大模型應用與LUI(自然語言交互)落地的關鍵模塊——語義路由實現總結
在傳統搜索應用中,有一個核心的模塊叫意圖識別,即識別用戶搜索請求時的意圖,基于意圖不同生成不同的Query或執行不同的邏輯。在RAG應用中,仍然存在著類似的路由模塊完成請求分發。這樣的路由分發需求無處不在,特別是在自然語言交互的應用中,并且會隨著系統支持的場景和功能增多而變得越來越重要。所謂路由就是一個能夠根據一段自然語言輸入進行意圖判斷形成離散輸出的模塊。
典型的場景比如智能客服中的指令任務分發,硬盤搜索助手根據用戶需求搜索圖片還是搜索文件。下面是一些常見的情景的總結。
1)基于問題不同生成不同Prompt的情況,這和意圖識別生成不同Query一樣。
2)根據數據存儲的多樣性分發到不同數據存儲和服務中,比如數據庫、API等
3)即使存儲介質相同,也可能存在多個需要分發的情況。
4)根據問題的類型分發到不同的組件。比如,根據問題的性質將查詢分發給向量數據庫、Agent或服務等。
對于路由的實現大致分為兩類,邏輯路由(Logical Routers)和 自然語言路由。相較于自然語言路由,邏輯路由不依賴于對路由輸入的語義理解,而自然語言路由是需要關注語義的。
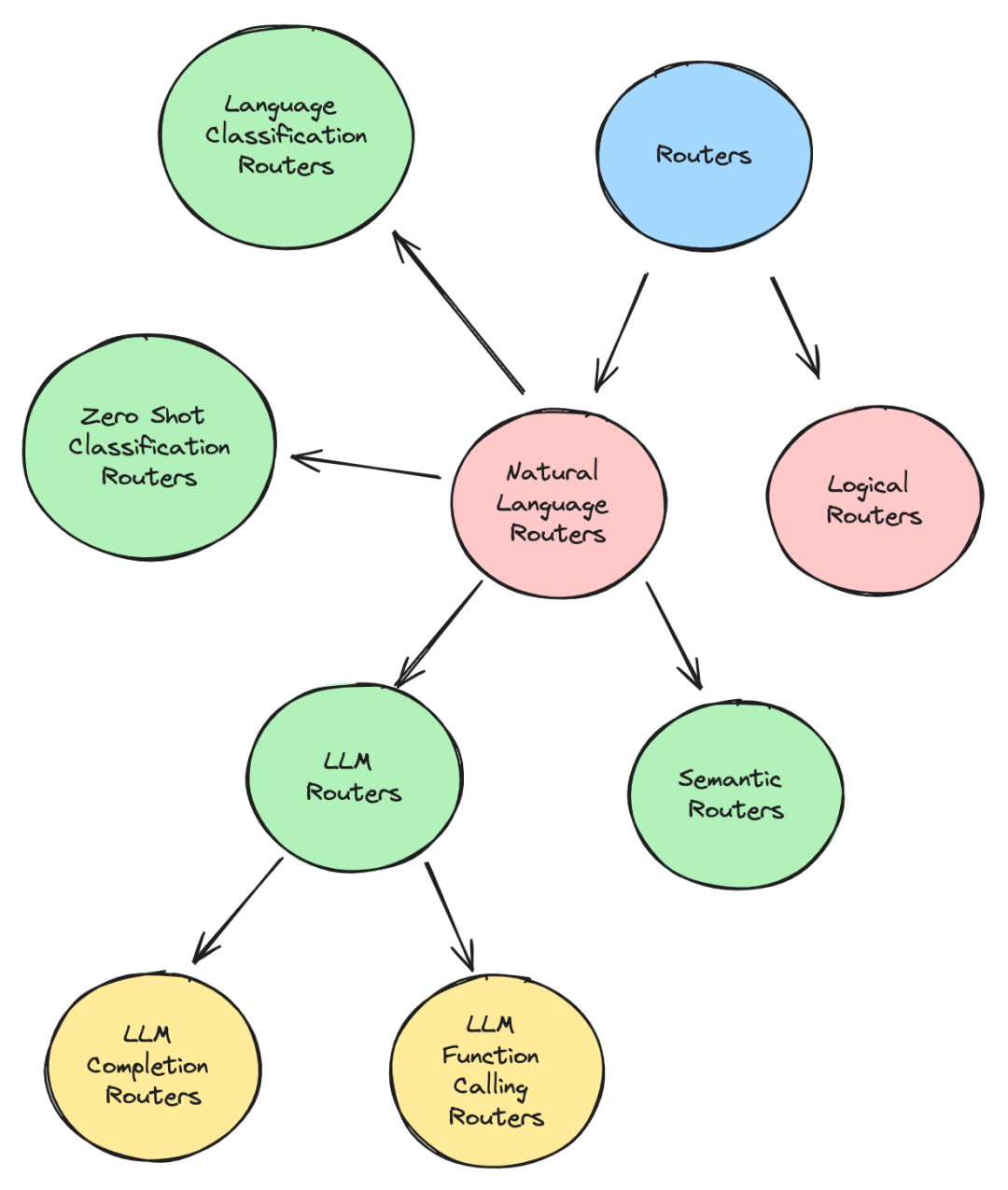
以下是這些路由的介紹:
1.LLM 路由
利用 LLM 的決策(decision making )能力根據用戶的查詢分發。
a.LLM生成路由
這類路由利用 LLM Completion接口實現,要求 LLM 從提示的單詞選項列表中返回最能描述查詢的單個單詞。然后,該詞可以作為 If/Else 條件的一部分來控制應用程序流程。
在llamaindex及LangChain都有這種思路的實現。下面是 LangChain 的一個使用例子。
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# Set up the LLM Chain to return a single word based on the query,
# and based on a list of words we provide to it in the prompt template
llm_completion_select_route_chain = (
PromptTemplate.from_template("""
Given the user question below, classify it as either
being about `LangChain`, `Anthropic`, or `Other`.
Do not respond with more than one word.
<question>
{question}
</question>
Classification:"""
)
| ChatAnthropic(model_name="claude-3-haiku")
| StrOutputParser()
)
# We setup an IF/Else condition to route the query to the correct chain
# based on the LLM completion call above
def route_to_chain(route_name):
if "anthropic" == route_name.lower():
return anthropic_chain
elif "langchain" == route_name.lower():
return langchain_chain
else:
return general_chain
...
# Later on in the application, we can use the response from the LLM
# completion chain to control (i.e route) the flow of the application
# to the correct chain via the route_to_chain method we created
route_name = llm_completion_select_route_chain.invoke(user_query)
chain = route_to_chain(route_name)
chain.invoke(user_query)b.LLM 函數調用路由器
利用了 LLM 的function call能力來選擇要執行的分支函數。
LlamaIndex中的Pydantic路由就是這個原理。大多數Agent選擇要使用的正確工具也是采用這樣的方式。它們利用 LLM 的函數調用能力,根據用戶的查詢選擇適合的工具。下面是Pydantic路由的使用例子:
from llama_index.core.query_engine import RouterQueryEngine
from llama_index.core.selectors import PydanticSingleSelector
from llama_index.core.selectors.pydantic_selectors import Pydantic
from llama_index.core.tools import QueryEngineTool
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, SummaryIndex
# define query engines
...
# initialize tools
list_tool = QueryEngineTool.from_defaults(
query_engine=list_query_engine,
descriptinotallow="Useful for summarization questions related to the data source",
)
vector_tool = QueryEngineTool.from_defaults(
query_engine=vector_query_engine,
descriptinotallow="Useful for retrieving specific context related to the data source",
)
# initialize router query engine (single selection, pydantic)
query_engine = RouterQueryEngine(
selector=PydanticSingleSelector.from_defaults(),
query_engine_tools=[
list_tool,
vector_tool,
],
)
query_engine.query("<query>")2.語義路由
利用語義相關性檢索來選擇最佳的分支。
每個路由都有一組與之關聯的示例查詢,這些查詢會被embedding并存儲為向量。傳入的查詢也會被embedding,并針對路由器中的其他示例查詢進行相似性搜索。匹配度最高的查詢的路由將被選中。
以semantic-router(https://github.com/aurelio-labs/semantic-router)這個項目為例了解其具體細節。例如,設置兩個路由,一個用于政治問題的問答,另一個用于一般閑聊類型的問答。對于每個路由都會分配一個通常可能被用來觸發該路由分支的問題列表。這些示例查詢(utterances)將被embedding,以便可以將它們用于針對用戶查詢的相似性搜索。
from semantic_router import Route
# we could use this as a guide for our chatbot to avoid political
# conversations
politics = Route(
name="politics",
utterances=[
"isn't politics the best thing ever",
"why don't you tell me about your political opinions",
"don't you just love the president",
"they're going to destroy this country!",
"they will save the country!",
],
)
# this could be used as an indicator to our chatbot to switch to a more
# conversational prompt
chitchat = Route(
name="chitchat",
utterances=[
"how's the weather today?",
"how are things going?",
"lovely weather today",
"the weather is horrendous",
"let's go to the chippy",
],
)
# we place both of our decisions together into single list
routes = [politics, chitchat]
#創建路由層
encoder = OpenAIEncoder()
from semantic_router.layer import RouteLayer
route_layer = RouteLayer(encoder=encoder, routes=routes)使用時,輸入問題,便能獲得路由決策。
route_layer("don't you love politics?").name
# -> 'politics'由于這種路由本質上是向量檢索,無需調用LLM,因而比其他基于 LLM 的路由器更快。
3.零樣本文本分類路由
零樣本文本分類(Zero-shot text classification)是NLP中的一項任務,其中模型在一個標記樣本集上進行訓練,進而獲得能夠對來自先前未見過的樣本進行分類,比如基于bert的分類器。
而這類路由便是利用零樣本分類模型給一段文本打上標簽,而這些標簽來自于預定義的標簽路由。
比如,Haystack 中的 ZeroShotTextRouter便是這種實現路徑。具體參考:https://github.com/deepset-ai/haystack/blob/main/haystack/components/routers/zero_shot_text_router.py#L130
4.語言分類路由
這類路由器能夠識別查詢所使用的語言,并根據該語言路由查詢。如果應用程序需要某種多語言解析能力,這將非常有用。
比如,Haystack 中的 TextClassificationRouter,它利用 langdetect 庫來檢測文本的語言,該庫本身使用樸素貝葉斯算法來檢測語言。參考:https://github.com/deepset-ai/haystack/blob/main/haystack/components/routers/text_language_router.py#L90
5.關鍵字路由
該類路由將嘗試通過匹配查詢和路由列表之間的關鍵字來選擇分支。
這個關鍵字路由器也可以由 LLM 來識別關鍵字,或者由其他一些關鍵字匹配庫來實現。
6.邏輯路由
它們使用邏輯檢查變量,例如字符串長度、文件名和值比較來處理如何路由查詢。它們與編程中使用的典型 If/Else 條件非常相似。它們不是基于必須理解自然語言查詢的意圖,而是可以根據現有和變量參數做出選擇。典型實現如HayStack 中的 ConditionalRouter 和 FileTypeRouter。
小結
不管是RAG應用還是普通的業務系統,都存在著大量的分支判斷,這種判斷早期由于自然語言技術的落后(準確率和性能)導致大多數實現為語法判斷,而隨著LLM技術的發展,必然會帶動語義判斷和分發需求的大發展,另一方面,隨著自然語言交互(LUI)的不斷普及,路由模塊將成為其中核心實現受到更大重視。
參考:
??https://towardsdatascience.com/routing-in-rag-driven-applications-a685460a7220??
本文轉載自?? AI工程化??,作者: ully

















