一種提高Android應用進程存活率新方法(上)
基礎知識
Android 進程優先級
1 進程優先級等級一般分法
- Activte process
- Visible Process
- Service process
- Background process
- Empty process
2 Service技巧
- onStartCommand返回START_STICKY
- onDestroy中startself
- Service后臺變前置,setForground(true)
- android:persistent = “true”
3 進程優先級號
ProcessList.java
- // Adjustment used in certain places where we don't know it yet.
- // (Generally this is something that is going to be cached, but we
- // don't know the exact value in the cached range to assign yet.)
- static final int UNKNOWN_ADJ = 16;
- // This is a process only hosting activities that are not visible,
- // so it can be killed without any disruption.
- static final int CACHED_APP_MAX_ADJ = 15;
- static final int CACHED_APP_MIN_ADJ = 9;
- // The B list of SERVICE_ADJ -- these are the old and decrepit
- // services that aren't as shiny and interesting as the ones in the A list.
- static final int SERVICE_B_ADJ = 8;
- // This is the process of the previous application that the user was in.
- // This process is kept above other things, because it is very common to
- // switch back to the previous app. This is important both for recent
- // task switch (toggling between the two top recent apps) as well as normal
- // UI flow such as clicking on a URI in the e-mail app to view in the browser,
- // and then pressing back to return to e-mail.
- static final int PREVIOUS_APP_ADJ = 7;
- // This is a process holding the home application -- we want to try
- // avoiding killing it, even if it would normally be in the background,
- // because the user interacts with it so much.
- static final int HOME_APP_ADJ = 6;
- // This is a process holding an application service -- killing it will not
- // have much of an impact as far as the user is concerned.
- static final int SERVICE_ADJ = 5;
- // This is a process with a heavy-weight application. It is in the
- // background, but we want to try to avoid killing it. Value set in
- // system/rootdir/init.rc on startup.
- static final int HEAVY_WEIGHT_APP_ADJ = 4;
- // This is a process currently hosting a backup operation. Killing it
- // is not entirely fatal but is generally a bad idea.
- static final int BACKUP_APP_ADJ = 3;
- // This is a process only hosting components that are perceptible to the
- // user, and we really want to avoid killing them, but they are not
- // immediately visible. An example is background music playback.
- static final int PERCEPTIBLE_APP_ADJ = 2;
- // This is a process only hosting activities that are visible to the
- // user, so we'd prefer they don't disappear.
- static final int VISIBLE_APP_ADJ = 1;
- // This is the process running the current foreground app. We'd really
- // rather not kill it!
- static final int FOREGROUND_APP_ADJ = 0;
- // This is a process that the system or a persistent process has bound to,
- // and indicated it is important.
- static final int PERSISTENT_SERVICE_ADJ = -11;
- // This is a system persistent process, such as telephony. Definitely
- // don't want to kill it, but doing so is not completely fatal.
- static final int PERSISTENT_PROC_ADJ = -12;
- // The system process runs at the default adjustment.
- static final int SYSTEM_ADJ = -16;
- // Special code for native processes that are not being managed by the system (so
- // don't have an oom adj assigned by the system).
- static final int NATIVE_ADJ = -17;
Android Low Memory Killer
Android系統內存不足時,系統會殺掉一部分進程以釋放空間,誰生誰死的這個生死大權就是由LMK所決定的,這就是Android系統中的Low Memory Killer,其基于Linux的OOM機制,其閾值定義如下面所示的lowmemorykiller文件中,當然也可以通過系統的init.rc實現自定義。
lowmemorykiller.c
- static uint32_t lowmem_debug_level = 1;
- static int lowmem_adj[6] = {
- 0,
- 1,
- 6,
- 12,
- };
- static int lowmem_adj_size = 4;
- static int lowmem_minfree[6] = {
- 3 * 512, /* 6MB */
- 2 * 1024, /* 8MB */
- 4 * 1024, /* 16MB */
- 16 * 1024, /* 64MB */
- };
- static int lowmem_minfree_size = 4;
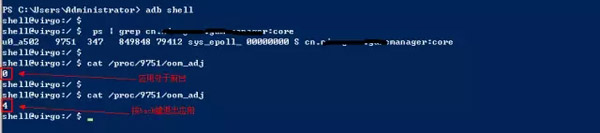
① 在Low Memory Killer中通過進程的oom_adj與占用內存的大小決定要殺死的進程,oom_adj值越小越不容易被殺死。其中,lowmem_minfree是殺進程的時機,誰被殺,則取決于lowmem_adj,具體值得含義參考上面 Android進程優先級 所述.
② 在init.rc中定義了init進程(系統進程)的oom_adj為-16,其不可能會被殺死(init的PID是1),而前臺進程是0(這里的前臺進程是指用戶正在使用的Activity所在的進程),用戶按Home鍵回到桌面時的優先級是6,普通的Service的進程是8.
init.rc
- # Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
- write /proc/1/oom_adj -16
關于Low Memory Killer的具體實現原理可參考Ref-2.
查看某個App的進程
步驟(手機與PC連接)
- adb shell
- ps | grep 進程名
- cat /proc/pid/oom_adj //其中pid是上述grep得到的進程號
Linux AM命令
am命令:在Android系統中通過adb shell 啟動某個Activity、Service、撥打電話、啟動瀏覽器等操作Android的命令.其源碼在Am.java中,在shell環境下執行am命令實際是啟動一個線程執行Am.java中的主函數(main方法),am命令后跟的參數都會當做運行時參數傳遞到主函數中,主要實現在Am.java的run方法中。
撥打電話
命令:am start -a android.intent.action.CALL -d tel:電話號碼
示例:am start -a android.intent.action.CALL -d tel:10086
打開一個網頁
命令:am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d 網址
示例:am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d http://www.skyseraph.com
啟動一個服務
命令:am startservice <服務名稱>
示例:am startservice -n com.android.music/ com.android.music.MediaPlaybackService
NotificationListenerService
“A service that receives calls from the system when new notifications are posted or removed, or their ranking changed.” From Google
用來監聽到通知的發送以及移除和排名位置變化,如果我們注冊了這個服務,當系統任何一條通知到來或者被移除掉,我們都能通過這個service來監聽到,甚至可以做一些管理工作。
Android賬號和同步機制
屬于Android中較偏冷的知識,具體參考 Ref 3 /4 /5
Android多進程
- 實現:android:process
- 好處:一個獨立的進程可以充分利用自己的RAM預算,使其主進程擁有更多的空間處理資源。此外,操作系統對待運行在不同組件中的進程是不一樣的。這意味著,當系統運行在低可用內存的條件時,并不是所有的進程都會被殺死
- 大坑:每一個進程將有自己的Dalvik VM實例,意味著你不能通過這些實例共享數據,至少不是傳統意義上的。例如,靜態字段在每個進程都有自己的值,而不是你傾向于相信的只有一個值。
- 更多詳細請參考Ref 9
現有方法
網絡連接保活方法
A. GCM
B. 公共的第三方push通道(信鴿等)
C. 自身跟服務器通過輪詢,或者長連接
具體實現請參考 微信架構師楊干榮的”微信Android客戶端后臺保活經驗分享” (Ref-1).
雙service(通知欄) 提高進程優先級
思路:(API level > 18 )
- 應用啟動時啟動一個假的Service(FakeService), startForeground(),傳一個空的Notification
- 啟動真正的Service(AlwaysLiveService),startForeground(),注意必須相同Notification ID
- FakeService stopForeground()
效果:通過adb查看,運行在后臺的服務其進程號變成了1(優先級僅次于前臺進程)
風險:Android系統前臺service的一個漏洞,可能在6.0以上系統中修復
實現:核心代碼如下
- AlwaysLiveService 常駐內存服務
- @Override
- public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
- startForeground(R.id.notify, new Notification());
- startService(new Intent(this, FakeService.class));
- return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
- }
- FakeService 臨時服務
- public class FakeService extends Service {
- @Nullable
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
- startForeground(R.id.notify, new Notification());
- stopSelf();
- return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
- }
- @Override
- public void onDestroy() {
- stopForeground(true);
- super.onDestroy();
- }
- }
Service及時拉起
AlarmReceiver, ConnectReceiver,BootReceiver等
- Service設置(見上面基礎部分)
- 通過監聽系統廣播,如開機,鎖屏,亮屏等重新啟動服務
- 通過alarm定時器,啟動服務
守護進程/進程互拉
在分析360手機助手app時,發現其擁有N多個進程,一個進程kill后會被其它未kill的進程拉起,這也是一種思路吧,雖然有點流氓~
守護進程一般有這樣兩種方式:
- 多個java進程守護互拉
- 底層C守護進程拉起App上層/java進程
Linux Am命令開啟后臺進程
一種底層實現讓進程不被殺死的方法,在Android4.4以上可能有兼容性問題,具體參考Ref-7
NotificationListenerService通知
一種需要用戶允許特定權限的系統拉起方式,4.3以上系統
前臺浮窗
有朋友提出一種應用退出后啟動一個不可交互的浮窗,個人覺得這種方法是無效的,讀者有興趣可以一試
新方法(AccountSync)
思路
利用Android系統提供的賬號和同步機制實現
效果
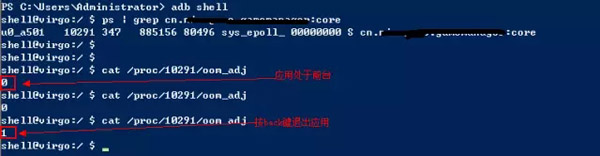
- 通過adb查看,運行在后臺的服務其進程號變成了1(優先級僅次于前臺進程),能提高進程優先級,對比如下圖
正常情況
采用AccountSyncAdapter方法后
- 進程被系統kill后,可以由syn拉起
風險
- SyncAdapter時間進度不高,往往會因為手機處于休眠狀態,而時間往后調整,同步間隔最低為1分鐘
- 用戶可以單獨停止或者刪除,有些手機賬號默認是不同步的,需要手動開啟
實現 (核心代碼)
1 建立數據同步系統(ContentProvider)
通過一個ContentProvider用來作數據同步,由于并沒有實際數據同步,所以此處就直接建立一個空的ContentProvider即可
- public class XXAccountProvider extends ContentProvider {
- public static final String AUTHORITY = "包名.provider";
- public static final String CONTENT_URI_BASE = "content://" + AUTHORITY;
- public static final String TABLE_NAME = "data";
- public static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(CONTENT_URI_BASE + "/" + TABLE_NAME);
- @Override
- public boolean onCreate() {
- return true;
- }
- @Nullable
- @Override
- public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection,
- String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
- return null;
- }
- @Nullable
- @Override
- public String getType(Uri uri) {
- return new String();
- }
- @Nullable
- @Override
- public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
- return 0;
- }
- @Override
- public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
- return 0;
- }
- }
然后再Manifest中聲明
- <provider
- android:name="**.XXAccountProvider"
- android:authorities="@string/account_auth_provider"
- android:exported="false"
- android:syncable="true"/>
2 建立Sync系統 (SyncAdapter)
通過實現SyncAdapter這個系統服務后, 利用系統的定時器對程序數據ContentProvider進行更新,具體步驟為:
- 創建Sync服務
- public class XXSyncService extends Service {
- private static final Object sSyncAdapterLock = new Object();
- private static XXSyncAdapter sSyncAdapter = null;
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- synchronized (sSyncAdapterLock) {
- if (sSyncAdapter == null) {
- sSyncAdapter = new XXSyncAdapter(getApplicationContext(), true);
- }
- }
- }
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
- return sSyncAdapter.getSyncAdapterBinder();
- }
- static class XXSyncAdapter extends AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter {
- public XXSyncAdapter(Context context, boolean autoInitialize) {
- super(context, autoInitialize);
- }
- @Override
- public void onPerformSync(Account account, Bundle extras, String authority, ContentProviderClient provider, SyncResult syncResult) {
- getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(XXAccountProvider.CONTENT_URI, null, false);
- }
- }
- }
- 聲明Sync服務
- <service
- android:name="**.XXSyncService"
- android:exported="true"
- android:process=":core">
- <intent-filter>
- <action
- android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter"/>
- </intent-filter>
- <meta-data
- android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter"
- android:resource="@xml/sync_adapter"/>
- </service>
其中sync_adapter為:
- <sync-adapter xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:accountType="@string/account_auth_type"
- android:allowParallelSyncs="false"
- android:contentAuthority="@string/account_auth_provide"
- android:isAlwaysSyncable="true"
- android:supportsUploading="false"
- android:userVisible="true"/>
參數說明:
android:contentAuthority 指定要同步的ContentProvider在其AndroidManifest.xml文件中有個android:authorities屬性。
android:accountType 表示進行同步的賬號的類型。
android:userVisible 設置是否在“設置”中顯示
android:supportsUploading 設置是否必須notifyChange通知才能同步
android:allowParallelSyncs 是否支持多賬號同時同步
android:isAlwaysSyncable 設置所有賬號的isSyncable為1
android:syncAdapterSettingsAction 指定一個可以設置同步的activity的Action。
- 賬戶調用Sync服務
首先配置好Account(第三步),然后再通過ContentProvider實現
手動更新
- public void triggerRefresh() {
- Bundle b = new Bundle();
- b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_MANUAL, true);
- b.putBoolean(ContentResolver.SYNC_EXTRAS_EXPEDITED, true);
- ContentResolver.requestSync(
- account,
- CONTENT_AUTHORITY,
- b);
- }
添加賬號
- Account account = AccountService.GetAccount();
- AccountManager accountManager = (AccountManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE);
- accountManager.addAccountExplicitly(...)
同步周期設置
- ContentResolver.setIsSyncable(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, 1);
- ContentResolver.setSyncAutomatically(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, true);
- ContentResolver.addPeriodicSync(account, CONTENT_AUTHORITY, new Bundle(), SYNC_FREQUENCY);
3 建立賬號系統 (Account Authenticator)
通過建立Account賬號,并關聯SyncAdapter服務實現同步
接下文