文帶你了解 Spring 的 @Enable 開頭的注解
前面的文章給大家介紹 Spring? 的重試機制的時候有提到過 Spring? 有很多 @Enable 開頭的注解,平時在使用的時候也沒有注意過為什么會有這些注解,今天就給大家介紹一下。
@Enable 注解
首先我們先看一下有哪些常用的 @Enable 開頭的注解,以及都是干什么用的。
- @EnableRetry?:開啟Spring 的重試功能;
- @EnableScheduling?:開啟Spring 的定時功能;
- @EnableAsync?:開啟Spring 的異步功能;
- @EnableAutoConfiguration?:開啟Spring 的自動裝配功能;
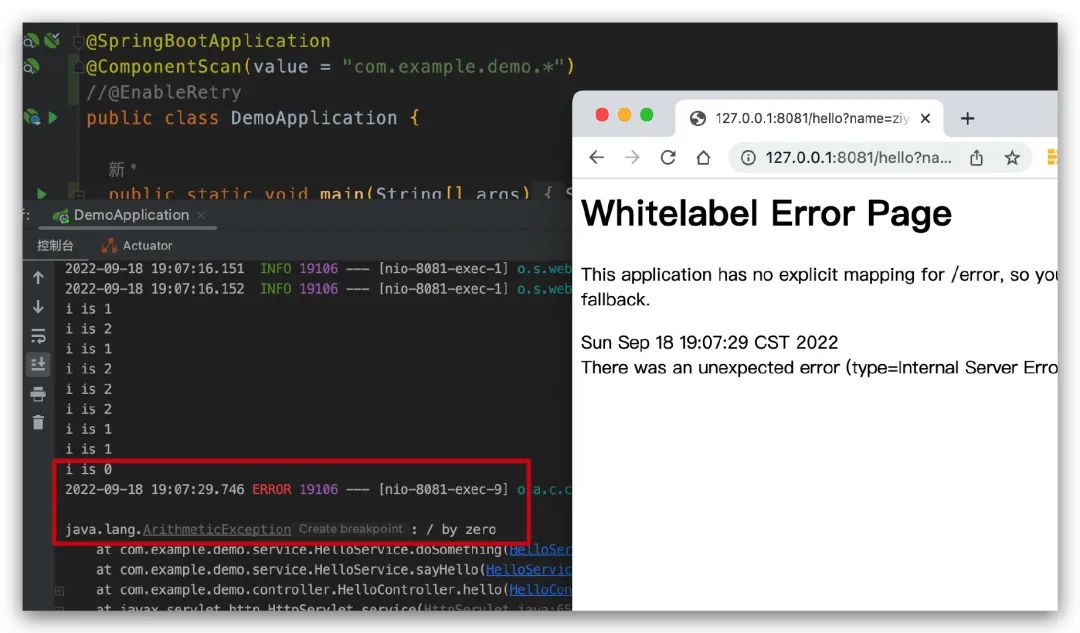
上面這幾個是我們經常會用到和看到的,都知道在使用相應的功能的時候,如果沒有配置上面的注解功能都是不生效的。以我們前面的文章的 Spring? 重試為例,我們需要在啟動類上面配置 @EnableRetry? ,否則自動重試注解 @Retryable? 是不會生效的,如下所示,沒看過的可以去看下,Java 遠程調用失敗?如何優雅的進行重試?。
@Import 注解
那有的小伙伴就要問了,這個 @EnableRetry 注解到底有什么作用呢?不用這個注解就沒辦法了嗎?
要知道這個注解有什么功效,我們可以點開看看源碼,代碼如下
package org.springframework.retry.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false)
@Import(RetryConfiguration.class)
@Documented
public @interface EnableRetry {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
}
可以看到源碼很簡單,其中最有用的就一行 @Import(RetryConfiguration.class)? ,我們可以嘗試把這一行代碼放到啟動類上面看看效果,如下所示,可以看到項目可以正常啟動,并且也還是有效果的,說明跟我們的 @EnableRetry 注解是一樣的。
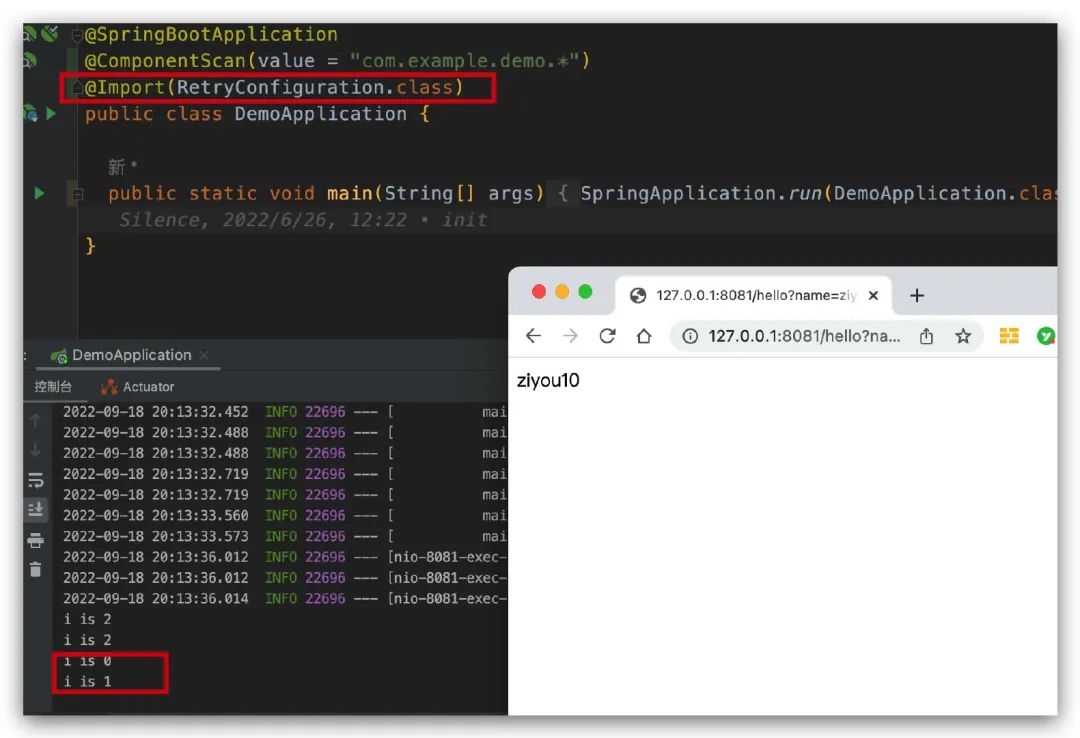
從上面的實驗效果我們可以看到 @EnableRetry? 注解其實就是對 @Import(RetryConfiguration.class)? 的一個封裝,同樣的通過源碼我們還可以看到 @EnableScheduling? 注解就是對 @Import({SchedulingConfiguration.class}) 的一個封裝。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Import({SchedulingConfiguration.class})
@Documented
public @interface EnableScheduling {
}
那如果在沒有 @Enablexxx? 注解的時候,我們直接通過 @Import? 注解是可以這樣寫的,在一個 @Import? 注解里面包含多個配置類,不過這種在配置類較多的場景下還是相對不夠簡潔的,因而才有了各自功能對應的 @Enable 注解。
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.RetryConfiguration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example.demo.*")
@Import({RetryConfiguration.class, SchedulingConfiguration.class})
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
為什么要使用 @Import 注解呢?
那么很多的小伙伴又要問了,為啥要通過使用 @Import? 注解將配置類加載進來呢?在項目中的 Spring? 上下文中不是能直接獲取到嗎?為此我們來實驗一下,通過下面的代碼我們看下是否能在 Spring? 的容器中獲取到 RetryConfiguration? 的 Bean
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.RetryConfiguration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.SchedulingConfiguration;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(value = "com.example.demo.*")
//@Import({RetryConfiguration.class, SchedulingConfiguration.class})
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("org.springframework.retry.annotation.RetryConfiguration");
System.out.println(bean.toString());
}
}
啟動過后我們可以看到結果如下,提示我們在容器中找不到這個 bean?,有點小伙伴會說是不是 bean 的名字寫錯了,其實并不是,緊接著我們再把注釋的那一行放開再運行一下。
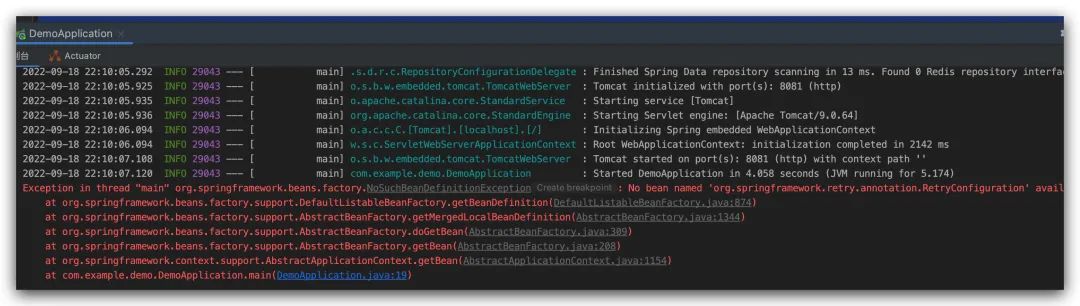
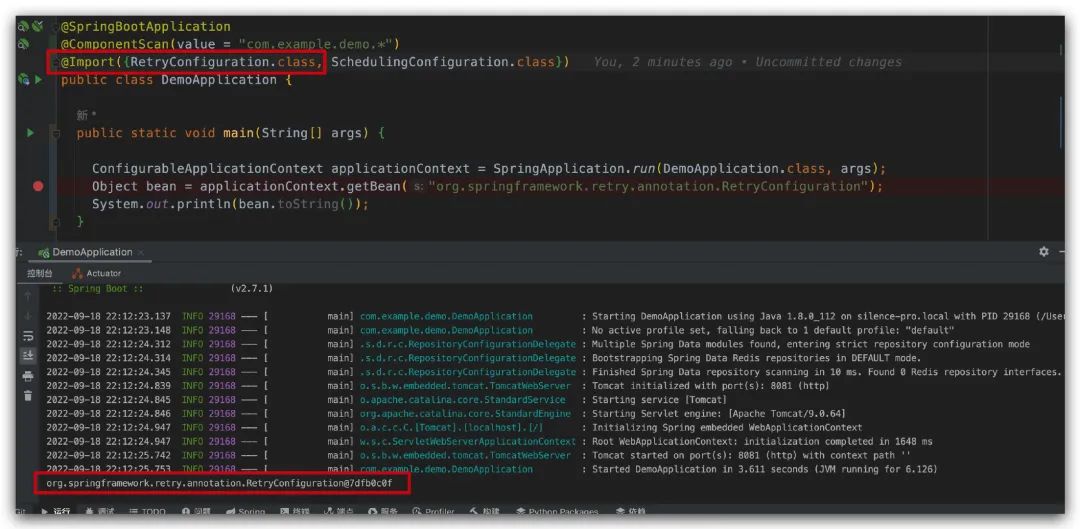
可以看到,這次我們成功的獲取到了這個 Bean?,這個實驗就是告訴我們,其實在默認情況下,Spring? 的容器中是找不到RetryConfiguration? 這個 Bean? 的,因此我們需要通過使用 @Import 注解,將該類加載到容器中。
那么為什么在容器中找不到這個 Bean 呢?
其實很簡單,因為這個 Bean? 跟我們當前環境的類是不是同一個包里面的,在項目啟動的過程中并不會掃描到 RetryConfiguration 類所在的包,因此找不到是很正常的。
總結
上面通過 @EnableRetry? 這個注解帶大家了解了一下 Spring? 的 @Enable? 開頭的注解的使用原理,相信大家對這些注解有了更深入的了解。簡單來說就是因為我們要使用的很多類并不在我們項目所在的包下面,我們不能將所有的依賴包都進行掃描,也不不方便將所有的配置類都通過 @Import? 的方式進行導入,而是讓每個功能的項目包都提供一個 @Enable 開頭的注解,我們直接啟用注解就可以達到效果。
這種方式我們在平時的開發中也可以自己實現,實現一個自己的 @Enable 開頭的注解來實現特定的功能。