行了,沒必要全都加上。
要做到參數可選,那么用注解的方式最好了
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @description 加上這個注解可以將參數設置為key
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface RequestKeyParam {
}這個注解加到參數上就行,沒有多余的屬性。
接下來就是lockKey的生成了。
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
public class RequestKeyGenerator {
/**
* 獲取LockKey
*
* @param joinPoint 切入點
* @return
*/
public static String getLockKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
//獲取連接點的方法簽名對象
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
//Method對象
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
//獲取Method對象上的注解對象
RequestLock requestLock = method.getAnnotation(RequestLock.class);
//獲取方法參數
final Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
//獲取Method對象上所有的注解
final Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
final RequestKeyParam keyParam = parameters[i].getAnnotation(RequestKeyParam.class);
//如果屬性不是RequestKeyParam注解,則不處理
if (keyParam == null) {
continue;
}
//如果屬性是RequestKeyParam注解,則拼接 連接符 "& + RequestKeyParam"
sb.append(requestLock.delimiter()).append(args[i]);
}
//如果方法上沒有加RequestKeyParam注解
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(sb.toString())) {
//獲取方法上的多個注解(為什么是兩層數組:因為第二層數組是只有一個元素的數組)
final Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
//循環注解
for (int i = 0; i < parameterAnnotations.length; i++) {
final Object object = args[i];
//獲取注解類中所有的屬性字段
final Field[] fields = object.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
//判斷字段上是否有RequestKeyParam注解
final RequestKeyParam annotation = field.getAnnotation(RequestKeyParam.class);
//如果沒有,跳過
if (annotation == null) {
continue;
}
//如果有,設置Accessible為true(為true時可以使用反射訪問私有變量,否則不能訪問私有變量)
field.setAccessible(true);
//如果屬性是RequestKeyParam注解,則拼接 連接符" & + RequestKeyParam"
sb.append(requestLock.delimiter()).append(ReflectionUtils.getField(field, object));
}
}
}
//返回指定前綴的key
return requestLock.prefix() + sb;
}
}
> 由于``@RequestKeyParam``可以放在方法的參數上,也可以放在對象的屬性上,所以這里需要進行兩次判斷,一次是獲取方法上的注解,一次是獲取對象里面屬性上的注解。重復提交判斷
Redis緩存方式
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import com.summo.demo.exception.biz.BizException;
import com.summo.demo.model.response.ResponseCodeEnum;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStringCommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisCallback;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.types.Expiration;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* @description 緩存實現
*/
@Aspect
@Configuration
@Order(2)
public class RedisRequestLockAspect {
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
public RedisRequestLockAspect(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
@Around("execution(public * * (..)) && @annotation(com.summo.demo.config.requestlock.RequestLock)")
public Object interceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
RequestLock requestLock = method.getAnnotation(RequestLock.class);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(requestLock.prefix())) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "重復提交前綴不能為空");
}
//獲取自定義key
final String lockKey = RequestKeyGenerator.getLockKey(joinPoint);
// 使用RedisCallback接口執行set命令,設置鎖鍵;設置額外選項:過期時間和SET_IF_ABSENT選項
final Boolean success = stringRedisTemplate.execute(
(RedisCallback<Boolean>)connection -> connection.set(lockKey.getBytes(), new byte[0],
Expiration.from(requestLock.expire(), requestLock.timeUnit()),
RedisStringCommands.SetOption.SET_IF_ABSENT));
if (!success) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "您的操作太快了,請稍后重試");
}
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "系統異常");
}
}
}這里的核心代碼是stringRedisTemplate.execute里面的內容,正如注釋里面說的“使用RedisCallback接口執行set命令,設置鎖鍵;設置額外選項:過期時間和SET_IF_ABSENT選項”,有些同學可能不太清楚SET_IF_ABSENT是個啥,這里我解釋一下:SET_IF_ABSENT是 RedisStringCommands.SetOption 枚舉類中的一個選項,用于在執行 SET 命令時設置鍵值對的時候,如果鍵不存在則進行設置,如果鍵已經存在,則不進行設置。
Redisson分布式方式
Redisson分布式需要一個額外依賴,引入方式
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.10.6</version>
</dependency>由于我之前的代碼有一個RedisConfig,引入Redisson之后也需要單獨配置一下,不然會沖突
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
// 這里假設你使用單節點的Redis服務器
config.useSingleServer()
// 使用與Spring Data Redis相同的地址
.setAddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
// 如果有密碼
//.setPassword("xxxx");
// 其他配置參數
//.setDatabase(0)
//.setConnectionPoolSize(10)
//.setConnectionMinimumIdleSize(2);
// 創建RedissonClient實例
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}配好之后,核心代碼如下:
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import com.summo.demo.exception.biz.BizException;
import com.summo.demo.model.response.ResponseCodeEnum;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* @description 分布式鎖實現
*/
@Aspect
@Configuration
@Order(2)
public class RedissonRequestLockAspect {
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
public RedissonRequestLockAspect(RedissonClient redissonClient) {
this.redissonClient = redissonClient;
}
@Around("execution(public * * (..)) && @annotation(com.summo.demo.config.requestlock.RequestLock)")
public Object interceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
RequestLock requestLock = method.getAnnotation(RequestLock.class);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(requestLock.prefix())) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "重復提交前綴不能為空");
}
//獲取自定義key
final String lockKey = RequestKeyGenerator.getLockKey(joinPoint);
// 使用Redisson分布式鎖的方式判斷是否重復提交
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
boolean isLocked = false;
try {
//嘗試搶占鎖
isLocked = lock.tryLock();
//沒有拿到鎖說明已經有了請求了
if (!isLocked) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "您的操作太快了,請稍后重試");
}
//拿到鎖后設置過期時間
lock.lock(requestLock.expire(), requestLock.timeUnit());
try {
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "系統異常");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BizException(ResponseCodeEnum.BIZ_CHECK_FAIL, "您的操作太快了,請稍后重試");
} finally {
//釋放鎖
if (isLocked && lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}Redisson的核心思路就是搶鎖,當一次請求搶到鎖之后,對鎖加一個過期時間,在這個時間段內重復的請求是無法獲得這個鎖,也不難理解。
測試一下。
- 第一次提交,"添加用戶成功"
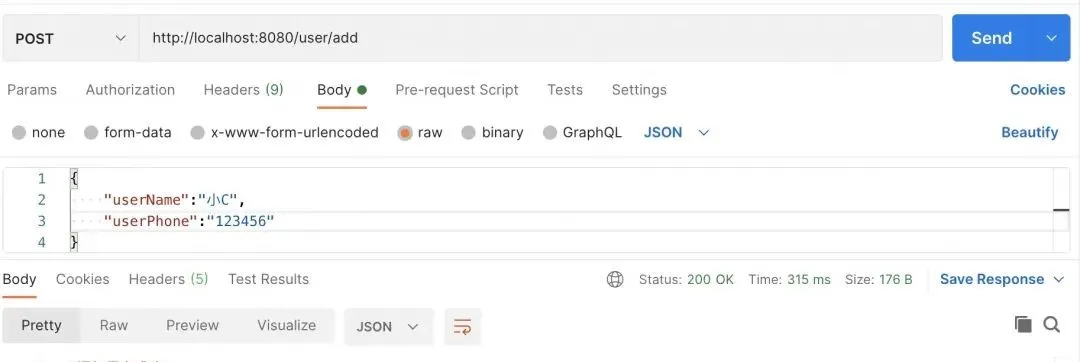 圖片
圖片
- 短時間內重復提交,"BIZ-0001:您的操作太快了,請稍后重試"
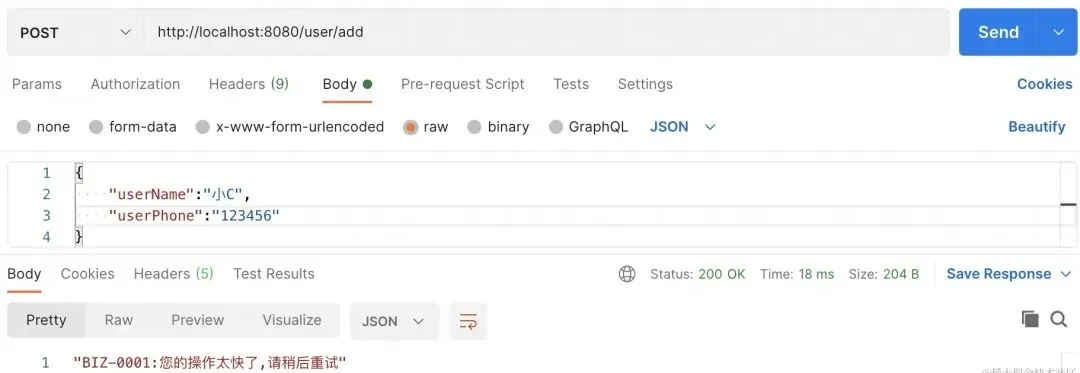 圖片
圖片
- 過幾秒后再次提交,"添加用戶成功"
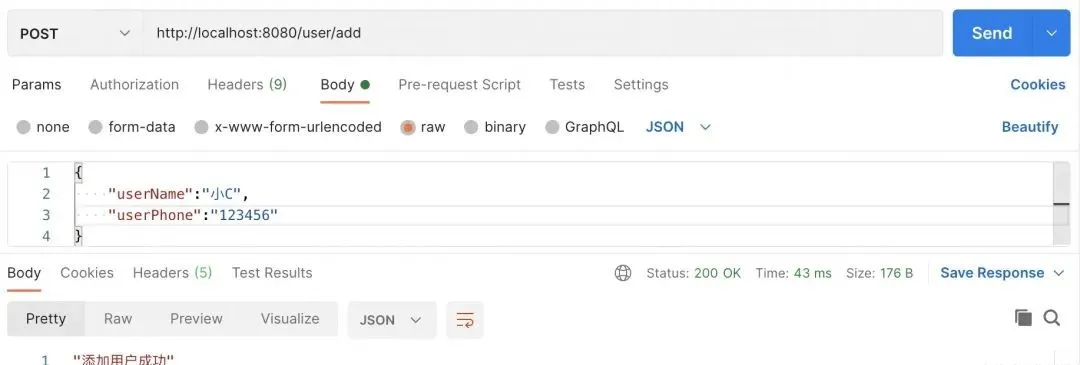 圖片
圖片
從測試的結果上看,防抖是做到了,但是隨著緩存消失、鎖失效,還是可以發起同樣的請求,所以要真正做到接口冪等性,還需要業務代碼的判斷、設置數據庫表的UK索引等操作。我在文章里面說到生成唯一key的時候沒有加用戶相關的信息,比如用戶ID、IP屬地等,真實生產環境建議加上這些,可以更好地減少誤判。








































