線程池遇到未處理的異常會崩潰嗎?
首先,這個問題考察的是你對線程池 execute 方法和 submit 方法的理解,在 Java 線程池的使用中,我們可以通過 execute 方法或 submit 方法給線程池添加任務,但如果線程池中的程序在執行時,遇到了未處理的異常會怎么呢?接下來我們一起來看。
1.execute方法
execute 方法用于提交一個不需要返回值的任務給線程池執行,它接收一個 Runnable 類型的參數,并且不返回任何結果。
它的使用示例代碼如下:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ExecuteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
// 使用 execute 方法提交任務
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Task running in " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
// 模擬任務執行
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.err.println("Task was interrupted");
}
System.out.println("Task finished");
}
});
// 關閉線程池
executor.shutdown();
}
}2.submit方法
submit 方法用于提交一個需要返回值的任務(Callable 對象),或者不需要返回值但希望獲取任務狀態的任務(Runnable 對象,但會返回一個 Future 對象)。
它接收一個 Callable 或 Runnable 類型的參數,并返回一個 Future 對象,通過該對象可以獲取任務的執行結果或檢查任務的狀態。
2.1 提交Callable任務
示例代碼如下:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class SubmitCallableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 創建一個固定大小的線程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提交一個 Callable 任務給線程池執行
Future<String> future = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(2000); // 模擬任務執行時間
return "Task's execution result";
}
});
try {
// 獲取任務的執行結果
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("Task result: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 關閉線程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}2.2 提交Runnable任務
提交 Runnable 任務并獲取 Future 對象,示例代碼如下:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class SubmitRunnableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 創建一個固定大小的線程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提交一個 Runnable 任務給線程池執行,并獲取一個 Future 對象
Future<?> future = executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Task is running in thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
// 檢查任務是否完成(這里只是為了示例,實際使用中可能不需要這樣做)
if (future.isDone()) {
System.out.println("Task is done");
} else {
System.out.println("Task is not done yet");
}
// 關閉線程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
}3.遇到未處理異常
線程池遇到未處理的異常執行行為和添加任務的方法有關,也就是說 execute 方法和 submit 方法在遇到未處理的異常時執行行為是不一樣的。
3.1 execute方法遇到未處理異常
示例代碼如下:
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100));
// 添加任務一
executor.execute(() -> {
String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("線程名:" + tName);
throw new RuntimeException("拋出異常");
});
// 添加任務二
executor.execute(() -> {
String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("線程名:" + tName);
throw new RuntimeException("拋出異常");
});
}
}以上程序的執行結果如下:
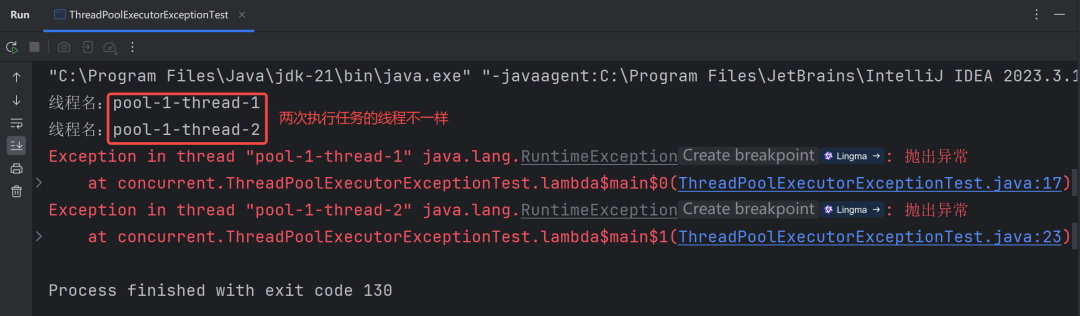 圖片
圖片
從上述結果可以看出,線程池中的核心和最大線程數都為 1 的情況下,到遇到未處理的異常時,執行任務的線程卻不一樣,這說明了:當使用 execute 方法時,如果遇到未處理的異常,會拋出未捕獲的異常,并將當前線程進行銷毀。
3.2 submit方法遇到未處理異常
然而,當我們將線程池的添加任務方法換成 submit() 之后,執行結果又完全不同了,以下是示例代碼:
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1,
1,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(100));
// 添加任務一
Future<?> future = executor.submit(() -> {
String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("線程名:" + tName);
throw new RuntimeException("拋出異常");
});
// 添加任務二
Future<?> future2 =executor.submit(() -> {
String tName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("線程名:" + tName);
throw new RuntimeException("拋出異常");
});
try {
future.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("遇到異常:"+e.getMessage());
}
try {
future2.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("遇到異常:"+e.getMessage());
}
}
}以上程序的執行結果如下:
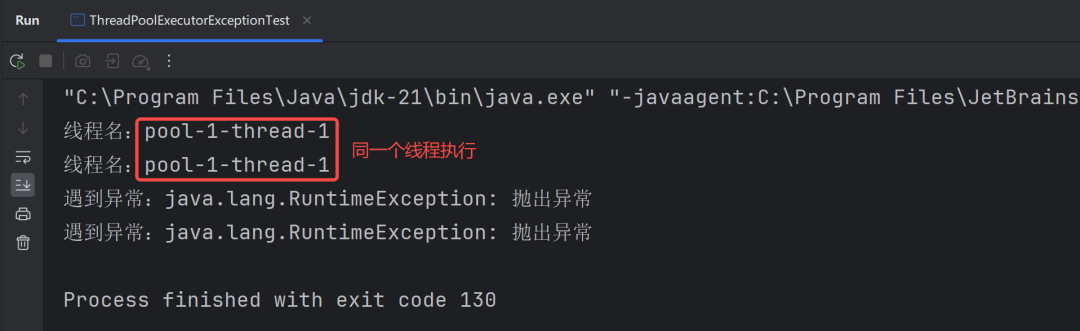 圖片
圖片
從上述結果可以看出,submit 方法遇到未處理的異常時,并將該異常封裝在 Future 的 get 方法中,而不會直接影響執行任務的線程,這樣線程就可以繼續復用了。
小結
線程池在遇到未處理的異常時,不同添加任務的方法的執行行為是不同的:
- execute 方法:遇到未處理的異常,線程會崩潰,并打印異常信息。
- submit 方法:遇到未處理的異常,線程本身不會受到影響(線程可以復用),只是將異常信息封裝到返回的對象 Future 中。






































