一口氣, 了解 Qt 的所有 IPC 方式
本文轉載自微信公眾號「老吳的嵌入式之旅」,作者吳偉東Jack。轉載本文請聯系老吳的嵌入式之旅公眾號。
大家好,我是老吳。
今天整理一下 Qt 里幾個重要的 IPC 方式。
Internet Socket
Qt 里的 Qt Network 模塊,提供了一些類,讓網絡編程變得更容易,且支持跨平臺。
具體地,有偏上層的 QNetworkAccessManager、QNetworkRequest、QNetworkReply。
以及偏底層的 QTcpSocket、QTcpServer、QUdpSocket。
示例
https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtnetwork-downloadmanager-example.html
這個例子演示了如何使用 QNetworkAccessManager 實現一個命令行下載工具,類似 wget 命令。
運行效果:
- $ ./downloadmanager https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
- Downloading https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb...
- [##################################################] 100% 21.1 MB/s
- Succeeded.
- 1/1 files downloaded successfully
支持進度顯示、多文件排隊下載。
代碼分析
- // send request
- void DownloadManager::startNextDownload()
- {
- QNetworkRequest request(url);
- // manager is QNetworkAccessManager,
- // currentDownload is QNetworkReply
- currentDownload = manager.get(request);
- connect(currentDownload, SIGNAL(readyRead()),
- SLOT(downloadReadyRead()));
- }
- // download data
- void DownloadManager::downloadReadyRead()
- {
- // output is QFile
- output.write(currentDownload->readAll());
- }
3 個步驟:
- 發 Request,
- 拿到 Reply,
- 從 Reply 中讀寫數據。
更詳細的說明:
https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtnetwork-index.html
Local Socket
Local Socket 用于在同一臺計算機上運行的進程之間的通信,相關的類是 QLocalServer and QLocalSocket。
雖然 Internet Socket 可用于同一目的,但 Local Socket 的效率更高。
Local Socket 僅復制數據,它們并不執行協議處理,不需要添加或刪除網絡報頭,無需計算校驗和,不要產生順序號,無需發送確認報文。
另外,后續如果有需要的話,可以很容易地升級成跨主機的版本。
示例
1. fortune server
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtcore-ipc-localfortuneserver-example.html
這個例子演示如何使用 QLocalServer 實現一個隨機應答服務器。
2. fortune client
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtcore-ipc-localfortuneclient-example.html
這個例子演示如何使用 QLocalSocket 去連接 Local Socket Server。
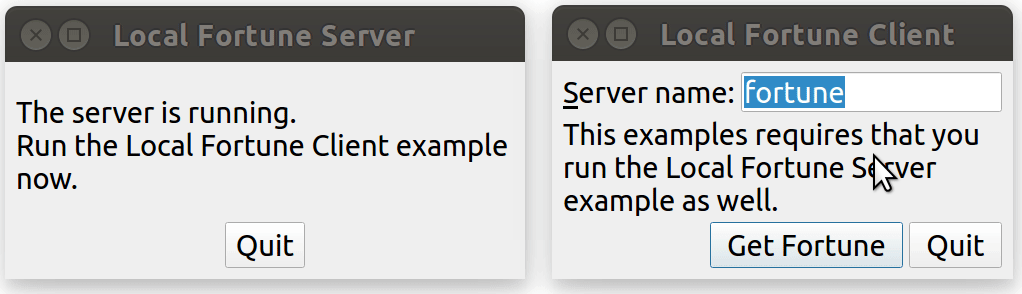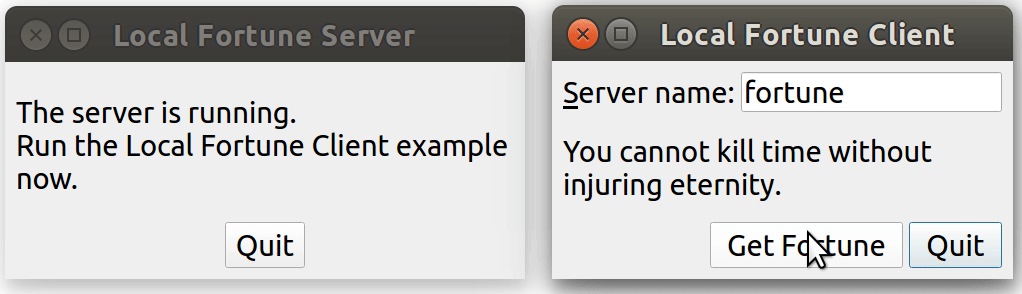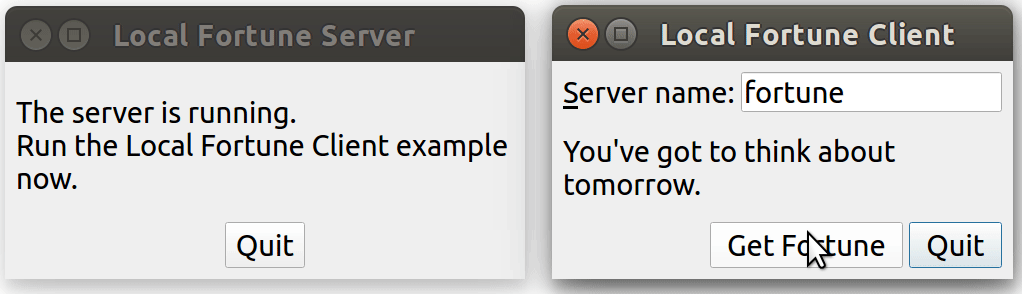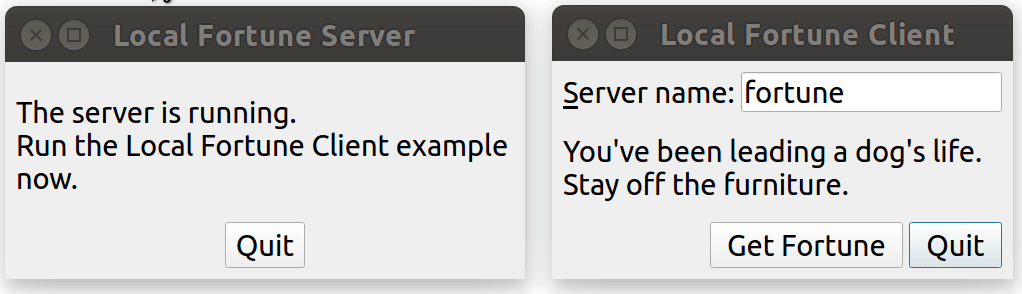
運行效果:
點擊 client 端的 "Get Forturn" 按鍵,會發起一個連接,server 端發現有新連接后,會隨機發送一句話過來。
代碼分析
Server 端:
- // create a local socket server
- Server::Server(QWidget *parent)
- : QDialog(parent)
- {
- server = new QLocalServer(this);
- server->listen("fortune")
- connect(server, &QLocalServer::newConnection, this, &Server::sendFortune);
- }
- // send data
- void Server::sendFortune()
- {
- QLocalSocket *clientConnection = server->nextPendingConnection();
- clientConnection->write(block);
- clientConnection->flush();
- clientConnection->disconnectFromServer();
- }
4 個步驟:
- new 一個 socket;
- 用 listen() 監聽;
- 用 nextPendingConnection() 獲取連接;
- 常規的 read()/write() 操作;
Client 端的代碼也很簡單,請自行查看。
Shared Memory
QSharedMemory 用于支持跨平臺的共享內存,它允許多個線程和進程安全地訪問共享內存段。
此外,QSystemSemaphore 可用于控制對系統共享資源的訪問和進程之間的通信。
示例
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qsharedmemory.html
這個例子演示進程間如何使用 QSharedMemory 以共享內存的方式進行通信。
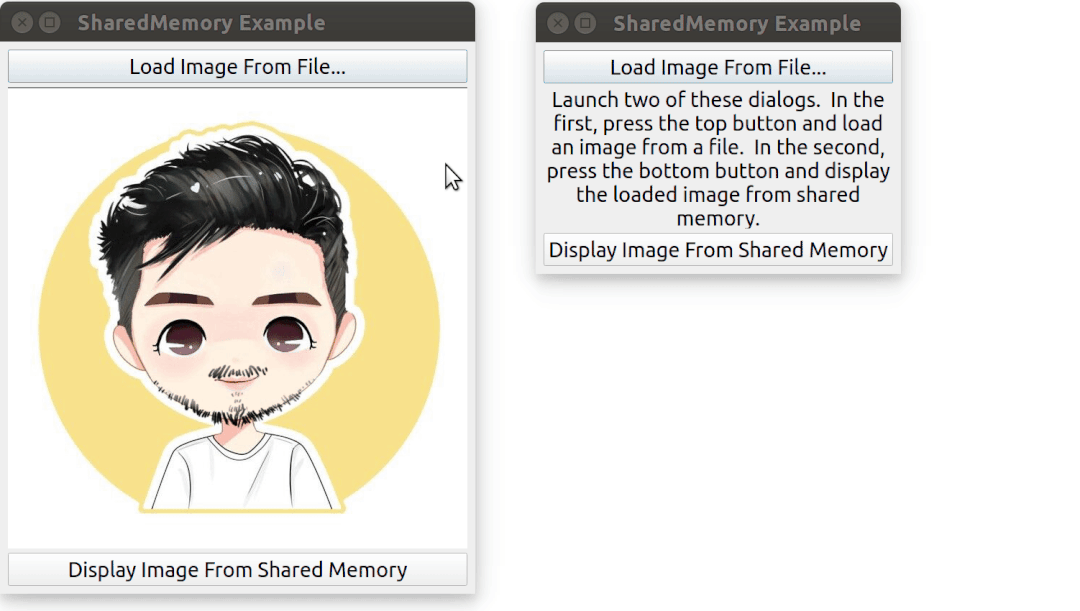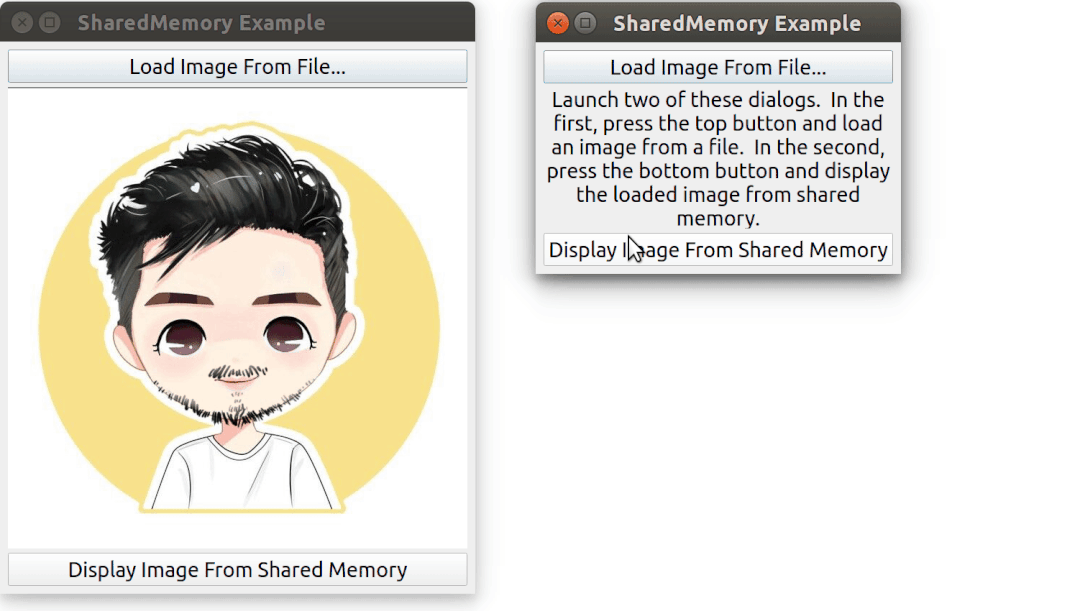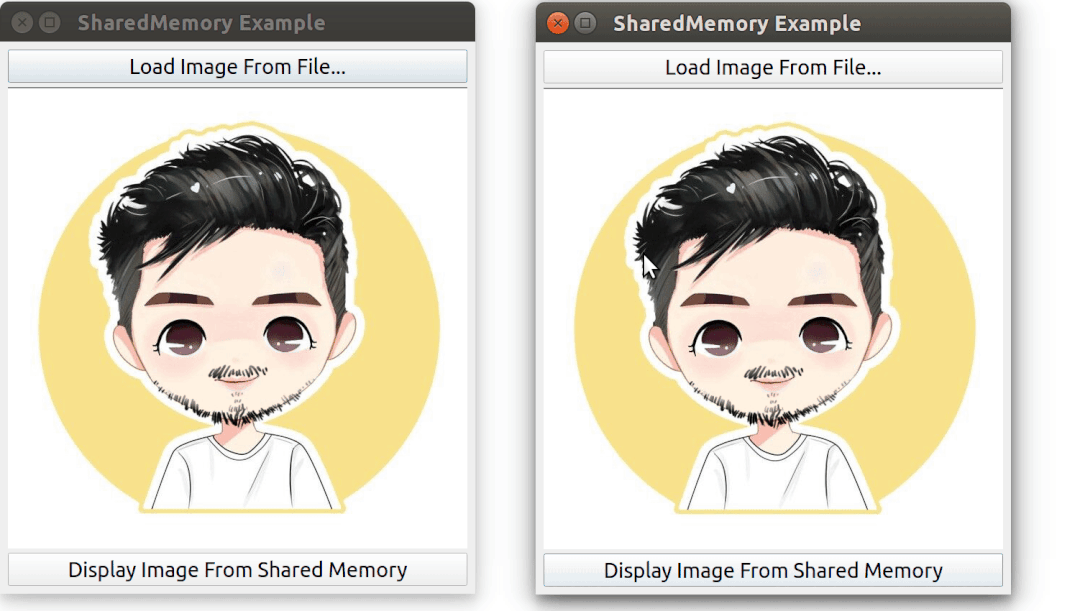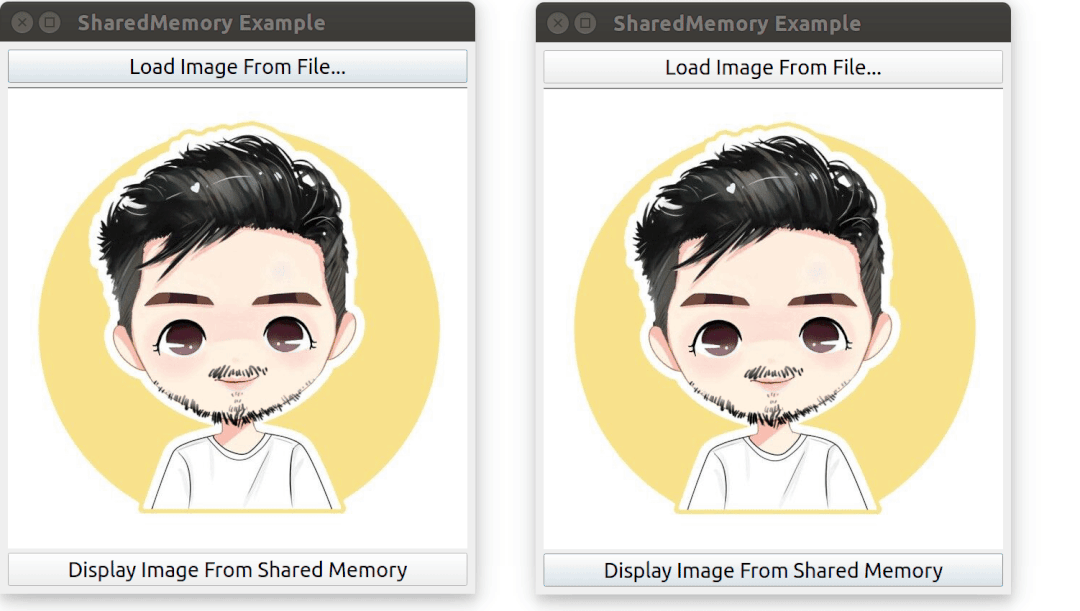
需要啟動 2 次該程序,其中一個程序先加載一張圖片,然后另外一個程序通過共享內存來訪問到同一張圖片。
運行效果:
代碼分析
創建 shared memory:
- void Dialog::loadFromFile()
- {
- [...]
- // load buffer into share memory
- // buffer is QBuffer
- sharedMemory.create(size))
- sharedMemory.lock();
- char *to = (char*)sharedMemory.data();
- const char *from = buffer.data().data();
- memcpy(to, from, qMin(sharedMemory.size(), size));
- sharedMemory.unlock();
- }
訪問 shared memory:
- void Dialog::loadFromMemory()
- {
- sharedMemory.attach();
- sharedMemory.lock();
- buffer.setData((char*)sharedMemory.constData(), sharedMemory.size());
- buffer.open(QBuffer::ReadOnly);
- in >> image;
- sharedMemory.unlock();
- sharedMemory.detach();
- ui.label->setPixmap(QPixmap::fromImage(image));
- }
接口很簡潔:
- create() 創建一塊共享內存;
- attach() 和 detach() 用于訪問;
- lock() 和 unlock() 用于同步;
D-Bus protocol
D-Bus 是一種進程間通信 (IPC) 和遠程過程調用 (RPC) 機制,最初是為 Linux 開發的,目的是用一個統一的協議替換現有的 IPC 方案。
D-Bus 實際上是基于 Unix Socket 的。它只提供了一個標準化的總線架構,允許許多進程相互通信。
Qt 提供了 Qt DBus 模塊,把信號槽機制擴展到進程級別,使得開發者可以在一個進程中發出信號,由其它進程的槽函數響應信號。
示例
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtdbus-chat-example.html
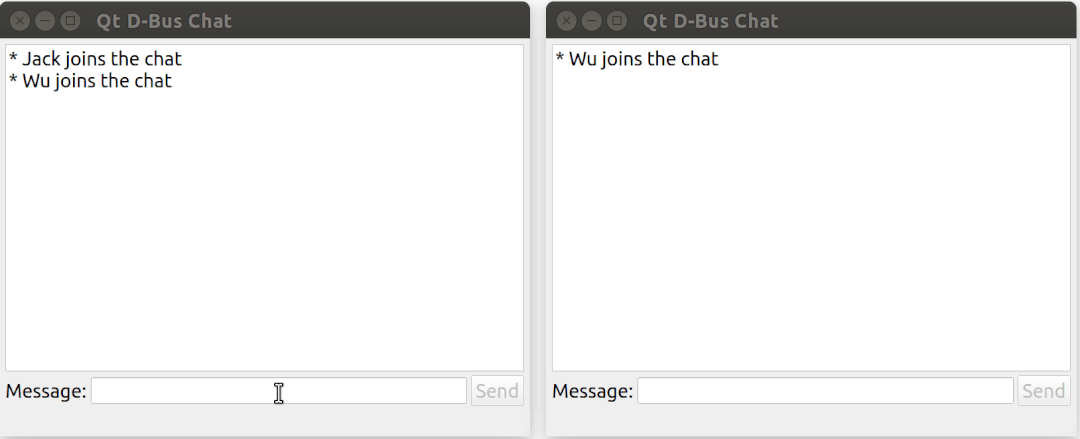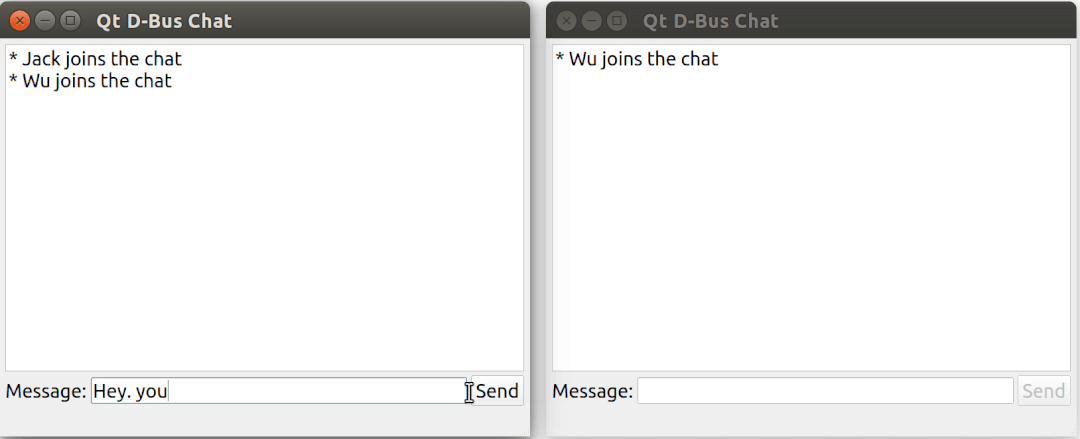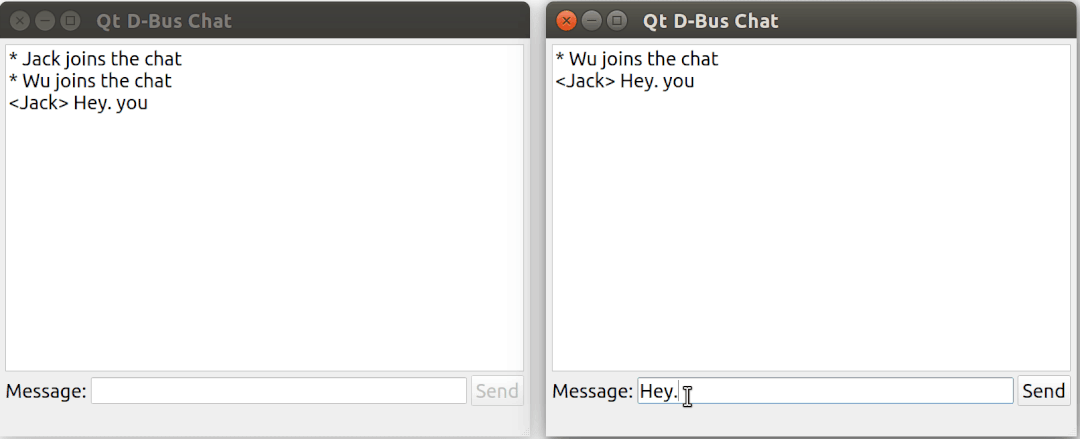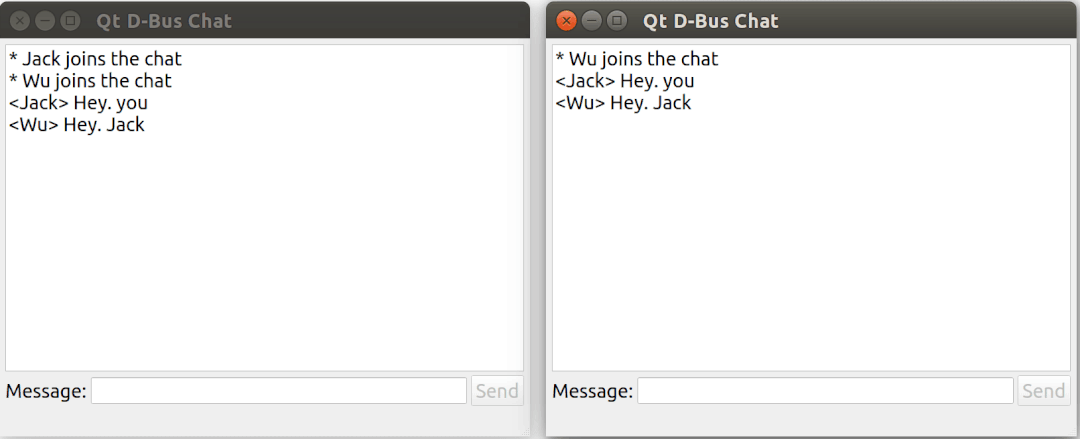
這個例子演示了如何使用 Qt DBus 實現一個基于 D-Bus 的簡易聊天室。
運行效果:
代碼分析
- ChatMainWindow::ChatMainWindow()
- : m_nickname(QLatin1String("nickname"))
- {
- [...]
- connect(sendButton, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)), this, SLOT(sendClickedSlot()));
- // add our D-Bus interface and connect to D-Bus
- new ChatAdaptor(this);
- QDBusConnection::sessionBus().registerObject("/", this);
- org::example::chat *iface;
- iface = new org::example::chat(QString(), QString(), QDBusConnection::sessionBus(), this);
- QDBusConnection::sessionBus().connect(QString(), QString(), "org.example.chat", "message", this, SLOT(messageSlot(QString,QString)));
- [...]
- }
接口感覺還是比較復雜,這里就不展開分析了。
更詳細的說明:
- https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtdbus-index.html
- https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/604258/what-is-d-bus-practically-useful-for
QProcess
QProcess 類可以用來啟動外部程序作為子進程,并與它們進行通信。
示例代碼
- QProcess gzip;
- gzip.start("gzip", QStringList() << "-c");
- if (!gzip.waitForStarted())
- return false;
- gzip.write("Qt rocks!");
- gzip.closeWriteChannel();
- if (!gzip.waitForFinished())
- return false;
- QByteArray result = gzip.readAll();
這里通過 QProcess 調用 gzip 命令來解壓文件,通訊的接口就是 read() / write()。
Qt 官方沒有提供示例,想看實例的話可以參考我之前的文章:
小伙子,要不要給你的 Linux 系統寫一個launcher
到此,Qt 里幾個重要的 IPC 機制就介紹完畢了,感謝閱讀。