RAS:Intel MCA-CMCI,你了解嗎?
Corrected machine-check error interrupt (CMCI)是MCA的增強特性,它提供了一種threshold-based的錯誤上報方式。這種模式下,軟件可以配置硬件corrected MC errors的閾值,硬件發生CE(Corrected Error)次數達到閾值后,會產生一個中斷通知到軟件處理。
值得一提的是,CMCI是隨MCA加入的特性,最開始只能通過軟件輪詢方式獲取CE信息。CMCI中斷通知方式的優點是每個CE都會經過IRQ Handle處理,不會丟失任一CE;而輪詢方式可能因為輪詢頻率低、存儲空間有限等原因,導致丟失CE。但是并不是說CMCI最優,CMCI的缺點是大量CE會產生中斷風暴,影響機器的性能。不幸的是在云服務器場景,CE風暴是比較常見的,那么當下Intel服務器是如何解決這個問題的呢?下面會講到。
CMCI機制
CMCI默認是關閉的,軟件需要通過配置IA32_MCG_CAP[10] = 1打開。
軟件通過IA32_MCi_CTL2 MSR來控制對應Bank使能/關閉CMCI功能。
通過IA32_MCi_CTL2 Bit 14:0設置閾值,如果設置非0,則使用配置的閾值;如果CMCI不支持,則全0;
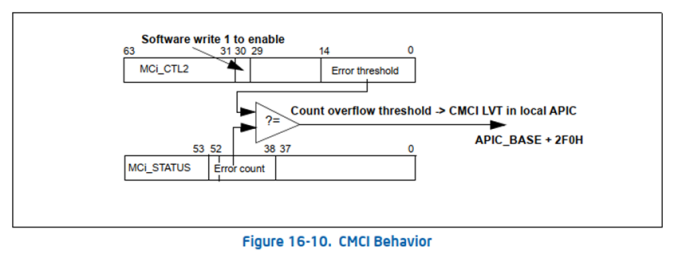
CMCI機制如下圖
 圖片
圖片
硬件通過比較IA32_MCi_CTL2 Bit 14:0和IA32_MCi_STATUS Bit 52:38,如果數值相等,那么overflow event發送到APIC的CMCI LVT entry。如果MC error涉及多個processors,那么CMCI中斷會同時發送到這些processors,比如2個cpu共享的cache發生CE,那么這兩個cpu都會收到CMCI。
CMCI初始化
以Linux v6.3分支為例,內核使能CMCI代碼
C++ arch/x86/kernel/cpu/mce/intel.c void intel_init_cmci(void) { int banks;
if (!cmci_supported(&banks))
return;
mce_threshold_vector = intel_threshold_interrupt;
cmci_discover(banks);
/*
* For CPU #0 this runs with still disabled APIC, but that's
* ok because only the vector is set up. We still do another
* check for the banks later for CPU #0 just to make sure
* to not miss any events.
*/
apic_write(APIC_LVTCMCI, THRESHOLD_APIC_VECTOR|APIC_DM_FIXED);
cmci_recheck();
}1.cmci_supported()函數主要事項包括
?根據內核啟動參數"mce=no_cmci,ignore_ce"判斷是否打開cmci和ce上報功能
?檢查硬件是否支持cmci
?通過MCG_CMCI_P bit判斷硬件是否使能cmci功能
2.mce_threshold_vector = intel_threshold_interrupt; 聲明cmci的中斷處理函數為intel_threshold_interrupt();
3.cmci_discover()函數主要完成
?遍歷所有banks,通過配置IA32_MCi_CTL2寄存器使能所有bank的cmci功能;
C++ rdmsrl(MSR_IA32_MCx_CTL2(i), val); ...
val |= MCI_CTL2_CMCI_EN;
wrmsrl(MSR_IA32_MCx_CTL2(i), val);
rdmsrl(MSR_IA32_MCx_CTL2(i), val);?設置cmci threshold值,代碼如下
C++ #define CMCI_THRESHOLD 1
if (!mca_cfg.bios_cmci_threshold) {
val &= ~MCI_CTL2_CMCI_THRESHOLD_MASK;
val |= CMCI_THRESHOLD;
} else if (!(val & MCI_CTL2_CMCI_THRESHOLD_MASK)) {
/*
* If bios_cmci_threshold boot option was specified
* but the threshold is zero, we'll try to initialize
* it to 1.
*/
bios_zero_thresh = 1;
val |= CMCI_THRESHOLD;
}如果用戶未通過啟動參數"mce=bios_cmci_threshold"配置值,則val = CMCI_THRESHOLD,為1;
如果啟動參數"mce=bios_cmci_threshold"配置,那么表示bios已配置threshold值,即val & MCI_CTL2_CMCI_THRESHOLD_MASK不為0,跳過else if判斷,采用bios配置值;如果bios未配置值,val & MCI_CTL2_CMCI_THRESHOLD_MASK為0,那么驅動初始化threshold為1。
4.cmci_recheck()
cmci_recheck函數通過調用machine_check_poll(),檢查CPU #0是否有遺漏的CE&UCE events。
CMCI處理
cmci中斷處理函數為intel_threshold_interrupt(),定義在arch/x86/kernel/cpu/mce/intel.c
C++
/*
* The interrupt handler. This is called on every event.
* Just call the poller directly to log any events.
* This could in theory increase the threshold under high load,
* but doesn't for now.
*/
static void intel_threshold_interrupt(void)
{
if (cmci_storm_detect())
return;
machine_check_poll(MCP_TIMESTAMP, this_cpu_ptr(&mce_banks_owned));
}machine_check_poll(MCP_TIMESTAMP, this_cpu_ptr(&mce_banks_owned));1.cmci_storm_detect()函數主要是對cmci storm的處理,代碼如下
C++ static bool cmci_storm_detect(void) { unsigned int cnt = __this_cpu_read(cmci_storm_cnt); unsigned long ts = __this_cpu_read(cmci_time_stamp); unsigned long now = jiffies; int r;
if (__this_cpu_read(cmci_storm_state) != CMCI_STORM_NONE)
return true;
if (time_before_eq(now, ts + CMCI_STORM_INTERVAL)) {
cnt++;
} else {
cnt = 1;
__this_cpu_write(cmci_time_stamp, now);
}
__this_cpu_write(cmci_storm_cnt, cnt);
if (cnt <= CMCI_STORM_THRESHOLD)
return false;
cmci_toggle_interrupt_mode(false);
__this_cpu_write(cmci_storm_state, CMCI_STORM_ACTIVE);
r = atomic_add_return(1, &cmci_storm_on_cpus);
mce_timer_kick(CMCI_STORM_INTERVAL);
this_cpu_write(cmci_backoff_cnt, INITIAL_CHECK_INTERVAL);
if (r == 1)
pr_notice("CMCI storm detected: switching to poll mode\n");
return true;
}該函數通過jiffies,判斷固定時間內發生的cmci次數是否大于CMCI_STORM_THRESHOLD(15),如果否則return,反之說明發生cmci storm,則執行cmci_toggle_interrupt_mode()關閉cmci功能, 切換為poll mode,通過輪詢方式獲取event;
2.非cmci storm情況下,通過machine_check_poll(MCP_TIMESTAMP, this_cpu_ptr(&mce_banks_owned))函數獲取并記錄故障信息
參數1定義如下,MCP_TIMESTAMP表示會記錄當前TSC
C++
enum mcp_flags {
MCP_TIMESTAMP = BIT(0), /* log time stamp */
MCP_UC = BIT(1), /* log uncorrected errors */
MCP_DONTLOG = BIT(2), /* only clear, don't log */
};machine_check_poll函數主要功能是通過讀取IA32_MCG_STATUS、IA32_MCi_STATUS寄存器信息和CPU的ip、cs等相關信息,然后故障分類,將CE event或其他故障類型event記錄到/dev/mcelog。用戶可以通過讀取/dev/mcelog獲取錯誤記錄。
執行流程如下,過程說明在代碼注釋中
C++
bool machine_check_poll(enum mcp_flags flags, mce_banks_t *b)
{
if (flags & MCP_TIMESTAMP)
m.tsc = rdtsc(); // 記錄當前TSC
/*CE Error記錄*/
/* If this entry is not valid, ignore it */
if (!(m.status & MCI_STATUS_VAL))
continue;
/*
* If we are logging everything (at CPU online) or this
* is a corrected error, then we must log it.
*/
if ((flags & MCP_UC) || !(m.status & MCI_STATUS_UC))
goto log_it;
/*UCNA Error記錄*/
/*
* Log UCNA (SDM: 15.6.3 "UCR Error Classification")
* UC == 1 && PCC == 0 && S == 0
*/
if (!(m.status & MCI_STATUS_PCC) && !(m.status & MCI_STATUS_S))
goto log_it;
/*通過mce_log記錄故障信息*/
log_it:
/*
* Don't get the IP here because it's unlikely to
* have anything to do with the actual error location.
*/
if (!(flags & MCP_DONTLOG) && !mca_cfg.dont_log_ce)
mce_log(&m);
else if (mce_usable_address(&m)) {
/*
* Although we skipped logging this, we still want
* to take action. Add to the pool so the registered
* notifiers will see it.
*/
if (!mce_gen_pool_add(&m))
mce_schedule_work();
}
}總結一下,CMCI是MCA的一個增強特性,主要用于將硬件CE、UCNA等類型故障通過中斷方式上報到軟件,軟件收到中斷后,執行中斷處理函數intel_threshold_interrupt()采取irq mode或poll mode記錄錯誤信息到/dev/mcelog,用戶態可以通過/dev/mcelog獲取硬件故障信息。
參考文檔:《Intel? 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual 》






























