HBase看上去很美 我的項目失敗之路
HBase設計:看上去很美
HBase是模仿Google bigtable的開源產品,又是hadoop的衍生品,hadoop作為離線計算系統已經得到業界的普遍認可,并經過N多公司大規模使用的驗證,自然地認為HBase也將隨之獲得成功。
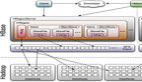
《HBase: The Definitive Guide》第8章講述HBase的架構,從架構上看,其架構很***:
LSM - 解決磁盤隨機寫問題(順序寫才是王道);
HFile - 解決數據索引問題(只有索引才能高效讀);
WAL - 解決數據持久化(面對故障的持久化解決方案);
zooKeeper - 解決核心數據的一致性和集群恢復;
Replication - 引入類似MySQL的數據復制方案,解決可用性;
此外還有:自動分拆Split、自動壓縮(compaction,LSM的伴生技術)、自動負載均衡、自動region遷移。
看上去如此美好,完全無需人工干預,貌似只要將HBase搭建好,一切問題HBase都將應對自如。面對如此***的系統,不動心很難。
但是,如此***的系統或許也意味著背后的復雜性是不容忽略的。HBase的代碼量也不是一星半點的。假如系統工作不正常,誰來解決?這是至關重要的。
性能與測試
HBase系統自身提供了性能測試工具:./bin/HBase org.apache.hadoop.HBase.PerformanceEvaluation,該工具提供了隨機讀寫、多客戶端讀寫等性能測試功能。根據工具測試的結果看,HBase的性能不算差。
對于HBase這樣的系統長期穩定運行比什么都重要。然而,這或許就不那么"***"。
測試版本:HBase 0.94.1、 hadoop 1.0.2、 jdk-6u32-linux-x64.bin、snappy-1.0.5.tar.gz
測試HBase搭建:14臺存儲機器+2臺master、DataNode和regionserver放在一起。
HBase env配置:
- ulimit -n 65536
- export HBASE_OPTS="$HBASE_OPTS -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode"
- export HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS="$HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS -Xmx20g -Xms20g -Xmn512m -XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:CMSIn
- itiatingOccupancyFraction=60 -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps -Xloggc:$HBASE_HOME/logs/gc-$(hostname)-hbase.lo
- g"
HBase-size.xml關鍵配置(根據《HBase: The Definitive Guide》第11章優化):
- <property>
- <name>hbase.regionserver.handler.count</name>
- <value>16</value>
- <description>Count of RPC Listener instances spun up on RegionServers.
- Same property is used by the Master for count of master handlers.
- Default is 10.
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit</name>
- <value>0.35</value>
- <description>Maximum size of all memstores in a region server before new
- updates are blocked and flushes are forced. Defaults to 40% of heap
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit</name>
- <value>0.3</value>
- <description>When memstores are being forced to flush to make room in
- memory, keep flushing until we hit this mark. Defaults to 35% of heap.
- This value equal to hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit causes
- the minimum possible flushing to occur when updates are blocked due to
- memstore limiting.
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hfile.block.cache.size</name>
- <value>0.35</value>
- <description>
- Percentage of maximum heap (-Xmx setting) to allocate to block cache
- used by HFile/StoreFile. Default of 0.25 means allocate 25%.
- Set to 0 to disable but it's not recommended.
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>zookeeper.session.timeout</name>
- <value>600000</value>
- <description>ZooKeeper session timeout.
- HBase passes this to the zk quorum as suggested maximum time for a
- session (This setting becomes zookeeper's 'maxSessionTimeout'). See
- http://hadoop.apache.org/zookeeper/docs/current/zookeeperProgrammers.html#ch_zkSessions
- "The client sends a requested timeout, the server responds with the
- timeout that it can give the client. " In milliseconds.
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.zookeeper.property.tickTime</name>
- <value>60000</value>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.regionserver.restart.on.zk.expire</name>
- <value>true</value>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.hregion.majorcompaction</name>
- <value>0</value>
- <description>The time (in miliseconds) between 'major' compactions of all
- HStoreFiles in a region. Default: 1 day(86400000).
- Set to 0 to disable automated major compactions.
- </description>
- </property>
- <property>
- <name>hbase.hregion.max.filesize</name>
- <value>536870912000</value>
- <description>
- Maximum HStoreFile size. If any one of a column families' HStoreFiles has
- grown to exceed this value, the hosting HRegion is split in two.
- Default: 1G(1073741824). Set 500G, disable file split!
- </description>
- </property>
測試一:高并發讀(4w+/s) + 少量寫(允許分拆、負載均衡)
癥狀:1-2天后,HBase掛掉(系統性能極差,不到正常的10%)。其實并非全部掛掉,而是某些regionserver掛了,并在幾個小時內引發其他regionserver掛掉。系統無法恢復:單獨啟regionserver無法恢復正常。重啟后正常。
測試二:高并發讀(4w+/s)
癥狀:1-2天后,HBase掛掉(系統性能極差,不到正常的10%)。后發現是由于zookeeper.session.timeout設置不正確導致(參見regionserver部分:http://HBase.apache.org/book.html#trouble)。重啟后正常。
測試三:高并發讀(4w+/s)
癥狀:1-2天后,HBase掛掉(系統性能極差,不到正常的10%)。從log未看出問題,但regionserver宕機,且datanode也宕機。重啟后正常。
測試四:高并發讀(4w+/s)+禁止分拆、禁止majorcompaction、禁止負載均衡(balance_switch命令)
癥狀:1-2天后,HBase掛掉(系統性能極差,不到正常的10%)。從log未看出問題,但regionserver宕機,且datanode也宕機。重啟后正常。
測試期間,還發現過:無法獲取".MATE."表的內容(想知道regionserver的分布情況)、HBase無法正確停止、HBase無法正確啟動(日志恢復失敗,文件錯誤,最終手動刪除日志重啟)。
其他缺陷
HBase使用JAVA開發,看上去很美的GC使用中代價可不小。HBase為了保證數據強一致性,每個key只能由一個regionserver提供服務。在下列情況下,HBase服務質量都將受損:
1) GC CMS -- CMS回收內存極其耗時,當HBase運行1-2天后,CMS可能耗時10分鐘,這期間該regionserver無法服務。CMS經常被觸發,這意味著HBase的服務經常會因為GC操作而部分暫停!
2) regionserver宕機 - 為了強一致性,每個key只由一個regionserver提供服務,故當regionserver宕機后,相應的region即無法服務!
3) major compaction、split不可控 - 大量磁盤操作將極大影響服務。(levelDB也需要major compaction,只是使用更加可控的方式做壓縮,比如一次只有一個壓縮任務。是否影響服務,待測試)
4) 數據恢復 - 數據恢復期間設置WAL log的相關操作,在數據恢復期間regionserver無法服務!
結論
或許通過研究HBase的源碼可讓HBase穩定運行,但從上述測試結果看:1)HBase還無法穩定長期運行;2)HBase系統很脆弱,故障恢復能力差。基于此,判斷HBase還無法滿足大規模線上系統的運維標準,只能放棄。考慮到HBase重啟基本可恢復正常,故HBase還是可作為離線存儲系統使用。
替代方案
面對大規模數據,基于磁盤的存儲系統是必不可少的。google雖然公開了bigtable的設計,但未開源,但google開源了levelDB KV存儲系統庫(http://code.google.com/p/leveldb/)。levelDB采用C++實現,1.7版本的代碼量大概2W,實現了LSM(自動壓縮)、LevelFile(基本同HFile),WAL,提供了簡單的Put、Get、Delete、Write(批量寫、事務功能)等接口。levelDB庫實現了單機單庫的磁盤存儲方案,開發者可根據自己需要開發定制的存儲系統(比如:數據Replication、自動調度、自動恢復、負載均衡等)。
參考文獻
HBase: The Definitive Guide
The Apache HBase™ Reference Guide
HBase運維碎碎念(尤其***的參考文獻): http://www.slideshare.net/NinGoo/HBase-8433555