聊聊 CountDownLatch 閉鎖源碼分析
本文轉(zhuǎn)載自微信公眾號(hào)「運(yùn)維開(kāi)發(fā)故事」,作者老鄭。轉(zhuǎn)載本文請(qǐng)聯(lián)系運(yùn)維開(kāi)發(fā)故事公眾號(hào)。
功能簡(jiǎn)介
閉鎖是一種同步工具類(lèi),可以延遲線(xiàn)程的進(jìn)度直到其到達(dá)終止?fàn)顟B(tài)【CPJ 3.4.2】。閉鎖的作用相當(dāng)于一扇門(mén)∶ 在閉鎖到達(dá)結(jié)束狀態(tài)之前,這扇門(mén)一直是關(guān)閉的,并且沒(méi)有任何線(xiàn)程能通過(guò),當(dāng)?shù)竭_(dá)結(jié)束狀態(tài)時(shí),這扇門(mén)會(huì)打開(kāi)并允許所有的線(xiàn)程通過(guò)。當(dāng)閉鎖到達(dá)結(jié)束狀態(tài)后,將不會(huì)再改變狀態(tài),因此這扇門(mén)將永遠(yuǎn)保持打開(kāi)狀態(tài)。閉鎖可以用來(lái)確保某些活動(dòng)直到其他活動(dòng)都完成后才繼續(xù)執(zhí)行,例如∶
- 確保某個(gè)計(jì)算在其需要的所有資源都被初始化之后才繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。二元閉鎖(包括兩個(gè)狀態(tài))可以用來(lái)表示"資源R已經(jīng)被初始化",而所有需要 R 的操作都必須先在這個(gè)閉鎖上等待。
- 確保某個(gè)服務(wù)在其依賴(lài)的所有其他服務(wù)都已經(jīng)啟動(dòng)之后才啟動(dòng)。每個(gè)服務(wù)都有一個(gè)相關(guān)的二元閉鎖。當(dāng)啟動(dòng)服務(wù)S 時(shí),將首先在S依賴(lài)的其他服務(wù)的閉鎖上等待,在所有依賴(lài)的服務(wù)都啟動(dòng)后會(huì)釋放閉鎖S,這樣其他依賴(lài) S 的服務(wù)才能繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。
- 等待直到某個(gè)操作的所有參與者(例如,在多玩家游戲中的所有玩家)都就緒再繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。在這種情況中,當(dāng)所有玩家都準(zhǔn)備就緒時(shí),閉鎖將到達(dá)結(jié)束狀態(tài)。
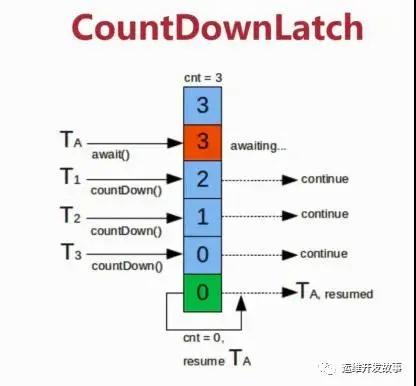
CountDownLatch.jpg
CountDownLatch是一種靈活的閉鎖實(shí)現(xiàn),可以在上述各種情況中使用,它可以使一個(gè)或多個(gè)線(xiàn)程等待一組事件發(fā)生。閉鎖狀態(tài)包括一個(gè)計(jì)數(shù)器,該計(jì)數(shù)器被初始化為一個(gè)正數(shù),表示需要等待的事件數(shù)量。countDown方法遞減計(jì)數(shù)器,表示有一個(gè)事件已經(jīng)發(fā)生了,而 await方法等待計(jì)數(shù)器達(dá)到零,這表示所有需要等待的事件都已經(jīng)發(fā)生。如果計(jì)數(shù)器的值非零,那么 await 會(huì)一直阻塞直到計(jì)數(shù)器為零,或者等待中的線(xiàn)程中斷,或者等待超時(shí)。
使用案例
TestHarness 中給出了閉鎖的兩種常見(jiàn)用法。TestHarness 創(chuàng)建一定數(shù)量的線(xiàn)程,利用它們并發(fā)地執(zhí)行指定的任務(wù)。它使用兩個(gè)閉鎖,分別表示"起始門(mén)(Starting Gate)"和"結(jié)束門(mén)(Ending Gate)"。起始門(mén)計(jì)數(shù)器的初始值為1,而結(jié)束門(mén)計(jì)數(shù)器的初始值為工作線(xiàn)程的數(shù)量。每個(gè)工作線(xiàn)程首先要做的就是在啟動(dòng)門(mén)上等待,從而確保所有線(xiàn)程都就緒后才開(kāi)始執(zhí)行。而每個(gè)線(xiàn)程要做的最后一件事情是將調(diào)用結(jié)束門(mén)的 countDown 方法減1,這能使主線(xiàn)程高效地等待直到所有工作線(xiàn)程都執(zhí)行完成,因此可以統(tǒng)計(jì)所消耗的時(shí)間。
- public class TestHarness {
- public long timeTasks(int nThreads, final Runnable task) throws InterruptedException {
- final CountDownLatch startGate = new CountDownLatch(1);
- final CountDownLatch endGate = new CountDownLatch(nThreads);
- for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i++) {
- Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
- try {
- startGate.await();
- try {
- task.run();
- } finally {
- endGate.countDown();
- }
- } catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
- }
- });
- t.start();
- }
- long start = System.nanoTime();
- startGate.countDown();
- endGate.await();
- long end = System.nanoTime();
- return end - start;
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- TestHarness testHarness = new TestHarness();
- AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
- long time = testHarness.timeTasks(10, () -> System.out.println(num.incrementAndGet()));
- System.out.println("cost time: " + time + "ms");
- }
- }
- //輸出結(jié)果
- 1
- 10
- 9
- 8
- 7
- 5
- 6
- 4
- 3
- 2
- cost time: 2960900ms
為什么要在 TestHarness 中使用閉鎖,而不是在線(xiàn)程創(chuàng)建后就立即啟動(dòng)? 或許,我們希望測(cè)試 n 個(gè)線(xiàn)程并發(fā)執(zhí)行某個(gè)任務(wù)時(shí)需要的時(shí)間。如果在創(chuàng)建線(xiàn)程后立即啟動(dòng)它們,那么先啟動(dòng)的線(xiàn)程將"領(lǐng)先"后啟動(dòng)的線(xiàn)程,并且活躍線(xiàn)程數(shù)量會(huì)隨著時(shí)間的推移而增加或減少,競(jìng)爭(zhēng)程度也在不斷發(fā)生變化。啟動(dòng)門(mén)將使得主線(xiàn)程能夠?qū)崟r(shí)釋放所有工作線(xiàn)程,而結(jié)束門(mén)則使主線(xiàn)程能夠等待最后一個(gè)線(xiàn)程執(zhí)行完成,而不是順序地等待每個(gè)線(xiàn)程執(zhí)行完成。
使用總結(jié)
CountDownLatch 是一次性的,計(jì)算器的值只能在構(gòu)造方法中初始化一次,之后沒(méi)有任何機(jī)制再次對(duì)其設(shè)置值,當(dāng)CountDownLatch 使用完畢后,它不能再次被使用。
源碼分析
代碼分析
CountDownLatch 在底層還是采用 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 實(shí)現(xiàn)。
- CountDownLatch startGate = **new **CountDownLatch(1);
我們先看它的構(gòu)造方法, 創(chuàng)建了一個(gè) sync 對(duì)象。
- public CountDownLatch(int count) {
- if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");
- this.sync = new Sync(count);
- }
Sync 是 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn), 按照字面意思我們可以猜到它是公平方式實(shí)現(xiàn)。
- private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 4982264981922014374L;
- // 構(gòu)造方法
- Sync(int count) {
- setState(count);
- }
- // 獲取資源數(shù)
- int getCount() {
- return getState();
- }
- // 獲取鎖
- protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
- return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
- }
- // 釋放鎖
- protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
- // Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
- for (;;) {
- int c = getState();
- if (c == 0)
- return false;
- int nextc = c-1;
- // CAS 解鎖
- if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
- return nextc == 0;
- }
- }
- }
在 await 方法中如果存在計(jì)算值, 那么當(dāng)前線(xiàn)程將進(jìn)入 AQS 隊(duì)列生成 Node 節(jié)點(diǎn), 線(xiàn)程進(jìn)入阻塞狀態(tài)。
- public void await() throws InterruptedException {
- sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
- }
其實(shí)主要是獲取共享鎖。
- public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
- throws InterruptedException {
- if (Thread.interrupted())
- throw new InterruptedException();
- if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
- doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
- }
CountDownLatch.Sync 實(shí)現(xiàn)了 tryAcquireShared 方法 ,如果 getState() == 0 返回 1 , 否則返回 -1. 也就是說(shuō)創(chuàng)建 CountDownLatch 實(shí)例后再執(zhí)行 await 方法將繼續(xù)調(diào)用 doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
- // 是否可獲取共享鎖
- protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
- return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
- }
- // 嘗試獲取鎖, 或者入隊(duì)
- private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
- throws InterruptedException {
- final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
- boolean failed = true;
- try {
- for (;;) {
- final Node p = node.predecessor();
- if (p == head) {
- int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
- if (r >= 0) {
- setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
- p.next = null; // help GC
- failed = false;
- return;
- }
- }
- if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
- parkAndCheckInterrupt())
- throw new InterruptedException();
- }
- } finally {
- if (failed)
- cancelAcquire(node);
- }
- }
在 countDown 方法如果存在等待的線(xiàn)程, 將對(duì)其進(jìn)行喚醒. 或者減少 CountDownLatch 資源數(shù)。
- public void countDown() {
- sync.releaseShared(1);
- }
通過(guò) releaseShared 對(duì)共享鎖進(jìn)行解鎖。
- public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
- if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
- doReleaseShared();
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
最終會(huì)調(diào)用 doReleaseShared 喚醒 AQS 中的頭節(jié)點(diǎn)。
- private void doReleaseShared() {
- /*
- * Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
- * in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
- * way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
- * signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
- * ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
- * Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
- * while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
- * unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
- * fails, if so rechecking.
- */
- for (;;) {
- Node h = head;
- if (h != null && h != tail) {
- int ws = h.waitStatus;
- if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
- if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
- continue; // loop to recheck cases
- unparkSuccessor(h);
- }
- else if (ws == 0 &&
- !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
- continue; // loop on failed CAS
- }
- if (h == head) // loop if head changed
- break;
- }
- }
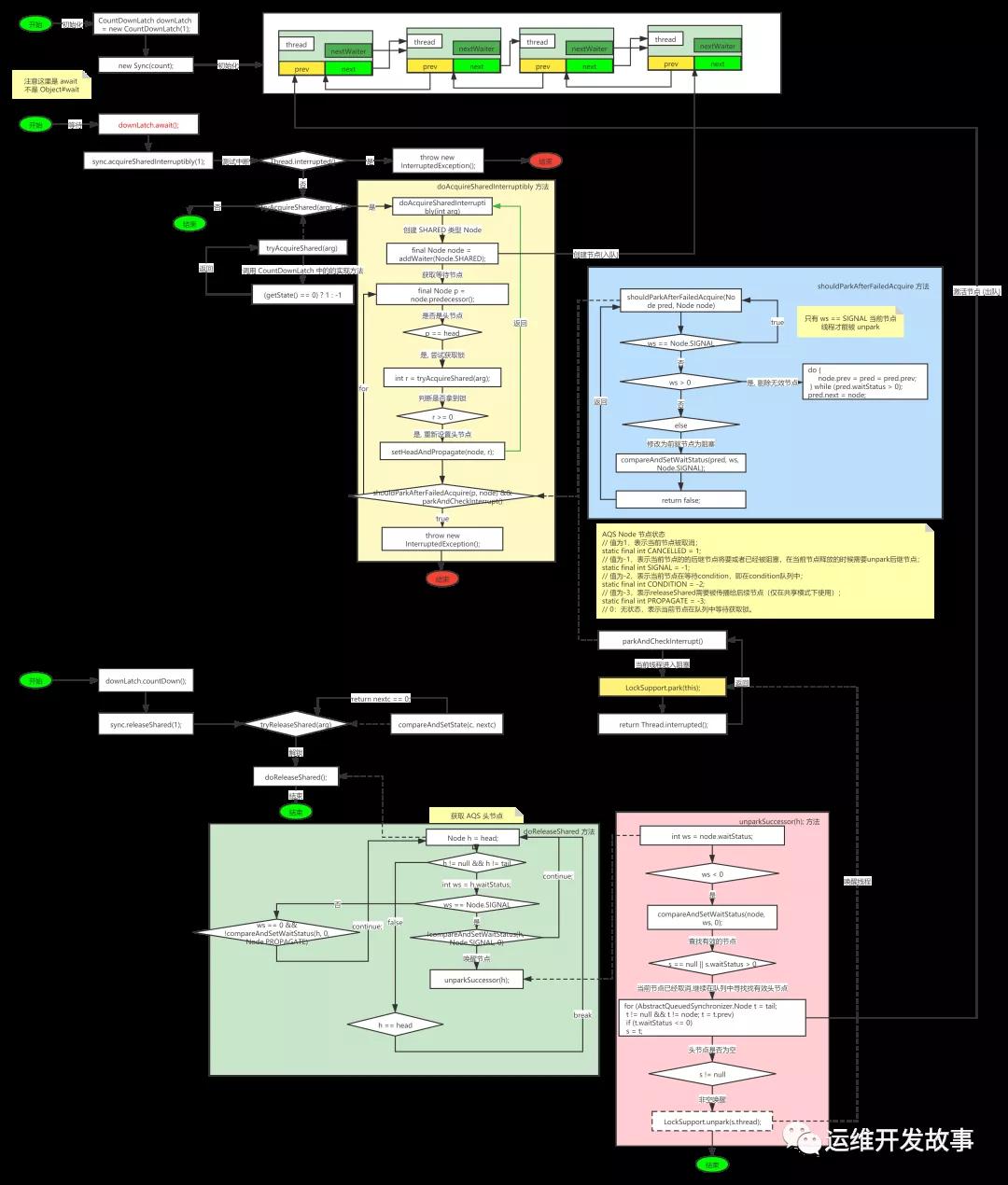
詳細(xì)流程如下圖:
源碼流程圖
CountDownLatch 閉鎖源碼分析.png
參考資料
《Java 并發(fā)編程實(shí)戰(zhàn)》
https://www.cnblogs.com/Lee_xy_z/p/10470181.html