硬核!如何在容器中做時間漫游者
本文轉載自微信公眾號「董澤潤的技術筆記」,作者董澤潤。轉載本文請聯系董澤潤的技術筆記公眾號。
題目稍有些標題黨,最近公司想用 chaos-mesh 對 k8s 做混沌測試,開始做前期的調研,發現 pingcap[1] 對時間的注入非常硬核,而且最終方案居然是實習生構思出來的 ^^ 感謝 pingcap 貢獻的項目
TL;DR: 通過劫持 vdso, 將時間函數跳轉到 hack 過的匯編指令來實現 time skew. 原理不難懂,但細節超多,參考官方文檔[2]
為什么需要 time skew
可以參考 Chaos Mesh - 讓時間在容器中自由搖擺[3], 簡單來說就是:
分布式數據庫要實現全局一致性快照,很多方案使用時間做邏輯時鐘,所以需要解決不同節點之間時鐘一致的問題。但往往物理節點上的物理時間總是會出現偏差,不管是使用 NPT 服務同步也好,或者其他方法總是沒辦法完全避免出現誤差,這時候如果我們的應用不能夠很好的處理這樣的情況的話,就可能造成無法預知的錯誤。
其實這很符合工程設計哲學:design for failure, 任何一個硬件或是軟件都會有錯誤(fault),系統如何在不影響對外提供服務的前提下,如何處理這些故障,就是我們常說的 fault tolerance
但是對于非金融業務來說,時間偏移一點影響并不大,相比其它 chaos, time的場景還是受限一些
如何注入
從實體機的經驗來看,所謂的混沌測試都比較直觀的,比如用 tc 做網絡的丟包,限速來模擬網絡故障,使用 stress 模擬 cpu 壓力。但是在容器中做如何模擬 time skew 呢?
如果直接使用 linux date 命令修改,會影響到宿主機上其它所有容器。有沒有方法能只影響某個容器?
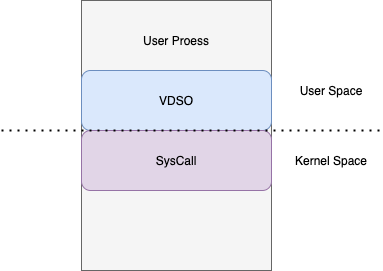
之前發過一篇文章 時鐘源為什么會影響性能[4], 從中可以看到,go 調用系統時間函數時,會先調用 vdso 的代碼,如果時鐘源符合條件,直接在用戶空間完成,并不會進入內核空間,所以針對這一現象,syscall 劫持的方法就不能使用了
那么是否可以直接修改 vdso 段代碼呢?
查看 vdso
- # cat /proc/1970/maps
- ......
- 7ffe8478a000-7ffe847ab000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack]
- 7ffe847bb000-7ffe847be000 r--p 00000000 00:00 0 [vvar]
- 7ffe847be000-7ffe847bf000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso]
- ffffffffff600000-ffffffffff601000 --xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vsyscall]
可以看到 vdso 代碼段的起始邏輯地址,同時注意權限位是 r-xp, 這就意味著用戶態的進程是無法直接修改該內容。
真的就沒辦法了嘛?有的,ptrace[5] 法力無邊
The ptrace() system call provides a means by which one process (the "tracer") may observe and control the execution of another process (the "tracee"), and examine and change the tracee's memory and registers. It is primarily used to implement breakpoint debugging and system call tracing.
ptrace 提供了一種修改和觀察其它進程的手段,包括修改內存值和寄存器,巧了這些 chaos-mesh 都用到了。如何實現 go 調試器[6] 這篇文章也講了 ptrace 的用途,很棒的文章。
整體實現
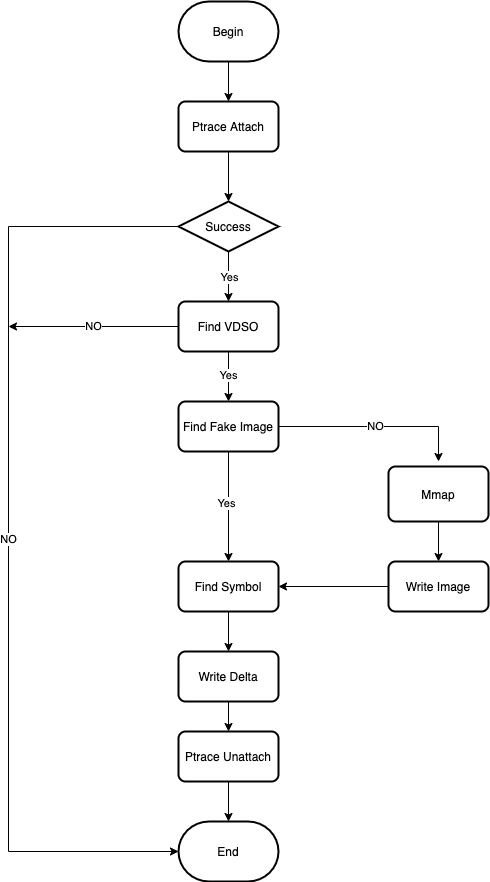
這就是簡單的流程圖,主要代碼都是 time_linux_amd64.go[7], 當前僅支持 linux amd64 平臺,不支持 Windows/MacOS
- // ModifyTime modifies time of target process
- func ModifyTime(pid int, deltaSec int64, deltaNsec int64, clockIdsMask uint64) error {
- ......
- runtime.LockOSThread() // 將當前 goroutine 綁定底層線程
- defer func() {
- runtime.UnlockOSThread()
- }()
- program, err := ptrace.Trace(pid) // ptrace 獲得 program
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- defer func() {
- err = program.Detach()
- if err != nil {
- log.Error(err, "fail to detach program", "pid", program.Pid())
- }
- }()
- var vdsoEntry *mapreader.Entry // 遍歷 entry 找到 vdso
- for index := range program.Entries {
- // reverse loop is faster
- e := program.Entries[len(program.Entries)-index-1]
- if e.Path == "[vdso]" {
- vdsoEntry = &e
- break
- }
- }
- if vdsoEntry == nil {
- return errors.New("cannot find [vdso] entry")
- }
- // minus tailing variable part
- // 24 = 3 * 8 because we have three variables
- constImageLen := len(fakeImage) - 24
- var fakeEntry *mapreader.Entry
- // find injected image to avoid redundant inject (which will lead to memory leak)
- for _, e := range program.Entries {
- e := e
- image, err := program.ReadSlice(e.StartAddress, uint64(constImageLen))
- if err != nil {
- continue
- }
- if bytes.Equal(*image, fakeImage[0:constImageLen]) {
- fakeEntry = &e // 遍歷找到 fake Image Entry,不能重復生成
- log.Info("found injected image", "addr", fakeEntry.StartAddress)
- break
- }
- }
- if fakeEntry == nil { // 如果 fakeEntry 不存在,用 Mmap 分配內存,內容是 fakeImage 匯編指令
- fakeEntry, err = program.MmapSlice(fakeImage)
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- }
- fakeAddr := fakeEntry.StartAddress
- // 139 is the index of CLOCK_IDS_MASK in fakeImage 寫 clockidsmask
- err = program.WriteUint64ToAddr(fakeAddr+139, clockIdsMask)
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- // 147 is the index of TV_SEC_DELTA in fakeImage 寫偏移量秒
- err = program.WriteUint64ToAddr(fakeAddr+147, uint64(deltaSec))
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- // 155 is the index of TV_NSEC_DELTA in fakeImage 寫偏移量納秒
- err = program.WriteUint64ToAddr(fakeAddr+155, uint64(deltaNsec))
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- // 找到 clock_gettime 在 vdso 中的位置
- originAddr, err := program.FindSymbolInEntry("clock_gettime", vdsoEntry)
- if err != nil {
- return err
- }
- // originAddr 位置 hijack, 寫上 jump 指令,跳轉到 fakeImage
- err = program.JumpToFakeFunc(originAddr, fakeAddr)
- return err
- }
代碼寫上了注釋,分別對應上面的流程圖。下面分解來看。
1. Ptrace
- type TracedProgram struct {
- pid int
- tids []int
- Entries []mapreader.Entry
- backupRegs *syscall.PtraceRegs
- backupCode []byte
- }
TracedProgram 結構體比較簡單,pid 是待注入 chaos 的進程 id, 同時 tids 保存所有的線程 id, Entries 是進程邏輯地址空間,
Trace 函數在代碼 ptrace_linux_amd64.go[8] 中
通過讀取 /proc/{pid}/task 獲取進程的所有線程,然后分別對所有線程執行 linux ptrace 調用。然后生成 Entries, 什么是 Entry 呢?就是上文提到的 /proc/{pid}/maps 內容
- ......
- 7ffe8478a000-7ffe847ab000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 [stack]
- 7ffe847bb000-7ffe847be000 r--p 00000000 00:00 0 [vvar]
- 7ffe847be000-7ffe847bf000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso]
- ffffffffff600000-ffffffffff601000 --xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vsyscall]
2. Mmap FakeImage
查找 vdso[9], 如何失敗,直接退出。一般 vdso 都在最后,所以從尾開始遍歷
同時還要查找 fakeEntry, 如果存在,直接復用。否則會造成內存泄漏,當然了,一直創建新的 fakeEntry .....
- // MmapSlice mmaps a slice and return it's addr
- func (p *TracedProgram) MmapSlice(slice []byte) (*mapreader.Entry, error) {
- size := uint64(len(slice))
- addr, err := p.Mmap(size, 0)
- if err != nil {
- return nil, errors.WithStack(err)
- }
- err = p.WriteSlice(addr, slice)
- if err != nil {
- return nil, errors.WithStack(err)
- }
- return &mapreader.Entry{
- StartAddress: addr,
- EndAddress: addr + size,
- Privilege: "rwxp",
- PaddingSize: 0,
- Path: "",
- }, nil
- }
注意,這不是簡單的調用 Mmap Syscall !!! ptrace.Syscall[12] 是利用 ptrace 控制進程,讓目標進程單步執行 syscall
- // Syscall runs a syscall at main thread of process
- func (p *TracedProgram) Syscall(number uint64, args ...uint64) (uint64, error) {
- err := p.Protect() // 保存目標進程的寄存器
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- var regs syscall.PtraceRegs
- err = syscall.PtraceGetRegs(p.pid, ®s)
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- regs.Rax = number // 設置操作 syscall number, 填充其它參數
- for index, arg := range args {
- // All these registers are hard coded for x86 platform
- if index == 0 {
- regs.Rdi = arg
- } else if index == 1 {
- regs.Rsi = arg
- } else if index == 2 {
- regs.Rdx = arg
- } else if index == 3 {
- regs.R10 = arg
- } else if index == 4 {
- regs.R8 = arg
- } else if index == 5 {
- regs.R9 = arg
- } else {
- return 0, fmt.Errorf("too many arguments for a syscall")
- }
- }
- err = syscall.PtraceSetRegs(p.pid, ®s)
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- ip := make([]byte, ptrSize)
- // We only support x86-64 platform now, so using hard coded `LittleEndian` here is ok. 設置 rip 寄存器
- binary.LittleEndian.PutUint16(ip, 0x050f)
- _, err = syscall.PtracePokeData(p.pid, uintptr(p.backupRegs.Rip), ip)
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- err = p.Step() // 單步執行
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- err = syscall.PtraceGetRegs(p.pid, ®s)
- if err != nil {
- return 0, err
- }
- return regs.Rax, p.Restore() // 獲取返回值,并且恢復寄存器
- }
參考代碼的注釋,搞過嵌入式的肯定熟悉:保存寄存器現場,設置新的寄存器值為 syscall number 以及參數,最后設置指令寄存器 rip 單步執行,就完成了讓目標進程執行 mmap 的操作,最后也要恢復寄存器,還原現場。
這里為什么 rip 寄存器要設置成 0x050f 呢???其實這是 syscall 的操作碼
另外 p.WriteSlice 是使用 syscall process_vm_writev 將數據寫入目標進程的內存邏輯地址空間。
3. FindSymbolInEntry
- ~# file /tmp/vdso.so
- /tmp/vdso.so: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, BuildID[sha1]=17d65245b85cd032de7ab130d053551fb0bd284a, stripped
- ~# objdump -T /tmp/vdso.so
- /tmp/vdso.so: file format elf64-x86-64
- DYNAMIC SYMBOL TABLE:
- 0000000000000950 w DF .text 00000000000000a1 LINUX_2.6 clock_gettime
- 00000000000008a0 g DF .text 0000000000000083 LINUX_2.6 __vdso_gettimeofday
- 0000000000000a00 w DF .text 000000000000000a LINUX_2.6 clock_getres
- 0000000000000a00 g DF .text 000000000000000a LINUX_2.6 __vdso_clock_getres
- 00000000000008a0 w DF .text 0000000000000083 LINUX_2.6 gettimeofday
- 0000000000000930 g DF .text 0000000000000015 LINUX_2.6 __vdso_time
- 0000000000000930 w DF .text 0000000000000015 LINUX_2.6 time
- 0000000000000950 g DF .text 00000000000000a1 LINUX_2.6 __vdso_clock_gettime
- 0000000000000000 g DO *ABS* 0000000000000000 LINUX_2.6 LINUX_2.6
- 0000000000000a10 g DF .text 000000000000002a LINUX_2.6 __vdso_getcpu
- 0000000000000a10 w DF .text 000000000000002a LINUX_2.6 getcpu
FindSymbolInEntry 函數很簡單,就是要找到 clock_gettime 在 vdso 中的地址,參考我之前的文章,上面是 dump 出來的符號表
4. JumpToFakeFunc
- // JumpToFakeFunc writes jmp instruction to jump to fake function
- func (p *TracedProgram) JumpToFakeFunc(originAddr uint64, targetAddr uint64) error {
- instructions := make([]byte, 16)
- // mov rax, targetAddr;
- // jmp rax ;
- instructions[0] = 0x48
- instructions[1] = 0xb8
- binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(instructions[2:10], targetAddr)
- instructions[10] = 0xff
- instructions[11] = 0xe0
- return p.PtraceWriteSlice(originAddr, instructions)
- }
JumpToFakeFunc[13], 修改 vdso 符號表中的匯編代碼,使所有調用 clock_gettime 的都跳轉到我們 fakeEntry 的地址,劫持 vdso
FakeImage
- var fakeImage = []byte{
- 0xb8, 0xe4, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //mov $0xe4,%eax
- 0x0f, 0x05, //syscall
- 0xba, 0x01, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //mov $0x1,%edx
- 0x89, 0xf9, //mov %edi,%ecx
- 0xd3, 0xe2, //shl %cl,%edx
- 0x48, 0x8d, 0x0d, 0x74, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //lea 0x74(%rip),%rcx # <CLOCK_IDS_MASK>
- 0x48, 0x63, 0xd2, //movslq %edx,%rdx
- 0x48, 0x85, 0x11, //test %rdx,(%rcx)
- 0x74, 0x6b, //je 108a <clock_gettime+0x8a>
- 0x48, 0x8d, 0x15, 0x6d, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //lea 0x6d(%rip),%rdx # <TV_SEC_DELTA>
- 0x4c, 0x8b, 0x46, 0x08, //mov 0x8(%rsi),%r8
- 0x48, 0x8b, 0x0a, //mov (%rdx),%rcx
- 0x48, 0x8d, 0x15, 0x67, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //lea 0x67(%rip),%rdx # <TV_NSEC_DELTA>
- 0x48, 0x8b, 0x3a, //mov (%rdx),%rdi
- 0x4a, 0x8d, 0x14, 0x07, //lea (%rdi,%r8,1),%rdx
- 0x48, 0x81, 0xfa, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, 0x3b, //cmp $0x3b9aca00,%rdx
- 0x7e, 0x1c, //jle <clock_gettime+0x60>
- 0x0f, 0x1f, 0x40, 0x00, //nopl 0x0(%rax)
- 0x48, 0x81, 0xef, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, 0x3b, //sub $0x3b9aca00,%rdi
- 0x48, 0x83, 0xc1, 0x01, //add $0x1,%rcx
- 0x49, 0x8d, 0x14, 0x38, //lea (%r8,%rdi,1),%rdx
- 0x48, 0x81, 0xfa, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, 0x3b, //cmp $0x3b9aca00,%rdx
- 0x7f, 0xe8, //jg <clock_gettime+0x48>
- 0x48, 0x85, 0xd2, //test %rdx,%rdx
- 0x79, 0x1e, //jns <clock_gettime+0x83>
- 0x4a, 0x8d, 0xbc, 0x07, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, //lea 0x3b9aca00(%rdi,%r8,1),%rdi
- 0x3b, //
- 0x0f, 0x1f, 0x00, //nopl (%rax)
- 0x48, 0x89, 0xfa, //mov %rdi,%rdx
- 0x48, 0x83, 0xe9, 0x01, //sub $0x1,%rcx
- 0x48, 0x81, 0xc7, 0x00, 0xca, 0x9a, 0x3b, //add $0x3b9aca00,%rdi
- 0x48, 0x85, 0xd2, //test %rdx,%rdx
- 0x78, 0xed, //js <clock_gettime+0x70>
- 0x48, 0x01, 0x0e, //add %rcx,(%rsi)
- 0x48, 0x89, 0x56, 0x08, //mov %rdx,0x8(%rsi)
- 0xc3, //retq
- // constant
- 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //CLOCK_IDS_MASK
- 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //TV_SEC_DELTA
- 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //TV_NSEC_DELTA
- }
fakeImage 最后三個參數是偏移量,以及傳遞的 CLOCK_IDS_MASK, 這些匯編是什么意思呢???
查看匯編操作碼[14],0xe4 是系統調用 clock_gettime 的操作碼,后續都是對結果進行注入,要么增要么減,制造偏移量 time skew
測試案例
- # git clone https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh
- # cd chaos-mesh; make watchmaker
首先下載 chaos-mesh, 然后編譯 watchmaker, 這是一個方便注入的小工具。
- package main
- import (
- "fmt"
- "time"
- )
- func main() {
- fmt.Println("start print time")
- for {
- fmt.Printf("now %v\n", time.Now())
- time.Sleep(time.Second * 20)
- }
- }
上面是測試的代碼,每隔 20 打印當前時間,編譯執行,同時用 watchmaker 注入 time skew
- # ./watchmaker -pid 1970 -sec_delta -300
隔一段時間間后,再次執行停止執行注入
- # ./watchmaker -pid 1970 -sec_delta 0
- # ./test
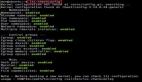
- start print time
- now 2021-05-26 03:31:46.701902309 +0000 UTC m=+0.000131483
- now 2021-05-26 03:32:06.702230391 +0000 UTC m=+20.000459585
- now 2021-05-26 03:32:26.702406569 +0000 UTC m=+40.000635793
- now 2021-05-26 03:27:46.702688433 +0000 UTC m=+60.000918297
- ^@now 2021-05-26 03:28:06.702914898 +0000 UTC m=+80.001145022
- now 2021-05-26 03:28:26.703120914 +0000 UTC m=+100.001350878
- now 2021-05-26 03:28:46.703398463 +0000 UTC m=+120.001628357
- ^@now 2021-05-26 03:29:06.703707514 +0000 UTC m=+140.001937468
- now 2021-05-26 03:29:26.704025346 +0000 UTC m=+160.002255480
- now 2021-05-26 03:29:46.704302832 +0000 UTC m=+180.002532766
- ^@now 2021-05-26 03:35:06.704505387 +0000 UTC m=+200.002735491
- now 2021-05-26 03:35:26.704931111 +0000 UTC m=+220.003161235
上面是代碼執行的輸出,可以看到 03:32:26 之后時間變成了 03:27:46, 停止注入后恢復
Limits
當前的實現,停止注入,并不會還原 vdso 代碼,也就是說 fakeEntry 會一直存在,每次 clock_gettime 都會跳轉,只不過偏移量為 0 而己
由于以上原因的存在,注入及注入之后的 clock_gettime 都是走的 syscall 系統調用,性能很慢,敏感業務需要重啟,細節可以參考我之前的文章《時鐘源為什么會影響性能》
當前注入,只能針對容器里的主進程,那些 fork 出來,派生出來的無做做到注入
以上限制有沒有優化空間呢?當然有,問題都是用來解決的嘛~
小結
這次分享就這些,以后面還會分享更多的內容,如果感興趣,可以關注并點擊左下角的分享轉發哦(:
參考資料
[1]Chaos Mesh - 讓時間在容器中自由搖擺: https://www.jianshu.com/p/6425050591b7,
[2]官方文檔: https://chaos-mesh.org/docs/chaos_experiments/timechaos_experiment/#limitation,
[3]讓時間在容器中自由搖擺: https://www.jianshu.com/p/6425050591b7,
[4]時鐘源為什么會影響性能: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/06SDQLzDprJf2AEaDnX-QQ,
[5]ptrace: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/ptrace.2.html,
[6]如何實現 go 調試器: https://studygolang.com/articles/12804,
[7]time_linux_amd64.go: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/time/time_linux_amd64.go#L72,
[8]ptrace_linux_amd64.go: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/ptrace/ptrace_linux_amd64.go#L87,
[9]time_linux_amd64.go#L102 vdso: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/time/time_linux_amd64.go#L102,
[10]program.MmapSlice: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/time/time_linux_amd64.go#L132,
[11]FakeImage: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/time/time_linux_amd64.go#L28,
[12]ptrace.Syscall: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/ptrace/ptrace_linux_amd64.go#L251,
[13]JumpToFakeFunc: https://github.com/chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh/blob/master/pkg/ptrace/ptrace_linux_amd64.go#L480,
[14]匯編操作碼: https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromiumos/docs/+/master/constants/syscalls.md,