Springboot3新特性異常信息ProblemDetail詳解
環境:Springboot3.0.5
概述
RFC 7807定義了為HTTP響應中錯誤的可讀詳細信息,以避免需要為HTTP API定義新的錯誤響應格式。HTTP [RFC7230]狀態碼有時不足以傳達關于錯誤的足夠信息。
RFC 7807 定義了簡單的JSON[RFC7159]和XML[W3C.REC-XML-20081126]文檔格式以滿足此目的。它們被設計為可由HTTP API重用,HTTP API可以識別特定于其需求的不同“問題類型”。
因此,API客戶端既可以知道高級錯誤類(使用狀態碼),也可以知道問題的細粒度細節。
例如,考慮一個響應,該響應表明客戶的賬戶沒有足夠的權限。403禁止狀態代碼可能被認為是最適合使用的,因為它將向HTTP通用軟件(如客戶端庫、緩存和代理)通知響應的一般語義。然而,這并沒有為API客戶端提供足夠的信息,說明為什么禁止請求、適用的帳戶余額或如何糾正問題。如果這些細節以可讀的格式包含在響應體中,則客戶端可以適當地處理它;例如觸發將更多的信用轉移到賬戶中。
RFC 7807規范通過使用URI[RFC3986]識別特定類型的問題(例如,“信用不足”)來實現這一點;HTTP API可以通過指定受其控制的新URI或重用現有URI來實現這一點。
此外,Problem Detail信息可以包含其他信息,例如標識問題具體發生的URI(有效地為“Joe上周四沒有足夠的信用”這一概念提供了標識符),這對于支持或取證目的可能很有用。
Problem Detail的數據模型是一個JSON[RFC7159]對象;當格式化為JSON文檔時,它使用“application/problem+json”媒體類型。
請注意,Problem Detail 不是在HTTP中傳達問題細節的唯一方式;例如,如果響應仍然是資源的表示,那么通常最好以該應用程序的格式來描述相關細節。同樣,在許多情況下,有一個適當的HTTP狀態代碼,不需要傳遞額外的細節。
Problem Detail消息格式
Problem Detail的規范模型是JSON對象。當序列化為JSON文檔時,該格式用“application/problem+json”媒體類型標識。
例如,一個帶有JSONProblem Detail的HTTP響應:
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
Content-Type: application/problem+json
Content-Language: en
{
"type": "https://pack.com/probs/out-of-credit",
"title": "你沒有足夠的信用。",
"detail": "你現在的余額是30,但是要花50。",
"instance": "/account/12345/msgs/abc",
"balance": 30,
"accounts": ["/account/12345", "/account/67890"]
}這里,結余不足問題(由其類型URI標識)
- type:標識問題類型的URI引用
- title:中指明了403的原因
- instance:給出了具體問題發生的參考
- detail:中給出了發生的具體細節,并添加了兩個擴展
- balance:表示帳戶的余額
- accounts:提供了可以充值帳戶的鏈接
傳遞問題特定擴展的能力允許傳遞多個問題。例如:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Content-Type: application/problem+json
Content-Language: en
{
"type": "https://example.net/validation-error",
"title": "Your request parameters didn't validate.",
"invalid-params": [ {
"name": "age",
"reason": "must be a positive integer"
},
{
"name": "color",
"reason": "must be 'green', 'red' or 'blue'"
}
]
}Spring支持
從Spring6.x開始支持Problem Detail。
REST服務的一個常見需求是在錯誤響應的主體中包含詳細信息。Spring框架支持“Problem Details for HTTP APIs”規范,即RFC 7807。
以下是此支持的主要抽象:
- ProblemDetail — ?RFC 7807問題細節的表示;一個簡單的容器,用于規范中定義的標準字段和非標準字段。
- ErrorResponse — 以RFC 7807的格式暴露HTTP錯誤響應細節,包括HTTP狀態、響應頭和響應體;這允許異常封裝并暴露它們如何映射到HTTP響應的細節。所有Spring MVC異常都實現了這一點。
- ErrorResponseException?—?基本的ErrorResponse實現,其他人可以作為一個方便的基類使用。
- ResponseEntityExceptionHandler?—?@ControllerAdvice的方便基類,它處理所有Spring MVC異常,以及任何ErrorResponseException,并渲染一個帶有主體的錯誤響應。
Spring中要使用ProblemDetail首先需要通過如下配置開啟:
spring:
mvc:
problemdetails:
enabled: true我們可以在任何使用@ExceptionHandler或任何@RequestMapping方法返回ProblemDetail或ErrorResponse以呈現RFC 7807響應。處理方式如下:
- ProblemDetail的status屬性決定了HTTP的狀態。
- 如果還沒有設置,則從當前URL路徑設置ProblemDetail的實例屬性。
- 對于內容協商,Jackson HttpMessageConverter在渲染ProblemDetail時更喜歡“application/problem+json”而不是“application/json”,如果沒有找到兼容的媒體類型,也會使用它。
要為Spring WebFlux異常和任何ErrorResponseException啟用RFC 7807響應,需要擴展 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler,并在Spring配置中把它聲明為@ControllerAdvice。處理程序有一個@ExceptionHandler方法,可以處理所有ErrorResponse異常,其中包括所有內置的web異常。您可以添加更多的異常處理方法,并使用protected方法將任何異常映射到ProblemDetail。
非標準字段
可以通過以下兩種方式之一使用非標準字段擴展RFC7807響應。
一、ProblemDetail類中有個Map集合的'properties'屬性。在使用Jackson庫時,Spring框架注冊了ProblemDetailJacksonMixin,以確保這個“properties”映射被展開,并在響應中作為頂級JSON屬性呈現,同樣,反序列化期間的任何未知屬性都會插入到這個Map中。
你還可以擴展ProblemDetail以添加專用的非標準屬性。ProblemDetail中的復制構造函數允許從現有的ProblemDetail中輕松創建子類。這可以集中完成,例如從@ControllerAdvice,如ResponseEntityExceptionHandler,它將異常的ProblemDetail重新創建到一個具有額外非標準字段的子類中。
ProblemDetail類
public class ProblemDetail {
private static final URI BLANK_TYPE = URI.create("about:blank");
private URI type = BLANK_TYPE;
@Nullable
private String title;
private int status;
@Nullable
private String detail;
@Nullable
private URI instance;
@Nullable
private Map<String, Object> properties;
}測試接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("")
public Object index(Integer age) {
System.out.println(1 / 0) ;
return "success" ;
}
}示例1:
基礎使用
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 當發生異常后直接返回ProblemDetail對象
@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class})
public ProblemDetail handle(Exception e) {
ProblemDetail detail = ProblemDetail.forStatusAndDetail(HttpStatusCode.valueOf(500), e.getMessage());
return detail ;
}
}運行結果:
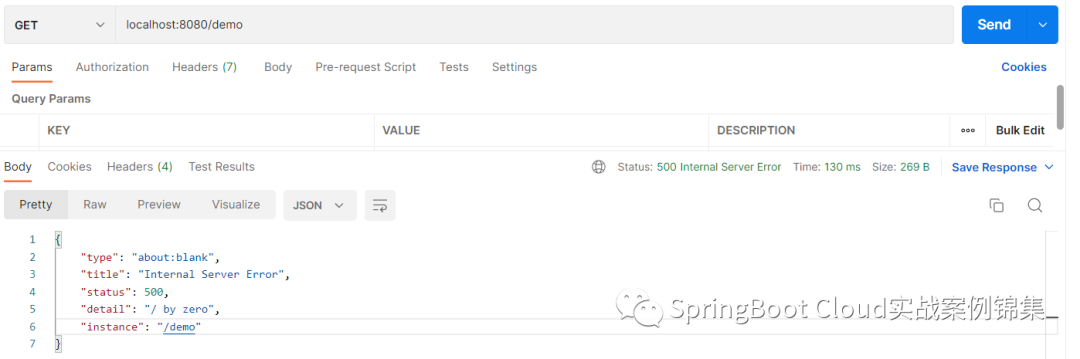
示例2:
添加擴展屬性
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
// 這里使用的是ErrorResponse
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class})
public ErrorResponse handle(Exception e) {
ErrorResponse errorResponse = new ErrorResponseException(HttpStatusCode.valueOf(500), e) ;
errorResponse.getBody().setProperty("operator_time", new Date()) ;
return errorResponse ;
}
}運行結果:
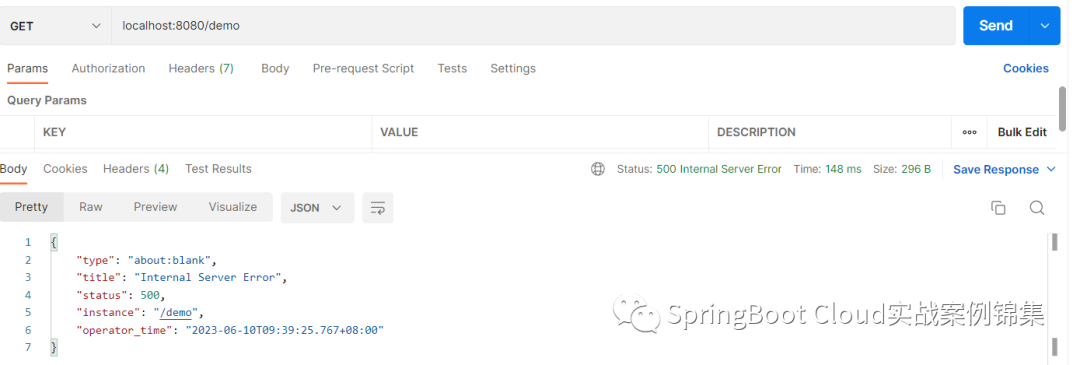
示例3:
繼承自ResponseEntityExceptionHandler該類中定義了@ExceptionHandler注解的方法,能夠處理大多數常見的異常。
@ControllerAdvice
final class ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
}ResponseEntityExceptionHandler
public abstract class ResponseEntityExceptionHandler implements MessageSourceAware {
@ExceptionHandler({
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class,
HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class,
HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class,
MissingPathVariableException.class,
MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,
MissingServletRequestPartException.class,
ServletRequestBindingException.class,
MethodArgumentNotValidException.class,
NoHandlerFoundException.class,
AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class,
ErrorResponseException.class,
ConversionNotSupportedException.class,
TypeMismatchException.class,
HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,
HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,
BindException.class
})
@Nullable
public final ResponseEntity<Object> handleException(Exception ex, WebRequest request) throws Exception {
if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException theEx) {
return handleHttpMessageNotWritable(theEx, headers, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, request);
}
// ...
}
protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpMessageNotWritable(HttpMessageNotWritableException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatusCode status, WebRequest request) {
ProblemDetail body = createProblemDetail(ex, status, "Failed to write request", null, null, request);
return handleExceptionInternal(ex, body, headers, status, request);
}
}該類是Spring提供的默認實現,要使用該類是需要通過如下配置開啟:
spring.mvc.problemdetails.enabled=true處理原理
當返回結果是ProblemDetail或者ErrorResponse時通過如下類進行解析處理:
public class HttpEntityMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
Class<?> type = returnType.getParameterType();
return ((HttpEntity.class.isAssignableFrom(type) && !RequestEntity.class.isAssignableFrom(type)) || ErrorResponse.class.isAssignableFrom(type) || ProblemDetail.class.isAssignableFrom(type));
}
public void handleReturnValue(...) throws Exception {
HttpEntity<?> httpEntity;
if (returnValue instanceof ErrorResponse response) {
httpEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(response.getBody(), response.getHeaders(), response.getStatusCode());
} else if (returnValue instanceof ProblemDetail detail) {
httpEntity = ResponseEntity.of(detail).build();
}
if (httpEntity.getBody() instanceof ProblemDetail detail) {
if (detail.getInstance() == null) {
URI path = URI.create(inputMessage.getServletRequest().getRequestURI());
detail.setInstance(path);
}
}
// ...
writeWithMessageConverters(httpEntity.getBody(), returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
outputMessage.flush();
}
}以上就是ProblemDetail在Spring中的實現原理。



































