Android自定義View
前言
Android自定義View的詳細步驟是我們每一個Android開發人員都必須掌握的技能,因為在開發中總會遇到自定義View的需求。為了提高自己的技術水平,自己就系統的去研究了一下,在這里寫下一點心得,有不足之處希望大家及時指出。
流程
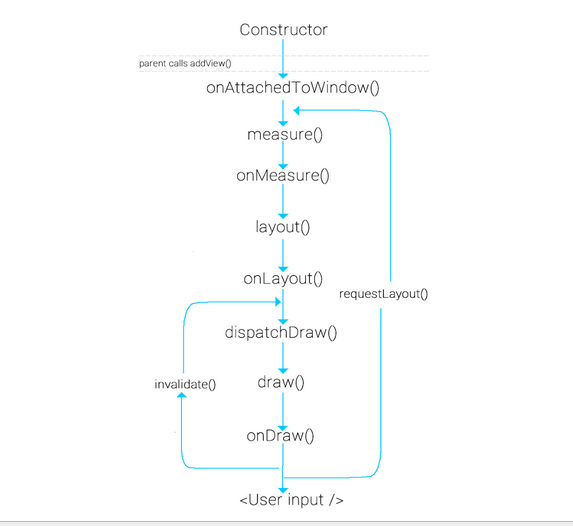
在Android中對于布局的請求繪制是在Android framework層開始處理的。繪制是從根節點開始,對布局樹進行measure與draw。在RootViewImpl中的performTraversals展開。它所做的就是對需要的視圖進行measure(測量視圖大小)、layout(確定視圖的位置)與draw(繪制視圖)。下面的圖能很好的展現視圖的繪制流程:
當用戶調用requestLayout時,只會觸發measure與layout,但系統開始調用時還會觸發draw
下面來詳細介紹這幾個流程。
measure
measure是View中的final型方法不可以進行重寫。它是對視圖的大小進行測量計算,但它會回調onMeasure方法,所以我們在自定義View的時候可以重寫onMeasure方法來對View進行我們所需要的測量。它有兩個參數widthMeasureSpec與heightMeasureSpec。其實這兩個參數都包含兩部分,分別為size與mode。size為測量的大小而mode為視圖布局的模式
我們可以通過以下代碼分別獲取:
- int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
- int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
- int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
- int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
獲取到的mode種類分為以下三種:
| MODE | EXPLAIN |
|---|---|
| UNSPECIFiED | 父視圖不對子視圖進行約束,子視圖大小可以是任意大小,一般是對ListView、ScrollView等進行自定義,一般用不到 |
| EXACTLY | 父視圖對子視圖設定了一個精確的尺寸,子視圖不超過該尺寸,一般為精確的值例如200dp或者使用了match_parent |
| AT_MOST | 父視圖對子視圖指定了一***的尺寸,確保子視圖的所以內容都剛好能在該尺寸中顯示出來,一般為wrap_content,這種父視圖不能獲取子視圖的大小,只能由子視圖自己去計算尺寸,這也是我們測量要實現的邏輯情況 |
setMeasuredDimension
通過以上邏輯獲取視圖的寬高,***要調用setMeasuredDimension方法將測量好的寬高進行傳遞出去。其實最終是調用setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法對傳過來的值進行屬性賦值。調用super.onMeasure()的調用邏輯也是一樣的。
下面以自定義一個驗證碼的View為例,它的onMeasure方法如下:
- @Override
- protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
- int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
- int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
- int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
- int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
- if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
- //直接獲取精確的寬度
- width = widthSize;
- } else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
- //計算出寬度(文本的寬度+padding的大小)
- width = bounds.width() + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
- }
- if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
- //直接獲取精確的高度
- height = heightSize;
- } else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
- //計算出高度(文本的高度+padding的大小)
- height = bounds.height() + getPaddingBottom() + getPaddingTop();
- }
- //設置獲取的寬高
- setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
- }
可以對自定義View的layout_width與layout_height進行設置不同的屬性,達到不同的mode類型,就可以看到不同的效果
measureChildren
如果你是對繼承ViewGroup的自定義View那么在進行測量自身的大小時還要測量子視圖的大小。一般通過measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)方法來測量子視圖的大小。
- protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
- final int size = mChildrenCount;
- final View[] children = mChildren;
- for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
- final View child = children[i];
- if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
- measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
- }
- }
- }
通過上面的源碼會發現,它其實是遍歷每一個子視圖,如果該子視圖不是隱藏的就調用measureChild方法,那么來看下measureChild源碼:
- protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
- int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
- final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
- final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
- mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
- final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
- mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
- child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
- }
會發現它首先調用了getChildMeasureSpec方法來分別獲取寬高,***再調用的就是View的measure方法,而通過前面的分析我們已經知道它做的就是對視圖大小的計算。而對于measure中的參數是通過getChildMeasureSpec獲取,再來看下其源碼:
- public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
- int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
- int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
- int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
- int resultSize = 0;
- int resultMode = 0;
- switch (specMode) {
- // Parent has imposed an exact size on us
- case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
- if (childDimension >= 0) {
- resultSize = childDimension;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
- // Child wants to be our size. So be it.
- resultSize = size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
- // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
- // bigger than us.
- resultSize = size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
- }
- break;
- // Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
- case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
- if (childDimension >= 0) {
- // Child wants a specific size... so be it
- resultSize = childDimension;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
- // Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
- // Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
- resultSize = size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
- // Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
- // bigger than us.
- resultSize = size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
- }
- break;
- // Parent asked to see how big we want to be
- case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
- if (childDimension >= 0) {
- // Child wants a specific size... let him have it
- resultSize = childDimension;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
- // Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
- // be
- resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
- } else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
- // Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
- // big it should be
- resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
- resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
- }
- break;
- }
- //noinspection ResourceType
- return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
- }
是不是容易理解了點呢。它做的就是前面所說的根據mode的類型,獲取相應的size。根據父視圖的mode類型與子視圖的LayoutParams類型來決定子視圖所屬的mode,***再將獲取的size與mode通過MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec方法整合返回。***傳遞到measure中,這就是前面所說的widthMeasureSpec與heightMeasureSpec中包含的兩部分的值。整個過程為measureChildren->measureChild->getChildMeasureSpec->measure->onMeasure->setMeasuredDimension,所以通過measureChildren就可以對子視圖進行測量計算。
layout
layout也是一樣的內部會回調onLayout方法,該方法是用來確定子視圖的繪制位置,但這個方法在ViewGroup中是個抽象方法,所以如果要自定義的View是繼承ViewGroup的話就必須實現該方法。但如果是繼承View的話就不需要了,View中有一個空實現。而對子視圖位置的設置是通過View的layout方法通過傳遞計算出來的left、top、right與bottom值,而這些值一般都要借助View的寬高來計算,視圖的寬高則可以通過getMeasureWidth與getMeasureHeight方法獲取,這兩個方法獲取的值就是上面onMeasure中setMeasuredDimension傳遞的值,即子視圖測量的寬高。
getWidth、getHeight與getMeasureWidth、getMeasureHeight是不同的,前者是在onLayout之后才能獲取到的值,分別為left-right與top-bottom;而后者是在onMeasure之后才能獲取到的值。只不過這兩種獲取的值一般都是相同的,所以要注意調用的時機。
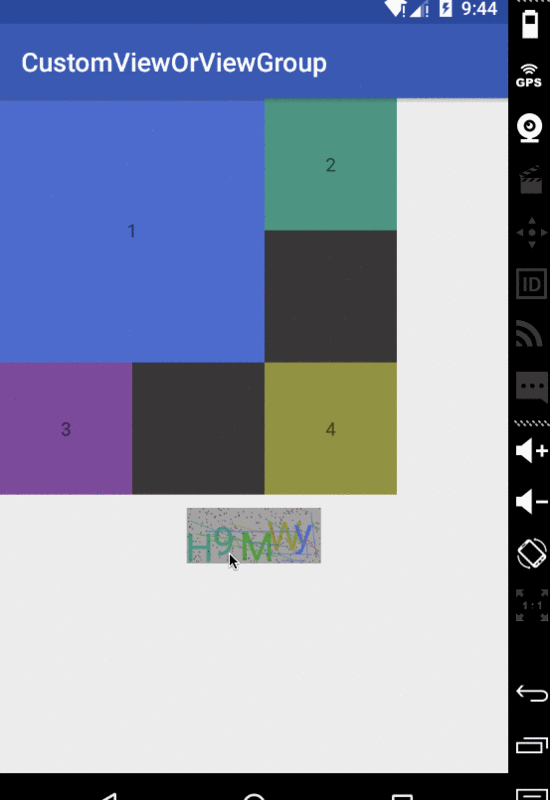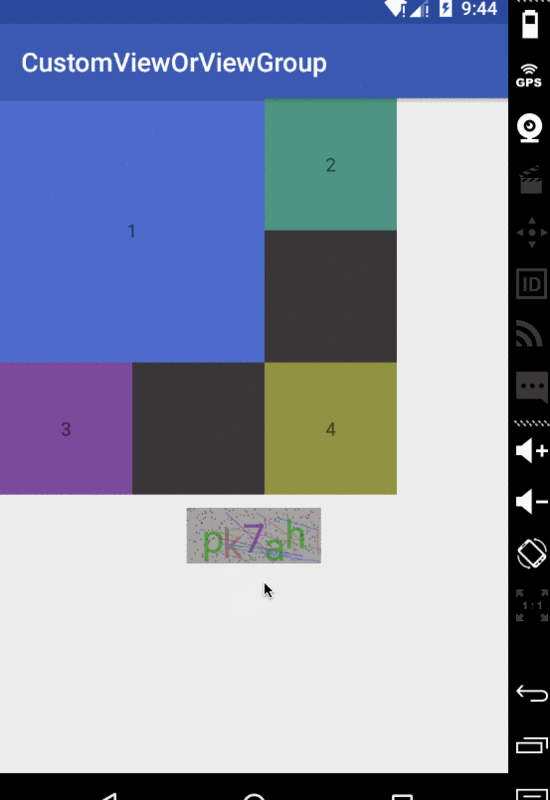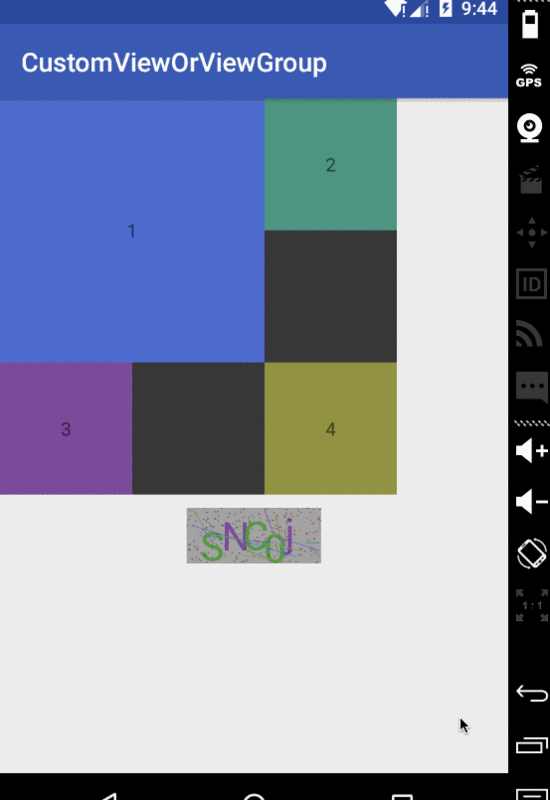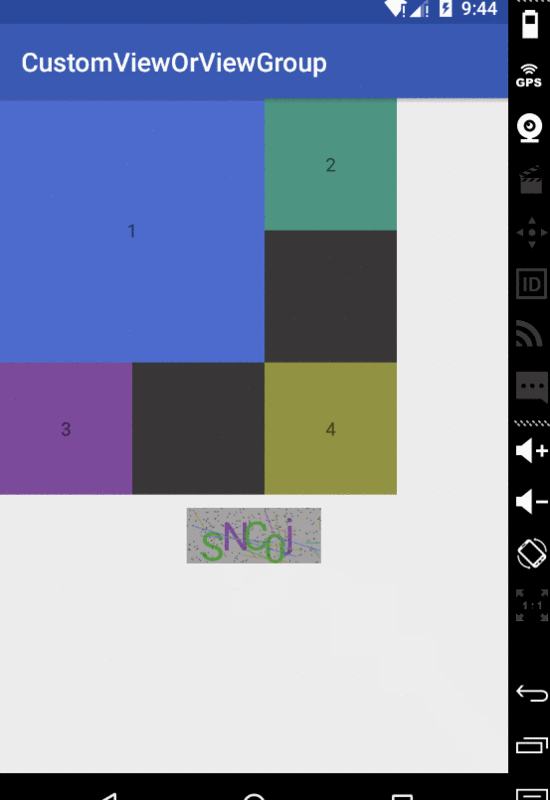
下面以定義一個把子視圖放置于父視圖的四個角的View為例:
- @Override
- protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
- int count = getChildCount();
- MarginLayoutParams params;
- int cl;
- int ct;
- int cr;
- int cb;
- for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
- View child = getChildAt(i);
- params = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
- if (i == 0) {
- //左上角
- cl = params.leftMargin;
- ct = params.topMargin;
- } else if (i == 1) {
- //右上角
- cl = getMeasuredWidth() - params.rightMargin - child.getMeasuredWidth();
- ct = params.topMargin;
- } else if (i == 2) {
- //左下角
- cl = params.leftMargin;
- ct = getMeasuredHeight() - params.bottomMargin - child.getMeasuredHeight()
- - params.topMargin;
- } else {
- //右下角
- cl = getMeasuredWidth() - params.rightMargin - child.getMeasuredWidth();
- ct = getMeasuredHeight() - params.bottomMargin - child.getMeasuredHeight()
- - params.topMargin;
- }
- cr = cl + child.getMeasuredWidth();
- cb = ct + child.getMeasuredHeight();
- //確定子視圖在父視圖中放置的位置
- child.layout(cl, ct, cr, cb);
- }
- }
至于onMeasure的實現源碼我后面會給鏈接,如果要看效果圖的話,我后面也會貼出來,前面的那個驗證碼的也是一樣
draw
draw是由dispatchDraw發動的,dispatchDraw是ViewGroup中的方法,在View是空實現。自定義View時不需要去管理該方法。而draw方法只在View中存在,ViewGoup做的只是在dispatchDraw中調用drawChild方法,而drawChild中調用的就是View的draw方法。那么我們來看下draw的源碼:
- public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
- final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
- final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
- (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
- mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
- /*
- * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
- * in the appropriate order:
- *
- * 1. Draw the background
- * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
- * 3. Draw view's content
- * 4. Draw children
- * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
- * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
- */
- // Step 1, draw the background, if needed
- int saveCount;
- if (!dirtyOpaque) {
- drawBackground(canvas);
- }
- // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
- final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
- boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
- boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
- if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
- // Step 3, draw the content
- if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
- // Step 4, draw the children
- dispatchDraw(canvas);
- // Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground
- if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
- mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
- }
- // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars)
- onDrawForeground(canvas);
- // we're done...
- return;
- }
- //省略2&5的情況
- ....
- }
源碼已經非常清晰了draw總共分為6步;
- 繪制背景
- 如果需要的話,保存layers
- 繪制自身文本
- 繪制子視圖
- 如果需要的話,繪制fading edges
- 繪制scrollbars
其中 第2步與第5步不是必須的。在第3步調用了onDraw方法來繪制自身的內容,在View中是空實現,這就是我們為什么在自定義View時必須要重寫該方法。而第4步調用了dispatchDraw對子視圖進行繪制。還是以驗證碼為例:
- @Override
- protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
- //繪制背景
- mPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.autoCodeBg));
- canvas.drawRect(0, 0, getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight(), mPaint);
- mPaint.getTextBounds(autoText, 0, autoText.length(), bounds);
- //繪制文本
- for (int i = 0; i < autoText.length(); i++) {
- mPaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(colorRes[random.nextInt(6)]));
- canvas.drawText(autoText, i, i + 1, getWidth() / 2 - bounds.width() / 2 + i * bounds.width() / autoNum
- , bounds.height() + random.nextInt(getHeight() - bounds.height())
- , mPaint);
- }
- //繪制干擾點
- for (int j = 0; j < 250; j++) {
- canvas.drawPoint(random.nextInt(getWidth()), random.nextInt(getHeight()), pointPaint);
- }
- //繪制干擾線
- for (int k = 0; k < 20; k++) {
- int startX = random.nextInt(getWidth());
- int startY = random.nextInt(getHeight());
- int stopX = startX + random.nextInt(getWidth() - startX);
- int stopY = startY + random.nextInt(getHeight() - startY);
- linePaint.setColor(getResources().getColor(colorRes[random.nextInt(6)]));
- canvas.drawLine(startX, startY, stopX, stopY, linePaint);
- }
- }
其實很簡單,就是一些繪制的業務邏輯。好了基本就到這里了,下面上傳一張示例的效果圖,與源碼鏈接
示例圖
對了還有自定義屬性,這里簡單說一下。自定義View時一般都要自定義屬性,所以都會在res/values/attr.xml中定義attr與declare-styleable,***在自定義View中通過TypedArray獲取。