Flink常見維表Join方案,收藏學習開發很有用!
本文轉載自微信公眾號「大數據左右手」,作者左右 。轉載本文請聯系大數據左右手公眾號。
前言
實時數倉,難免會遇到join維表的業務。現總結幾種方案,供各位看官選擇:
- 查找關聯(同步,異步)
- 狀態編程,預加載數據到狀態中,按需取
- 冷熱數據
- 廣播維表
- Temporal Table Join
- Lookup Table Join
其中中間留下兩個問題,供大家思考,可留言一起討論?
查找關聯
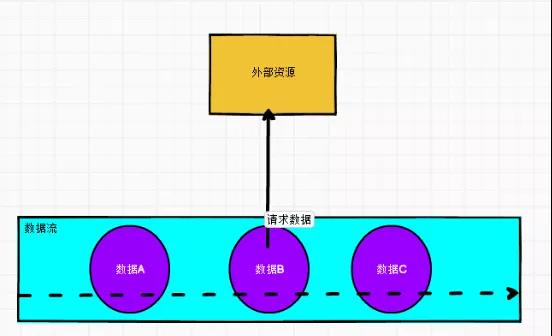
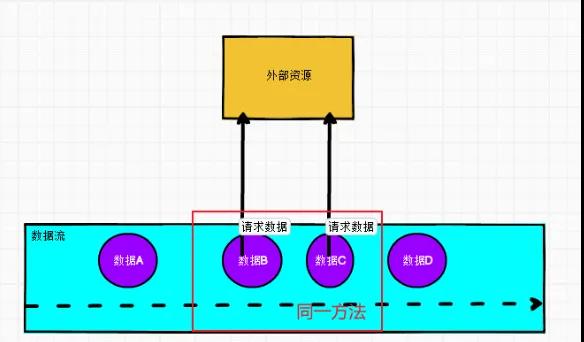
查找關聯就是在主流數據中直接訪問外部數據(mysql,redis,impala ...)去根據主鍵或者某種關鍵條件去關聯取值。
適合: 維表數據量大,但是主數據不大的業務實時計算。
缺點:數據量大的時候,會給外部數據源庫帶來很大的壓力,因為某條數據都需要關聯。
同步
訪問數據庫是同步調用,導致 subtak 線程會被阻塞,影響吞吐量
- import com.alibaba.fastjson.{JSON, JSONArray, JSONObject}
- import com.wang.stream.env.{FlinkStreamEnv, KafkaSourceEnv}
- import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.FlatMapFunction
- import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.SimpleStringSchema
- import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
- import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.FlinkKafkaProducer
- import org.apache.flink.util.Collector
- def analyses(): Unit ={
- val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = FlinkStreamEnv.get()
- KafkaSourceEnv.getKafkaSourceStream(env,List("test"))
- .map(JSON.parseObject(_))
- .filter(_!=null)
- .flatMap(
- new FlatMapFunction[JSONObject,String] {
- override def flatMap(jSONObject: JSONObject, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- // 如果topic就一張表,不用區分,如果多張表,可以通過database 與 table 區分,放到下一步去處理
- // 表的名字
- val databaseName:String = jSONObject.getString("database")
- // 表的名字
- val tableName:String = jSONObject.getString("table")
- // 數據操作類型 INSERT UPDATE DELETE
- val operationType:String = jSONObject.getString("type")
- // 主體數據
- val tableData: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray("data")
- // old 值
- val old: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray("old")
- // canal json 可能存在批處理出現data數據多條
- for (i <- 0 until tableData.size()) {
- val data: String = tableData.get(i).toString
- val nObject: JSONObject = JSON.parseObject(data)
- val orderId: AnyRef = nObject.get("order_id")
- // 下面寫(mysql,redis或者hbase)的連接,利用api 通過orderId查找
- // 最后封裝數據格式 就是join所得
- collector.collect(null)
- }
- }
- }
- )
- .addSink(
- new FlinkKafkaProducer[String](
- "",
- "",
- new SimpleStringSchema()
- )
- )
- env.execute("")
異步
AsyncIO 可以并發地處理多個請求,很大程度上減少了對 subtask 線程的阻塞。
- def analyses(): Unit ={
- val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = FlinkStreamEnv.get()
- val source: DataStream[String] = KafkaSourceEnv.getKafkaSourceStream(env, List("test"))
- .map(JSON.parseObject(_))
- .filter(_ != null)
- .flatMap(
- new FlatMapFunction[JSONObject, String] {
- override def flatMap(jSONObject: JSONObject, collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- // 如果topic就一張表,不用區分,如果多張表,可以通過database 與 table 區分,放到下一步去處理
- // 表的名字
- val databaseName: String = jSONObject.getString("database")
- // 表的名字
- val tableName: String = jSONObject.getString("table")
- // 數據操作類型 INSERT UPDATE DELETE
- val operationType: String = jSONObject.getString("type")
- // 主體數據
- val tableData: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray("data")
- // old 值
- val old: JSONArray = jSONObject.getJSONArray("old")
- // canal json 可能存在批處理出現data數據多條
- for (i <- 0 until tableData.size()) {
- val data: String = tableData.get(i).toString
- collector.collect(data)
- }
- }
- }
- )
- AsyncDataStream.unorderedWait(
- source,
- new RichAsyncFunction[String,String] {//自定義的數據源異步處理類
- override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
- // 初始化
- }
- override def asyncInvoke(input: String, resultFuture: ResultFuture[String]): Unit = {
- // 將數據搜集
- resultFuture.complete(null)
- }
- override def close(): Unit = {
- // 關閉
- }
- },
- 1000,//異步超時時間
- TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,//時間單位
- 100)//最大異步并發請求數量
- .addSink(
- new FlinkKafkaProducer[String](
- "",
- "",
- new SimpleStringSchema()
- )
- )
- env.execute("")
- }
狀態編程,預加載數據到狀態中,按需取
首先把維表數據初始化到state中,設置好更新時間,定時去把維表。
優點:flink 自己維護狀態數據,"榮辱與共",不需要頻繁鏈接外部數據源,達到解耦。
缺點:不適合大的維表和變化大的維表。
- .keyBy(_._1)
- .process(
- new KeyedProcessFunction[String,(String,String,String,String,String), String]{
- private var mapState:MapState[String,Map[String,String]] = _
- private var first: Boolean = true
- override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
- val config: StateTtlConfig = StateTtlConfig
- .newBuilder(org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time.minutes(5))
- .setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnReadAndWrite)
- .setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired)
- .build()
- val join = new MapStateDescriptor[String,Map[String,String]]("join",classOf[String],classOf[Map[String,String]])
- join.enableTimeToLive(config)
- mapState = getRuntimeContext.getMapState(join)
- }
- override def processElement(
- in: (String, String, String, String, String),
- context: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#Context,
- collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- // 加載維表
- if(first){
- first = false
- val time: Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
- getSmallDimTableInfo()
- // 設置好更新時間,定時去把維表
- context.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(time + 86400000)
- }
- // 數據處理,過來一條條數據,然后按照自己的業務邏輯去取維表的數據即可
- // 然后封裝 放到collect中
- collector.collect(null)
- }
- override def onTimer(
- timestamp: Long,
- ctx: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#OnTimerContext,
- out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- println("觸發器執行")
- mapState.clear()
- getSmallDimTableInfo()
- println(mapState)
- ctx.timerService().registerProcessingTimeTimer(timestamp + 86400000)
- }
- def getSmallDimTableInfo(): Unit ={
- // 加載 字典數據
- val select_dictionary="select dic_code,pre_dictionary_id,dic_name from xxxx"
- val dictionary: util.List[util.Map[String, AnyRef]] = MysqlUtil.executeQuery(select_dictionary, null)
- dictionary.foreach(item=>{
- mapState.put("dic_dictionary_"+item.get("pre_dictionary_id").toString,item)
- })
- }
- }
- )
- .filter(_!=null)
- .addSink(
- new FlinkKafkaProducer[String](
- "",
- "",
- new SimpleStringSchema()
- )
- )
- v.execute("")
思考下:直接定義一個Map集合這樣的優缺點是什么?可以留言說出自己的看法?
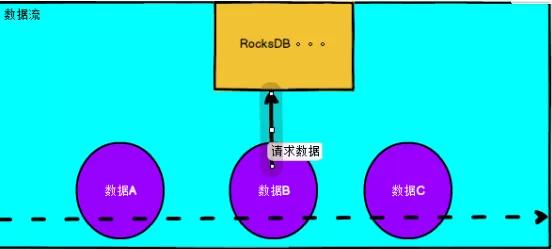
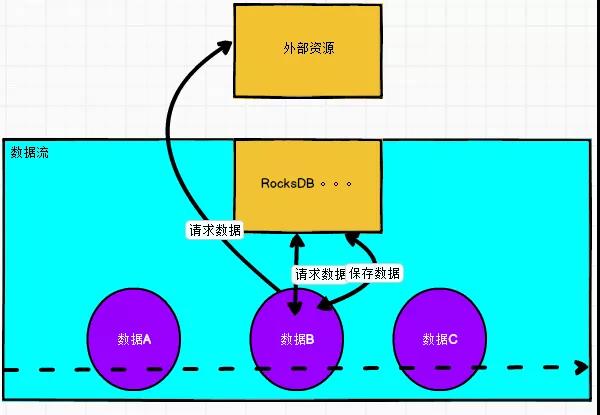
冷熱數據
思想:先去狀態去取,如果沒有,去外部查詢,同時去存到狀態里面。StateTtlConfig 的過期時間可以設置短點。
優點:中庸取值方案,熱備常用數據到內存,也避免了數據join相對過多外部數據源。
缺點:也不能一勞永逸解決某些問題,熱備數據過多,或者冷數據過大,都會對state 或者 外部數據庫造成壓力。
- .filter(_._1 != null)
- .keyBy(_._1)
- .process(
- new KeyedProcessFunction[String,(String,String,String,String,String), String]{
- private var mapState:MapState[String,Map[String,String]] = _
- private var first: Boolean = true
- override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
- val config: StateTtlConfig = StateTtlConfig
- .newBuilder(org.apache.flink.api.common.time.Time.days(1))
- .setUpdateType(StateTtlConfig.UpdateType.OnReadAndWrite)
- .setStateVisibility(StateTtlConfig.StateVisibility.NeverReturnExpired)
- .build()
- val join = new MapStateDescriptor[String,Map[String,String]]("join",classOf[String],classOf[Map[String,String]])
- join.enableTimeToLive(config)
- mapState = getRuntimeContext.getMapState(join)
- }
- override def processElement(
- in: (String, String, String, String, String),
- context: KeyedProcessFunction[String, (String, String, String, String, String),String]#Context,
- collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- // 數據處理,過來一條條數據,然后按照自己的業務邏輯先去mapState去找,如果沒有再去 外部去找
- if (mapState.contains("xx_id")){
- // 如果存在就取
- }else{
- // 如果不存在去外部拿,然后放到mapState中
- val dim_sql="select dic_code,pre_dictionary_id,dic_name from xxxx where id=xx_id"
- val dim: util.List[util.Map[String, AnyRef]] = MysqlUtil.executeQuery(dim_sql, null)
- mapState.put("xx_id",null)
- }
- // 然后封裝 放到collect中
- collector.collect(null)
- }
- }
- )
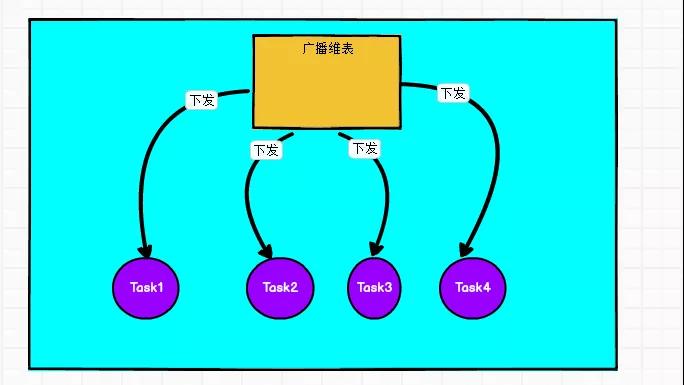
廣播維表
比如上面提到的字典表,每一個Task都需要這份數據,那么需要join這份數據的時候就可以使用廣播維表。
- val dimStream=env.addSource(MysqlSource)
- // 廣播狀態
- val broadcastStateDesc=new MapStateDescriptor[String,String]("broadcaststate", BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO, new MapTypeInfo<>(Long.class, Dim.class))
- // 廣播流
- val broadStream=dimStream.broadcast()
- // 主數據流
- val mainConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer[String]("topic", new SimpleStringSchema(), kafkaConfig)
- val mainStream=env.addSource(mainConsumer)
- // 廣播狀態與維度表關聯
- val connectedStream=mainStream.connect(broadStream).map(..User(id,name)).key(_.1)
- connectedStream.process(new KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction[String,User,Map[Long,Dim],String] {
- override def processElement(value: User, ctx: KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction[String,User,Map[Long,Dim],String]#ReadOnlyContext, out: Collector[String]): Unit = {
- // 取到數據就可以愉快的玩耍了
- val state=ctx.getBroadcastState(broadcastStateDesc)
- xxxxxx
- }
- }
「思考:」 如果把維表流也通過實時監控binlog到kafka,當維度數據發生變化時,更新放到狀態中,這種方式,是不是更具有時效性呢?
(1)通過canal把變更binlog方式發送到kafka中。
(2)數據流定義成為廣播流,廣播到數據到主數據流中。
(3)定義一個廣播狀態存儲數據,在主數據進行查找匹配,符合要求則join成功。
Temporal Table Join(FlinkSQL與Flink Table API)
由于維表是一張不斷變化的表(靜態表只是動態表的一種特例)。那如何 JOIN 一張不斷變化的表呢?如果用傳統的 JOIN 語法來表達維表 JOIN,是不完整的。因為維表是一直在更新變化的,如果用這個語法那么關聯上的是哪個時刻的維表呢?我們是不知道的,結果是不確定的。所以 Flink SQL 的維表 JOIN 語法引入了Temporal Table 的標準語法,用來聲明關聯的是維表哪個時刻的快照。
普通關聯會一直保留關聯雙側的數據,數據也就會一直膨脹,直到撐爆內存導致任務失敗,Temporal Join則可以定期清理過期數據,在合理的內存配置下即可避免內存溢出。
Event Time Temporal Join
語法
- SELECT [column_list]
- FROM table1 [AS <alias1>]
- [LEFT] JOIN table2 FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF table1.{ proctime | rowtime } [AS <alias2>]
- ON table1.column-name1 = table2.column-name1
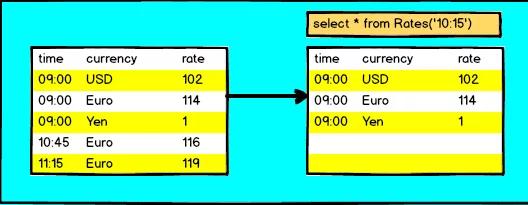
使用事件時間屬性(即行時間屬性),可以檢索過去某個時間點的鍵值。這允許在一個共同的時間點連接兩個表。
舉例
假設我們有一個訂單表,每個訂單都有不同貨幣的價格。為了將此表正確地規范化為單一貨幣,每個訂單都需要與下訂單時的適當貨幣兌換率相結合。
- CREATE TABLE orders (
- order_id STRING,
- price DECIMAL(32,2),
- currency STRING,
- order_time TIMESTAMP(3),
- WATERMARK FOR order_time AS order_time
- ) WITH (/* ... */);
- CREATE TABLE currency_rates (
- currency STRING,
- conversion_rate DECIMAL(32, 2),
- update_time TIMESTAMP(3) METADATA FROM `values.source.timestamp` VIRTUAL
- WATERMARK FOR update_time AS update_time,
- PRIMARY KEY(currency) NOT ENFORCED
- ) WITH (
- 'connector' = 'upsert-kafka',
- /* ... */
- );
- event-time temporal join需要temporal join條件的等價條件中包含的主鍵
- SELECT
- order_id,
- price,
- currency,
- conversion_rate,
- order_time,
- FROM orders
- LEFT JOIN currency_rates FOR SYSTEM TIME AS OF orders.order_time
- ON orders.currency = currency_rates.currency
Processing Time Temporal Join
處理時間時態表連接使用處理時間屬性將行與外部版本表中鍵的最新版本相關聯。
根據定義,使用processing-time屬性,連接將始終返回給定鍵的最新值。可以將查找表看作是一個簡單的HashMap,它存儲來自構建端的所有記錄。這種連接的強大之處在于,當在Flink中無法將表具體化為動態表時,它允許Flink直接針對外部系統工作。
使用FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF table1.proctime表示當左邊表的記錄與右邊的維表join時,只匹配當前處理時間維表所對應的的快照數據。
Lookup Table Join
Lookup Join 通常用于通過連接外部表(維度表)補充信息,要求一個表具有處理時間屬性,另一個表使 Lookup Source Connector。
JDBC 連接器可以用在時態表關聯中作為一個可 lookup 的 source (又稱為維表)。用到的語法是 Temporal Joins 的語法。
- s"""
- |CREATE TABLE users(
- |id int,
- |name string,
- |PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED
- |)
- |WITH (
- |'connector' = 'jdbc',
- |'url' = 'xxxx',
- |'driver'='$DRIVER_CLASS_NAME',
- |'table-name'='$tableName',
- |'lookup.cache.max-rows'='100',
- |'lookup.cache.ttl'='30s'
- |)
- |""".stripMargin
- s"""
- |CREATE TABLE car(
- |`id` bigint ,
- |`user_id` bigint,
- |`proctime` as PROCTIME()
- |)
- |WITH (
- | 'connector' = 'kafka',
- | 'topic' = '$topic',
- | 'scan.startup.mode' = 'latest-offset',
- | 'properties.bootstrap.servers' = '$KAFKA_SERVICE',
- | 'properties.group.id' = 'indicator',
- | 'format' = 'canal-json'
- |)
- |""".stripMargin
- SELECT
- mc.user_id user_id,
- count(1) AS `value`
- FROM car mc
- inner join users FOR SYSTEM_TIME AS OF mc.proctime as u on mc.user_id=s.id
- group by mc.user_id
總結
總體來講,關聯維表有四個基礎的方式:
(1)查找外部數據源關聯
(2)預加載維表關聯(內存,狀態)
(3)冷熱數據儲備(算是1和2的結合使用)
(4)維表變更日志關聯(廣播也好,其他方式的流關聯也好)
「同時考慮:」 吞吐量,時效性,外部數據源的負載,內存資源,解耦性等等方面。
四種join方式不存在絕對的一勞永逸,更多的是針對業務場景在各指標上的權衡取舍,因此看官需要結合場景來選擇適合的。