前言
viper是適用于go應用程序的配置解決方案,這款配置管理神器,支持多種類型、開箱即用、極易上手。
本地配置文件的接入能很快速的完成,那么對于遠程apollo配置中心的接入,是否也能很快速完成呢?如果有多個apollo實例都需要接入,是否能支持呢?以及apollo遠程配置變更后,是否能支持熱加載,實時更新呢?
擁抱開源
帶著上面的這些問題,結合實際商業項目的實踐,已經有較成熟的解決方案。本著分享的原則,現已將xconfig包脫敏開源:github地址[1],歡迎體驗和star。
下面快速介紹下xconfig包的使用與能力,然后針對包的封裝實踐做個講解
獲取安裝
go get -u github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig
Features
- 支持viper包諸多同名方法
- 支持本地配置文件和遠程apollo配置熱加載,實時更新
- 使用sync.RWMutex讀寫鎖,解決了viper并發讀寫不安全問題
- 支持apollo配置中心多實例配置化快速接入
接入示例
本地配置文件
指定配置文件路徑完成初始化,即可通過xconfig.GetLocalIns().xxx()鏈式操作,讀取配置
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig"
)
func main() {
if xconfig.IsLocalLoaded() {
fmt.Println("local config is loaded")
return
}
//初始化
configIns := xconfig.New(xconfig.WithFile("example/config.yml"))
xconfig.InitLocalIns(configIns)
//讀取配置
fmt.Println(xconfig.GetLocalIns().GetString("appId"))
fmt.Println(xconfig.GetLocalIns().GetString("env"))
fmt.Println(xconfig.GetLocalIns().GetString("apollo.one.endpoint"))
}
xxx支持的操作方法:
- IsSet(key string) bool
- Get(key string) interface{}
- AllSettings() map[string]interface{}
- GetStringMap(key string) map[string]interface{}
- GetStringMapString(key string) map[string]string
- GetStringSlice(key string) []string
- GetIntSlice(key string) []int
- GetString(key string) string
- GetInt(key string) int
- GetInt32(key string) int32
- GetInt64(key string) int64
- GetUint(key string) uint
- GetUint32(key string) uint32
- GetUint64(key string) uint64
- GetFloat(key string) float64
- GetFloat64(key string) float64
- GetFloat32(key string) float32
- GetBool(key string) bool
- SubAndUnmarshal(key string, i interface{}) error
遠程apollo配置中心
指定配置類型與apollo信息完成初始化,即可通過xconfig.GetRemoteIns(key).xxx()鏈式操作,讀取配置
單實例場景
//初始化
configIns := xconfig.New(xconfig.WithConfigType("properties"))
err := configIns.AddApolloRemoteConfig(endpoint, appId, namespace, backupFile)
if err != nil {
...handler
}
xconfig.AddRemoteIns("ApplicationConfig", configIns)
//讀取配置
fmt.Println(xconfig.GetRemoteIns("ApplicationConfig").AllSettings())
多實例場景
在本地配置文件config.yaml維護apollo配置信息,然后批量完成多個實例的初始化,即可通過xconfig.GetRemoteIns(key).xxx()鏈式操作,讀取配置
#apollo配置,支持多實例多namespace
apollo:
one:
endpoint: xxx
appId: xxx
namespaces:
one:
key: ApplicationConfig #用于讀取配置,保證全局唯一,避免相互覆蓋
name: application #注意:name不要帶類型(例如application.properties),這里name和type分開配置
type: properties
two:
key: cipherConfig
name: cipher
type: properties
backupFile: /tmp/xconfig/apollo_bak/test.agollo #每個appId使用不同的備份文件名,避免相互覆蓋
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig"
)
type ApolloConfig struct {
Endpoint string `json:"endpoint"`
AppId string `json:"appId"`
Namespaces map[string]ApolloNameSpace `json:"namespaces"`
BackupFile string `json:"backupFile"`
}
type ApolloNameSpace struct {
Key string `json:"key"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Type string `json:"type"`
}
func main() {
//本地配置初始化
xconfig.InitLocalIns(xconfig.New(xconfig.WithFile("example/config.yml")))
if !xconfig.GetLocalIns().IsSet("apollo") {
fmt.Println("without apollo key")
return
}
apolloConfigs := make(map[string]ApolloConfig, 0)
err := xconfig.GetLocalIns().SubAndUnmarshal("apollo", &apolloConfigs)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(apolloConfigs)
fmt.Println("SubAndUnmarshal error:", err.Error())
return
}
//多實例初始化
for _, apolloConfig := range apolloConfigs {
for _, namespaceConf := range apolloConfig.Namespaces {
configIns := xconfig.New(xconfig.WithConfigType(namespaceConf.Type))
err = configIns.AddApolloRemoteConfig(apolloConfig.Endpoint, apolloConfig.AppId, namespaceConf.Name, apolloConfig.BackupFile)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("AddApolloRemoteConfig error:" + err.Error())
}
xconfig.AddRemoteIns(namespaceConf.Key, configIns)
}
}
//讀取
fmt.Println(xconfig.GetRemoteIns("ApplicationConfig").AllSettings())
}
封裝實踐
學會使用xconfig包后,能快速的實現本地配置文件和遠程apollo配置中心多實例的接入。
再進一步了解這個包在封裝過程都中遇到過哪些問題,以及對應的解決方案,能更深入的理解與使用這個包,同時也有助于增加讀者自己在封裝新包時的實踐理論基礎。
1.viper遠程連接不支持apollo
查看viper的使用文檔,會發現viper是支持遠程K/V存儲連接的,所以一開始我嘗試著連接apollo
v := viper.New()
v.SetConfigType("properties")
err := v.AddRemoteProvider("apollo", "http://endpoint", "application")
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("AddRemoteProvider error: %s", err))
}
fmt.Println("AddRemoteProvider success")
//執行結果:
//panic: AddRemoteProvider error: Unsupported Remote Provider Type "apollo"
執行后發現,并不支持apollo,隨即查看viper源碼,發現只支持以下3個provider
// SupportedRemoteProviders are universally supported remote providers.
var SupportedRemoteProviders = []string{"etcd", "consul", "firestore"}
解決方案:
安裝shima-park/agollo包: go get -u github.com/shima-park/agollo
安裝成功后,只需要在上面代碼基礎上,最前面加上 remote.SetAppID("appId") 即可連接成功
import (
"fmt"
remote "github.com/shima-park/agollo/viper-remote"
"github.com/spf13/viper"
)
remote.SetAppID("appId")
v := viper.New()
v.SetConfigType("properties")
err := v.AddRemoteProvider("apollo", "http://endpoint", "application")
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("AddRemoteProvider error: %s", err))
}
fmt.Println("AddRemoteProvider success")
//執行結果:
//AddRemoteProvider success
2.agollo是怎么讓viper支持apollo連接的呢
不難發現,在執行 remote.SetAppID("appId") 之前,remote.go 中init方法,會往viper.SupportedRemoteProviders中append一個"apollo",其實就是讓viper認識一下這個provider,隨后將viper.RemoteConfig 做重新賦值,并重新實現了viper中的Get Watch WatchChannel這3個方法,里邊就會做apollo連接的適配。
//github.com/shima-park/agollo/viper-remote/remote.go 278-284行
func init() {
viper.SupportedRemoteProviders = append(
viper.SupportedRemoteProviders,
"apollo",
)
viper.RemoteConfig = &configProvider{}
}
//github.com/spf13/viper/viper.go 113-120行
type remoteConfigFactory interface {
Get(rp RemoteProvider) (io.Reader, error)
Watch(rp RemoteProvider) (io.Reader, error)
WatchChannel(rp RemoteProvider) (<-chan *RemoteResponse, chan bool)
}
// RemoteConfig is optional, see the remote package
var RemoteConfig remoteConfigFactory
3.agollo只支持apollo單實例,怎么擴展為多實例呢
執行remote.SetAppID("appId")之后,這個appId是往全局變量appID里寫入的,并且在初始化時也是讀取的這個全局變量。帶來的問題就是不支持apollo多實例,那么解決呢
//github.com/shima-park/agollo/viper-remote/remote.go 26行
var (
// apollod的appid
appID string
...
)
func SetAppID(appid string) {
appID = appid
}
//github.com/shima-park/agollo/viper-remote/remote.go 252行
switch rp.Provider() {
...
case "apollo":
return newApolloConfigManager(appID, rp.Endpoint(), defaultAgolloOptions)
}
解決方案:
既然agollo包能讓viper支持apollo連接,那么為什么我們自己的包不能讓viper也支持apollo連接呢?并且我們還可以定制化的擴展成多實例連接。實現步驟如下:
- shima-pack/agollo/viper-remote/remote.go復制一份出來,把全局變量appID刪掉
- 定義"providers sync.Map",實現AddProviders()方法,將多個appId往里邊寫入,里邊帶上agollo.Option相關配置;同時關鍵操作要將新的provider往viper.SupportedRemoteProviders append,讓viper認識這個新類型
- 使用的地方,根據寫入時用的provider 串,去讀取,這樣多個appId和Option就都區分開了
- 其他代碼有標紅的地方就相應改改就行了
核心代碼 查看GitHub即可[2]:
//github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig/remote/remote.go
var (
...
providers sync.Map
)
func init() {
viper.RemoteConfig = &configProvider{} //目的:重寫viper.RemoteConfig的相關方法
}
type conf struct {
appId string
opts []agollo.Option
}
//【重要】這里是實現支持多個appId的核心操作
func AddProviders(appId string, opts ...agollo.Option) string {
provider := "apollo:" + appId
_, loaded := providers.LoadOrStore(provider, conf{
appId: appId,
opts: opts,
})
//之前未存儲過,則向viper新增一個provider,讓viper認識這個新提供器
if !loaded {
viper.SupportedRemoteProviders = append(
viper.SupportedRemoteProviders,
provider,
)
}
return provider
}
//使用的地方
func newApolloConfigManager(rp viper.RemoteProvider) (*apolloConfigManager, error) {
//讀取provider相關配置
providerConf, ok := providers.Load(rp.Provider())
if !ok {
return nil, ErrUnsupportedProvider
}
p := providerConf.(conf)
if p.appId == "" {
return nil, errors.New("The appid is not set")
}
...
}
4.viper開啟熱加載后會有并發讀寫不安全問題
首先 viper的使用文檔[3],也說明了這個并發讀寫不安全問題,建議使用sync包避免panic

然后本地通過-race試驗,也發現會有這個競態問題
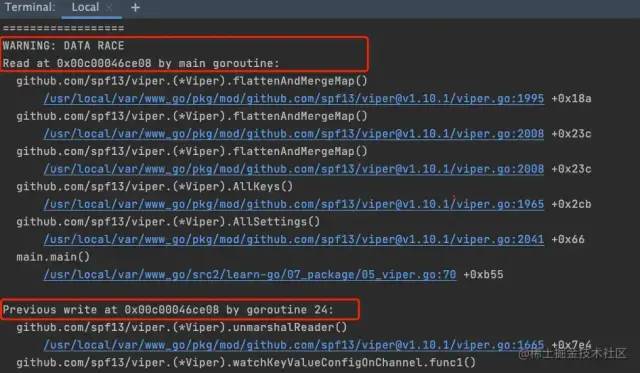
進一步分析viper實現熱加載的源代碼:其實是通過協程實時更新kvstrore這個map,讀取數據的時候也是從kvstore讀取,并沒有加鎖,所以會有并發讀寫不安全問題
// 在github.com/spf13/viper/viper.go 1909行
// Retrieve the first found remote configuration.
func (v *Viper) watchKeyValueConfigOnChannel() error {
if len(v.remoteProviders) == 0 {
return RemoteConfigError("No Remote Providers")
}
for _, rp := range v.remoteProviders {
respc, _ := RemoteConfig.WatchChannel(rp)
// Todo: Add quit channel
go func(rc <-chan *RemoteResponse) {
for {
b := <-rc
reader := bytes.NewReader(b.Value)
v.unmarshalReader(reader, v.kvstore)
}
}(respc)
return nil
}
return RemoteConfigError("No Files Found")
}
解決方案:
寫:不使用viper自帶熱加載方法,而是采用重寫,也是使用協程實時更新,但會加讀寫鎖。
讀:也加讀寫鎖
讀寫鎖核心代碼GitHub[4]:
//github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig/config.go
type Config struct {
configType string
viper *viper.Viper
viperLock sync.RWMutex
}
//寫
//_ = c.viper.WatchRemoteConfigOnChannel()
respc, _ := viper.RemoteConfig.WatchChannel(remote.NewProviderSt(provider, endpoint, namespace, ""))
go func(rc <-chan *viper.RemoteResponse) {
for {
<-rc
c.viperLock.Lock()
err = c.viper.ReadRemoteConfig()
c.viperLock.Unlock()
}
}(respc)
//讀
func (c *Config) Get(key string) interface{} {
c.viperLock.RLock()
defer c.viperLock.RUnlock()
return c.viper.Get(key)
}
5.如何正確的輸入namespace參數
問題描述:
調用agollo包中的相關方法,輸入namespace=application.properties(帶類型),發現主動拉取數據成功,遠程變更通知后數據拉取失敗;輸入namespace=application(不帶類型),發現主動拉取數據成功,遠程變更通知后數據拉取也能成功。兩者輸入差異就在于是否帶類型
問題原因:
查看Apollo官方接口文檔[5],配置更新推送接口notifications/v2 notifications字段說明,一目了然。

基于上述說明,我們在代碼里做了兼容處理,并且配置文件也加上了使用說明
//github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig/config.go 72行
func (c *Config) AddApolloRemoteConfig(endpoint, appId, namespace, backupFile string) error {
...
//namespace默認類型不用加后綴,非默認類型需要加后綴(備注:這里會涉及到apollo變更通知后的熱加載操作 Start->longPoll)
if c.configType != "properties" {
namespace = namespace + "." + c.configType
}
...
}
//config.yml配置說明
namespaces:
one:
key: ApplicationConfig #用于讀取配置,保證全局唯一,避免相互覆蓋
name: application #注意:name不要帶類型(例如application.properties),這里name和type分開配置
type: properties
總結
基于實際商業項目實踐,提升配置管理組件能力,實現了本地配置文件與遠程apollo配置中心多實例快速接入;
從xconfig包的快速上手的使用說明到封裝實踐難點痛點的解析,雙管齊下,讓你更深入的理解,希望對你有所幫助與收獲。
相關資料
[1]github地址: https://github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig
[2]查看GitHub即可: https://github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig
[3]viper的使用文檔: https://github.com/spf13/viper#is-it-safe-to-concurrently-read-and-write-to-a-viper
[4]讀寫鎖核心代碼GitHub: https://github.com/jinzaigo/xconfig
[5]Apollo官方接口文檔: https://www.apolloconfig.com/#/zh/usage/other-language-client-user-guide?id=_14-應用感知配置更新
本文轉載自微信公眾號「 程序員升級打怪之旅」,作者「王中陽Go」,可以通過以下二維碼關注。

轉載本文請聯系「 程序員升級打怪之旅」公眾號。



































