實時顯示iOS編寫UI代碼效果
編寫iOS應用UI的方式大概有兩種,一種是Storyboard/Xib,另一種是手寫代碼。采用Storyboard/Xib方式組織UI,由于提供可視化的特性,只要從UI庫中拖動UI控件,便可以顯示結果,極大地提高開發速度。但面臨一個問題就是多人協作開發,由于所有的UI都放在同一個Storyboard文件中,使用Git/SVN合并代碼就會出現沖突。多人協作開發還不是主要問題,有人提出可以創建多個Storyboard來分開UI編寫,而Storyboard/Xib最主要問題是代碼復用性比較差。所以有些人就選擇手寫UI代碼,這樣不僅可以解決多人協作開發問題,而且通過自定義控件在多個View使用。但每次手寫UI代碼后都要編譯、構建和運行,***在模擬器顯示,這樣會拖慢開發速度。如果每次修改UI控件后,保存修改便實時在模擬器顯示修改后結果,就可以極大的提高編寫UI的速度。
Auto Layout
Auto Layout是什么
Auto Layout是一個基于constraint(約束)的布局系統,它根據UI元素之間約束關系來調整UI元素的位置和大小。
Auto Layout解決什么問題
- 更容易適配不同分辨率設備的屏幕(iPhone 6 Plus, iPhone 6, iPhone 5s/5, iPhone 4s/4)
- 當設備旋轉時不需要做額外處理
- 使用constraint來描述布局邏輯,更利于理解和清晰
如何使用Auto Layout
Auto Layout中約束的類對應是NSLayoutConstraint, 而創建NSLayoutConstraint對象主要有兩種方式,***種是
- + (id)constraintWithItem:(id)view1
- attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute1
- relatedBy:(NSLayoutRelation)relation
- toItem:(id)view2
- attribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)attribute2
- multiplier:(CGFloat)multiplier
- constant:(CGFloat)constant;
上面方法主要意思是,某個view1的attribute1等于(小于或等于/大于或等于)某個view2的attribute2的multiplier倍加上constant。而attribute主要由表示位置(上/下/左/右)和大小(寬/高)的以下幾個值:
- typedef enum: NSInteger {
- NSLayoutAttributeLeft = 1,
- NSLayoutAttributeRight,
- NSLayoutAttributeTop,
- NSLayoutAttributeBottom,
- NSLayoutAttributeLeading,
- NSLayoutAttributeTrailing,
- NSLayoutAttributeWidth,
- NSLayoutAttributeHeight,
- NSLayoutAttributeCenterX,
- NSLayoutAttributeCenterY,
- NSLayoutAttributeBaseline,
- NSLayoutAttributeNotAnAttribute = 0
- } NSLayoutAttribute;
簡化一下,使用公式可以表達為:
- view1.attribute1 = view2.attribute2 * multiplier + constant
第二種方式是:
- + (NSArray *)constraintsWithVisualFormat:(NSString *)format
- options:(NSLayoutFormatOptions)opts
- metrics:(NSDictionary *)metrics
- views:(NSDictionary *)views;
這種方式主要是采用Visual Format Language(可視化格式語言)來描述約束布局,雖然語法比較簡潔,但是可讀性比較差和容易出錯。
Auto Layout存在問題
雖然Auto Layout在布局view方面是非常強大和靈活,但是創建constraint的語法過于繁雜,引用Masonry一個例子:
- UIView *superview = self;
- UIView *view1 = [[UIView alloc] init];
- view1.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
- view1.backgroundColor = [UIColor greenColor];
- [superview addSubview:view1];
- UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
- [superview addConstraints:@[
- //view1 constraints
- [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
- relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
- toItem:superview
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
- multiplier:1.0
- constant:padding.top],
- [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft
- relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
- toItem:superview
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeft
- multiplier:1.0
- constant:padding.left],
- [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
- relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
- toItem:superview
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
- multiplier:1.0
- constant:-padding.bottom],
- [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:view1
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight
- relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
- toItem:superview
- attribute:NSLayoutAttributeRight
- multiplier:1
- constant:-padding.right],
- ]];
如此簡單的一個例子都要編寫這么多行代碼,想象一下如果創建多個view的constraint時會多么痛苦啊。另一個方式是采用Visual Format Language (VFL),雖然語法比較簡潔,但是可讀性比較差和容易出錯。
Masonry
為什么使用Masonry
Masonry是采用鏈式DSL(Domain-specific language)來封裝NSLayoutConstraint,通過這種方式編寫Auto Layout布局代碼更加易讀和簡潔。
使用Masonry的MASConstraintMaker來表達相同constraint
- UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);
- [view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top); //with is an optional semantic filler
- make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left);
- make.bottom.equalTo(superview.mas_bottom).with.offset(-padding.bottom);
- make.right.equalTo(superview.mas_right).with.offset(-padding.right);
- }];
甚至可以更短
- [view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.edges.equalTo(superview).with.insets(padding);
- }];
#p#
如何使用
使用Masonry創建constraint來定義布局的方式有三種:mas_makeConstraints,mas_updateConstraints,mas_remakeConstraints。
1. mas_makeConstraints
使用mas_makeConstraints創建constraint后,你可以使用局部變量或屬性來保存以便下次引用它;如果創建多個constraints,你可以采用數組來保存它們。
- // in public/private interface
- @property (nonatomic, strong) MASConstraint *topConstraint;
- ...
- // when making constraints
- [view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- self.topConstraint = make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top);
- make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left);
- }];
- ...
- // then later you can call
- [self.topConstraint uninstall];
2. mas_updateConstraints
有時你需要更新constraint(例如,動畫和調試)而不是創建固定constraint,可以使用mas_updateConstraints方法
- // this is Apple's recommended place for adding/updating constraints
- // this method can get called multiple times in response to setNeedsUpdateConstraints
- // which can be called by UIKit internally or in your code if you need to trigger an update to your constraints
- - (void)updateConstraints {
- [self.growingButton mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.center.equalTo(self);
- make.width.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.width)).priorityLow();
- make.height.equalTo(@(self.buttonSize.height)).priorityLow();
- make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
- make.height.lessThanOrEqualTo(self);
- }];
- //according to apple super should be called at end of method
- [super updateConstraints];
- }
3. mas_remakeConstraints
mas_remakeConstraints與mas_updateConstraints比較相似,都是更新constraint。不過,mas_remakeConstraints是刪除之前constraint,然后再添加新的constraint(適用于移動動畫);而mas_updateConstraints只是更新constraint的值。
- - (void)changeButtonPosition {
- [self.button mas_remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.size.equalTo(self.buttonSize);
- if (topLeft) {
- make.top.and.left.offset(10);
- } else {
- make.bottom.and.right.offset(-10);
- }
- }];
- }
想了解以上三個代碼片段的更多細節,可以下載Masonry iOS Examples工程查閱。
Classy
Classy簡介和特性
Classy是一個能與UIKit無縫結合stylesheet(樣式)系統。它借鑒CSS的思想,但引入新的語法和命名規則。
靈活內嵌的語法
{ } : ; 這些語法符號是可選的,你可以選擇適合自己的風格來表達stylesheet。
你可以使用{ } : ; 來限定stylesheet
- $main-color = #e1e1e1;
- MYCustomView {
- background-color: $main-color;
- title-insets: 5, 10, 5, 10;
- > UIProgressView.tinted {
- progress-tint-color: black;
- track-tint-color: yellow;
- }
- }
- ^UIButton.warning, UIView.warning ^UIButton {
- title-color[state:highlighted]: #e3e3e3;
- }
或者你使用空格來限定stylesheet
- $main-color = #e1e1e1
- MYCustomView
- background-color $main-color
- title-insets 5, 10, 5, 10
- > UIProgressView.tinted
- progress-tint-color black
- track-tint-color yellow
- ^UIButton.warning, UIView.warning ^UIButton
- title-color[state:highlighted] #e3e3e3
默認樣式
Classy在應用程序Bundle默認查找文件名為stylesheet.cas的樣式文件。如果你采用這個文件名,你可以不用做任何東西就能加載樣式文件。
但如果你想指定其他file path(樣式文件名),你可以創建[CASStyler defaultStyler]
- [CASStyler defaultStyler].filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"myStyles.cas" ofType:nil];
如果你還想當發生錯誤時,獲取錯誤信息以便于調試,可以使用-(void)setFilePath:error:
- NSError *error = nil;
- NSString filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"myStyles.cas" ofType:nil];
- [[CASStyler defaultStyler] setFilePath:filePath error:&error];
如果你是使用Storyboard/Xib組織UI界面,那就需要在main.m的int main(int argc, char * argv[])方法設置 filePath,這樣可以確保在創建UIWindow之前加載stylesheet。否則(采用手寫UI代碼),你在 AppDelegate.m的- (BOOL)application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:方法設置filePath
Live Reload
Live Reload是實時顯示編寫UI代碼效果的關鍵特性,它能夠實時檢查stylesheet文件變化,無需重新編譯、構建和運行模擬器,從而極大提高開發速度。
為了啟用Live Reload,你需要指定stylesheet路徑,并且只運行在模擬器上。
- #if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR
- NSString *absoluteFilePath = CASAbsoluteFilePath(@"../Styles/stylesheet.cas");
- [CASStyler defaultStyler].watchFilePath = absoluteFilePath;
- #endif
Selectors
Style Selectors是指定哪個view使用哪種樣式的方式。主要有三種方法來指定目標view:
- Object Class
- View Hierarchy
- Style Class
你可以混合使用三種方法,例子如下:
- /* match views
- * where class is UIButton or UIButton subclass
- * and styleClass is "large"
- * and superview class is UITabBar
- */
- UITabBar > ^UIButton.large { }
想了解具體如何使用,請查閱官網Selectors章節
為了避免與Objective-C的message selectors混淆,術語style selectors表示Classy stylesheets的selectors
Properties
Classy支持所有UIAppearance的屬性和方法,也支持與UIAppearance無關的很多屬性。Classy使用與UIKit相同屬性命名,所以你不必考慮如何將style property映射到Objective-C的property。
UIPageControl類的屬性如下:
- @property (nonatomic,retain) UIColor *pageIndicatorTintColor;
- @property (nonatomic,retain) UIColor *currentPageIndicatorTintColor;
style property的名字采用與objective-c一樣的名字
- UIPageControl {
- pageIndicatorTintColor black
- currentPageIndicatorTintColor purple
- }
style property的命名規則采用kebab case
- UIPageControl {
- page-indicator-tint-color black
- current-page-indicator-tint-color purple
- }
想了解具體如何使用,請查閱官網Properties章節
Keep it DRY(Don't Repeat Yourself)
在編程中一個很重要的原則就是避免重復,這不僅可以大量減少重復代碼,并且使得代碼更加容易復用和維護。Classy提供三種方式避免代碼重復:grouping,nesting,variables
Grouping
如果有兩個以上的style selectors共用相同的屬性時
- UISlider.info {
- minimum-track-tint-color black
- maximum-track-tint-color purple
- }
- UISlider.error {
- minimum-track-tint-color black
- maximum-track-tint-color purple
- thumb-tint-color red
- }
我們可以提取相同的屬性到分組style selector中
- UISlider.info, UISlider.error {
- minimum-track-tint-color black
- maximum-track-tint-color purple
- }
- UISlider.error {
- thumb-tint-color red
- }
#p#
Nesting
如果兩個以上style selectors共用相同的view hierarchy時
- UICollectionView {
- background-color #a2a2a2
- }
- UICollectionView > UICollectionViewCell {
- clips-to-bounds NO
- }
- UICollectionView > UICollectionViewCell UILabel {
- text-color purple
- }
- UICollectionView > UICollectionViewCell UILabel.title {
- font 20
- }
我們通過nesting方式將view hierarchies表達成這樣方式
- UICollectionView {
- background-color #a2a2a2
- > UICollectionViewCell {
- clips-to-bounds NO
- UILabel {
- text-color purple
- &.title {
- font 20
- }
- }
- }
- }
Variables
Classy讓你通過定義variables來將多個相同的style property值存儲以便共享。Variable命名規則如下:
- 必須以大小寫字母或$符號開頭
-
可以包含_,-或任何字母數字
- // prefix with ' $ ' to help distinguish variables
- $brand-color = #e1e1e1
- // OR not
- insets = 5, 10, 5, 10
- UIButton {
- background-color $brand-color
- contentEdgeInsets insets
- background-image[state:selected] bg_button insets
- }
***官方還提供一個實例來解釋具體如何使用:Custom Views Example
ClassyLiveLayout
ClassyLiveLayout通過結合Classy stylesheets與Masonry一起使用,能夠在運行的模擬器中微調Auto Layout約束實時顯示效果的工具。
ClassyLiveLayout一個核心category:UIView+ClassyLayoutProperties,在UIView定義以下屬性:
- @property(nonatomic, assign) UIEdgeInsets cas_margin;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGSize cas_size;
- // shorthand properties for setting only a single constant value
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_sizeWidth;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_sizeHeight;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_marginTop;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_marginLeft;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_marginBottom;
- @property(nonatomic, assign) CGFloat cas_marginRight;
cas_margin和cas_size分別表示UI元素的位置和大小,而其余的屬性都是對兩個屬性進一步細分。我們可以從stylesheets中訪問style properties來定義constraints布局,做到將數據與代碼分離,有利于修改和復用代碼。
- UIView.blue-box {
- cas_size: 80 100
- cas_margin-top: 60
- cas_margin-left: 50
- }
- UIView.red-box {
- cas_size-width: 120
- cas_margin-left: 20
- }
我們可以在updateConstraints或updateViewConstrains定義布局時引用style properties
- - (void)updateViewConstraints {
- [super updateViewConstraints];
- [_blueBoxView mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.width.equalTo(@(_blueBoxView.cas_size.width));
- make.height.equalTo(@(_blueBoxView.cas_size.height));
- make.top.equalTo(@(_blueBoxView.cas_margin.top));
- make.left.equalTo(@(_blueBoxView.cas_margin.left));
- }];
- [_redBoxView mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
- make.width.equalTo(@(_redBoxView.cas_size.width));
- make.height.equalTo(_blueBoxView);
- make.top.equalTo(_blueBoxView);
- make.left.equalTo(_blueBoxView.mas_right).with.offset(_redBoxView.cas_margin.left);
- }];
- }
當定義view layouts時,將Auto Layout的constraints都放在stylesheets中實時加載(Live reload)。如果你修改constraints,無需重新編譯、構建和運行模擬器便能實時看到修改后的效果。
示例工程
配置工程
由于需要引用Masonry,Classy和ClassyLiveLayout,Podfile配置如下:
- pod 'Masonry', '~> 0.6.1'
- pod 'Classy', '~> 0.2.4'
- pod 'ClassyLiveLayout', '~> 0.6.0'
編寫代碼
1. 添加stylesheet.cas文件到工程
當安裝好Masonry,Classy和ClassyLiveLayout后,***次運行項目會出現沒有stylesheet.cas文件錯誤:

No stylesheet.cas file error.png
只要向工程添加空的stylesheet.cas文件即可。
Create stylesheet.cas file.png
2. 創建LiveView類,該類繼承SHPAbstractView。
Create LiveView inherit SHPAbstractView.png
在ViewController創建LiveView對象,然后被self.view引用。
Setup root view in ViewController.png
當編譯運行時,在SHPAbstractView.h由于找不到UIView出現編譯錯誤。
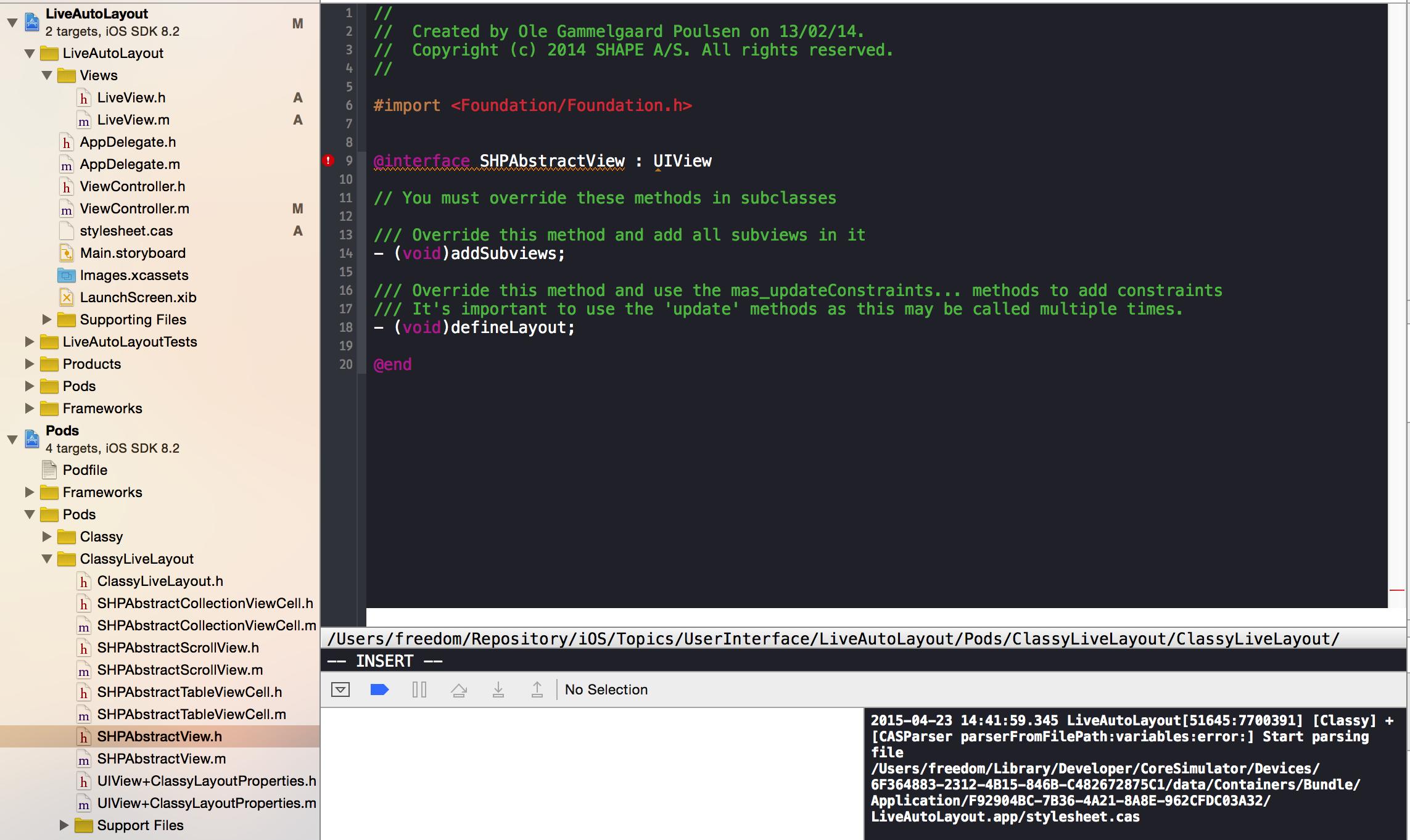
SHPAbstractView Compile error.png
#p#
只需引入UIKit便可以解決,但運行一下應用程序,出現一下錯誤:

Must override methods.png
主要原因是任何自定義UIView繼承SHPAbstractView都需要override兩個方法:- (void)addSubviews和- (void)defineLayout,我們可以查看SHPAbstractView的源碼可知:
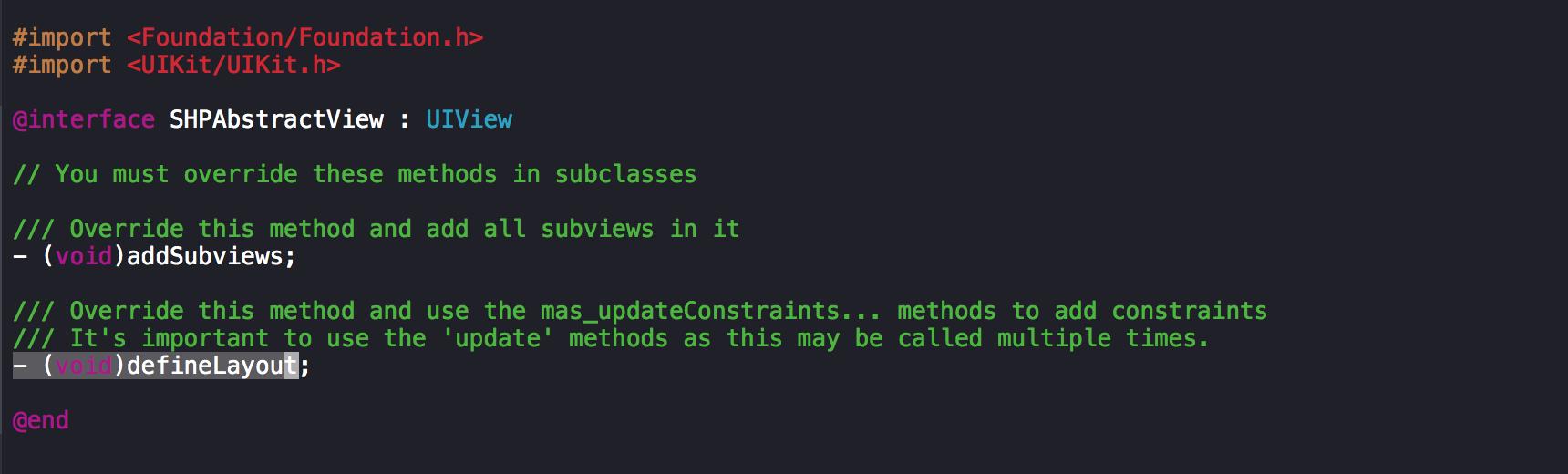
SHPAbstractView Source Code .png
所以只要在LiveView.m文件覆蓋兩個方法即可
- #pragma mark - Add subviews and define layout
- - (void)addSubviews
- {
- }
- - (void)defineLayout
- {
- }
3. LiveView類設計
LiveView主要由包含redBoxView和blueBoxView兩個屬性,redBoxView表示紅色方塊,blueBoxView表示藍色方塊。
- #import "SHPAbstractView.h"
- @interface LiveView : SHPAbstractView
- @property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *redBoxView;
- @property (strong, nonatomic) UIView *blueBoxView;
- @end
4. LiveView類實現
由于SHPAbstractView類如何初始化View已經做了處理,暴露兩個接口- (void)addSubviews和-(void)defineLayout分別處理構建view hierarchy和定義布局,子類只要覆蓋SHPAbstractView這兩個方法就可以創建LiveView了。
但是我們將Auto Layout的constraints都放在stylesheets中實時加載(Live reload),即放在本工程的stylesheet.cas文件,將布局數據和布局代碼分離。
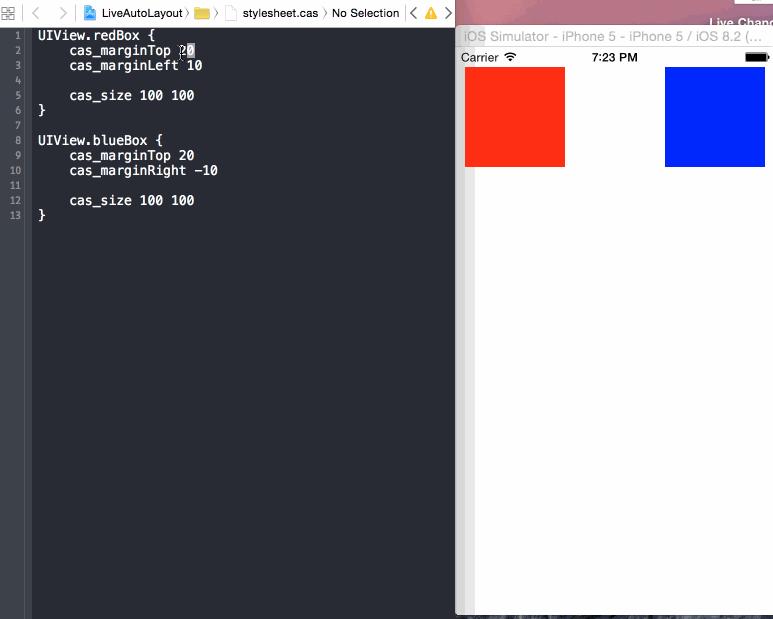
- UIView.redBox {
- cas_marginTop 50
- cas_marginLeft 20
- cas_size 100 100
- }
- UIView.blueBox {
- cas_marginTop 50
- cas_marginRight -20
- cas_size 100 100
- }
有了constraints數據后,便可以在代碼布局:
- @implementation LiveView
- #pragma mark - Add subviews and define layout
- - (void)addSubviews
- {
- self.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
- [self addSubview:self.redBoxView];
- [self addSubview:self.blueBoxView];
- }
- - (void)defineLayout
- {
- [self.redBoxView mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker* make){
- make.top.equalTo(@(self.redBoxView.cas_marginTop));
- make.left.equalTo(@(self.redBoxView.cas_marginLeft));
- make.width.equalTo(@(self.redBoxView.cas_sizeWidth));
- make.height.equalTo(@(self.redBoxView.cas_sizeHeight));
- }];
- [self.blueBoxView mas_updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make){
- make.top.equalTo(@(self.blueBoxView.cas_marginTop));
- make.right.equalTo(@(self.blueBoxView.cas_marginRight));
- make.width.equalTo(@(self.blueBoxView.cas_sizeWidth));
- make.height.equalTo(@(self.blueBoxView.cas_sizeHeight));
- }];
- }
- #pragma mark - Lazy initialization
- - (UIView*)redBoxView
- {
- if (!_redBoxView) {
- _redBoxView = [UIView new];
- _redBoxView.cas_styleClass = @"redBox";
- _redBoxView.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor];
- }
- return _redBoxView;
- }
- - (UIView*)blueBoxView
- {
- if (!_blueBoxView) {
- _blueBoxView = [UIView new];
- _blueBoxView.cas_styleClass = @"blueBox";
- _blueBoxView.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor];
- }
- return _blueBoxView;
- }
5. 模擬器支持Live Reload
為了啟用Live Reload,你需要指定stylesheet路徑,并且只運行在模擬器上。
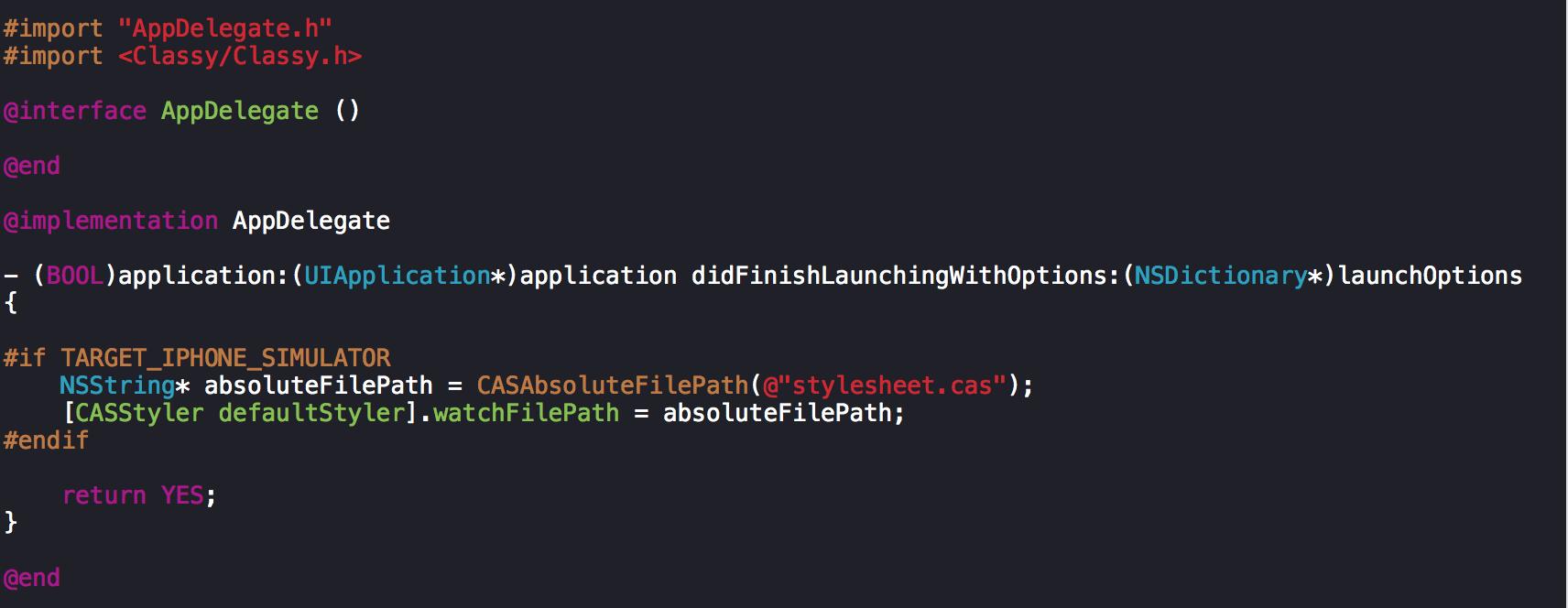
Support Live Reload.png
此時效果:
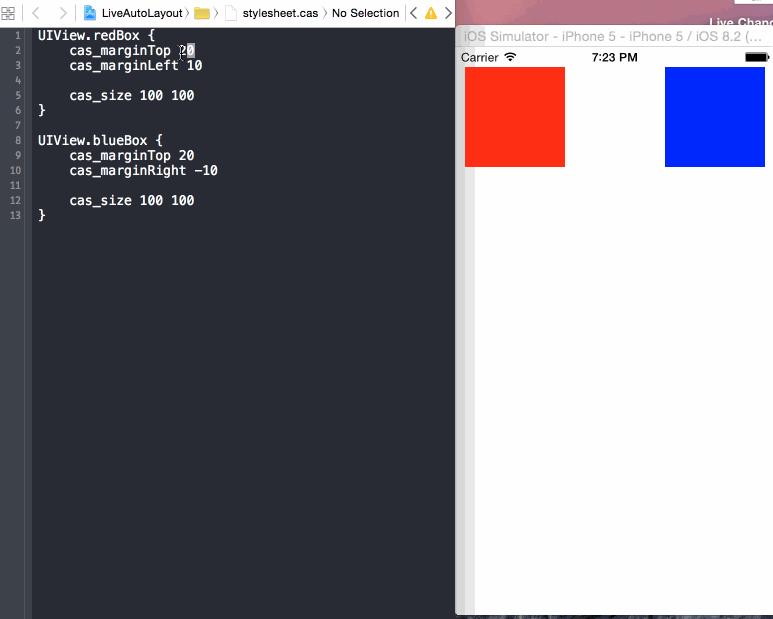
#p#
6. 分離樣式文件
由于有網友提出這樣一個問題:如果所有view的樣式都放在同一個stylesheet.cas文件,會讓stylesheet.cas文件繁雜,并且當多個人協同開發時,不易于合并代碼,所以有必要將樣式文件分離到多個文件中。
-
創建variable.cas文件,并將redBox對應UIView的樣式放在variable.cas文件中。
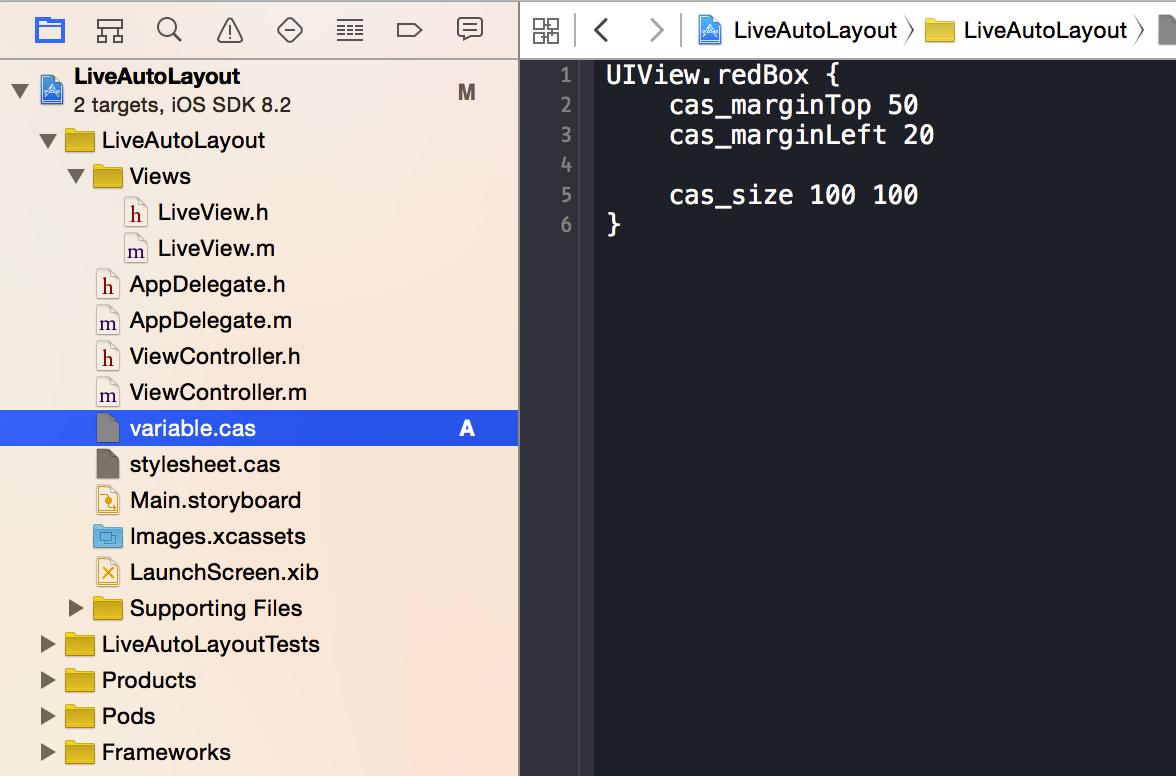
variable.cas file.png
-
在stylesheet.cas樣式文件使用@import指令引用variable.cas文件
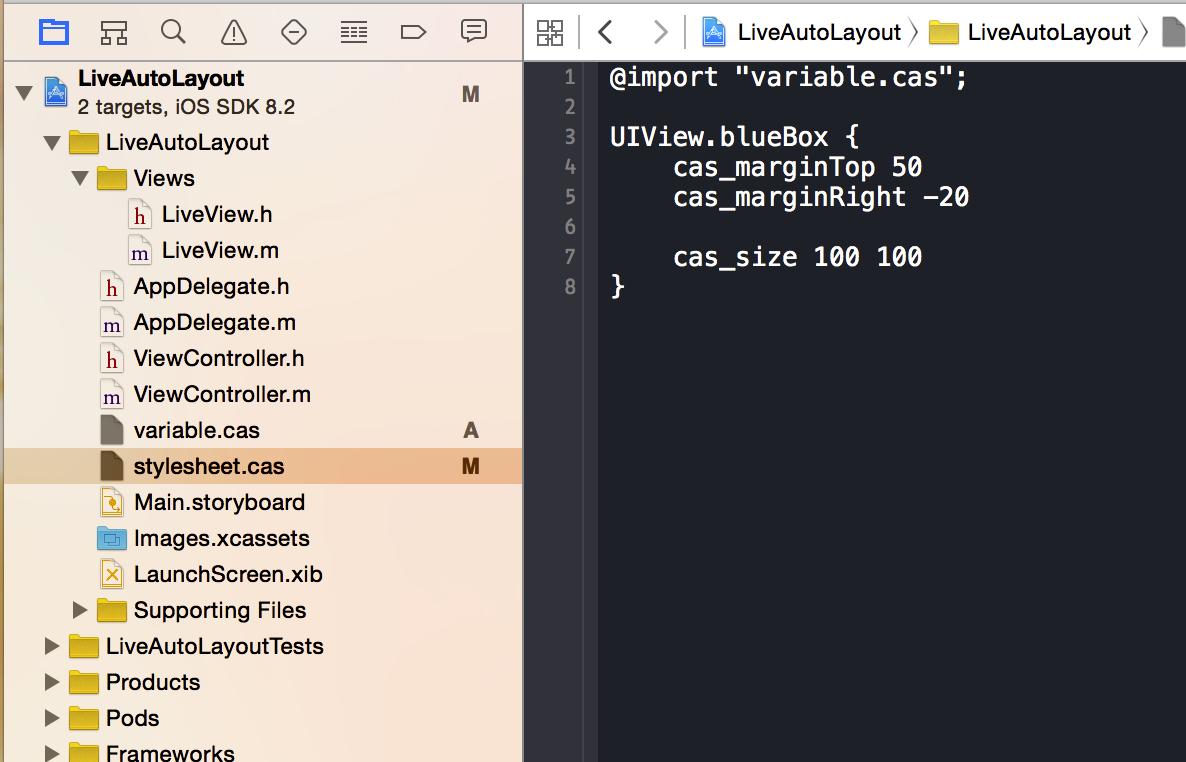
stylesheet.cas file.png
***效果
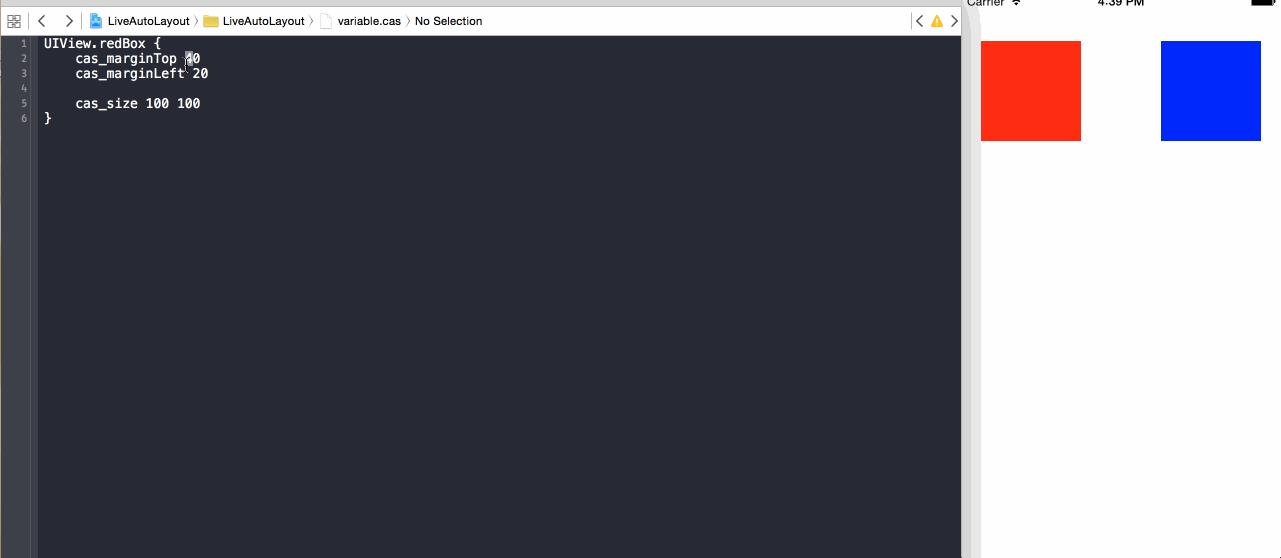
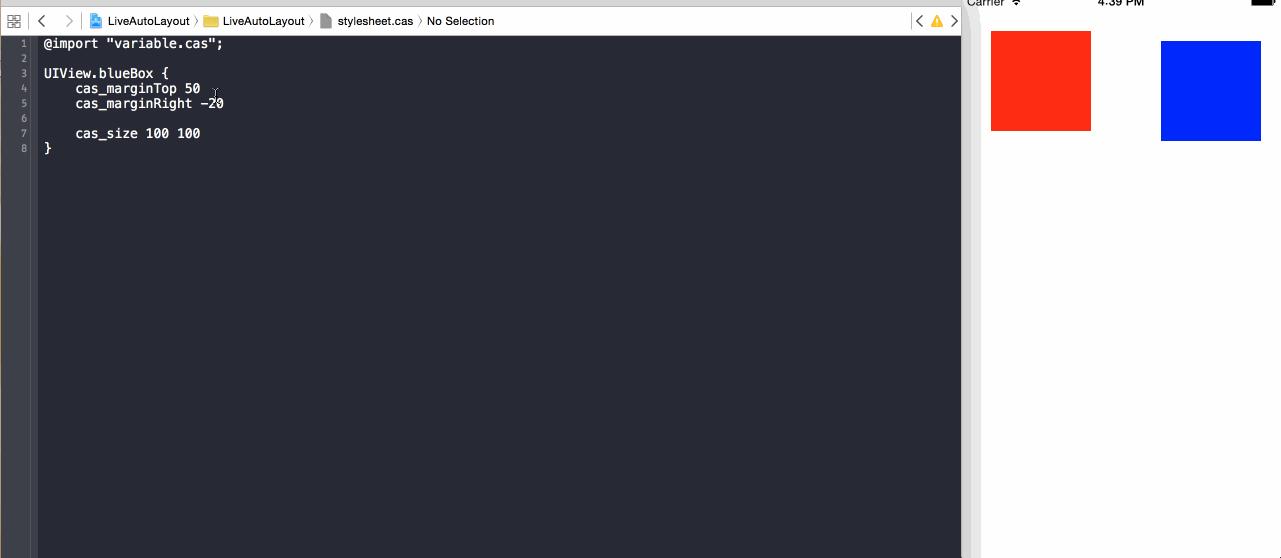
示例代碼存放地址:LiveAutoLayout
總結
之前手寫UI代碼每次更改一般都要重新編譯、構建和運行模擬器才能看到效果,但結合使用Masonry,Classy和ClassLiveLayout之后,告別這個費時過程,極大地提高開發速度;不僅如此,我們將Auto Layout的constraints都放在stylesheets中實時加載(Live reload),將布局數據和布局代碼分離,使得代碼更加復用和維護。Classy還提供三種避免重復方法:Grouping, Nestting和Variable,盡可能復用樣式數據。
這是本人***次編寫技術博客,可能有很多錯誤和漏洞,希望大家多多指點,也希望這篇文章能夠幫助到大家。






























