Kubernetes Informer基本原理,你明白了嗎?
本文分析 k8s controller 中 informer 啟動的基本流程
不論是 k8s 自身組件,還是自己編寫 controller,都需要通過 apiserver 監聽 etcd 事件來完成自己的控制循環邏輯。
如何高效可靠進行事件監聽,k8s 客戶端工具包 client-go 提供了一個通用的 informer 包,通過 informer,可以方便和高效的進行 controller 開發。
informer 包提供了如下的一些功能:
1、本地緩存(store)
2、索引機制(indexer)
3、Handler 注冊功能(eventHandler)
1、informer 架構
整個 informer 機制架構如下圖(圖片源自 Client-go):
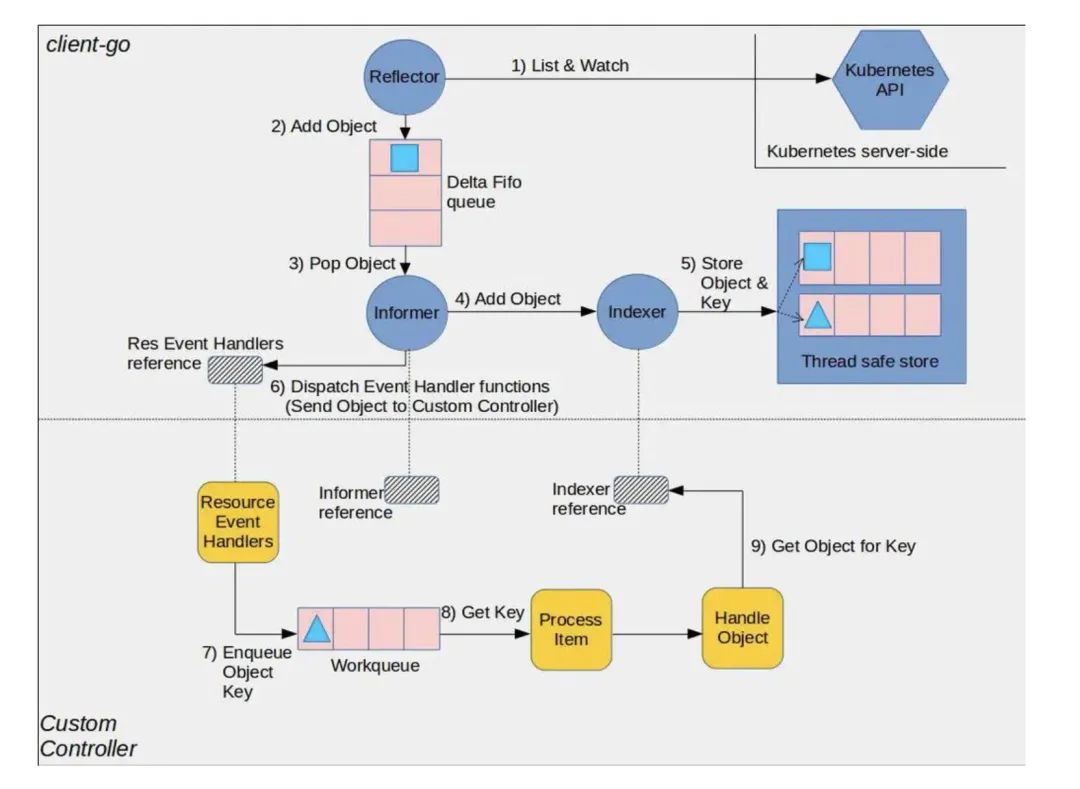 圖片
圖片
可以看到這張圖分為上下兩個部分,上半部分由 client-go 提供,下半部分則是需要自己實現的控制循環邏輯
本文主要分析上半部分的邏輯,包括下面幾個組件:
1.1、Reflector:
從圖上可以看到 Reflector 是一個和 apiserver 交互的組件,通過 list 和 watch api 將資源對象壓入隊列
1.2、DeltaFifo:
DeltaFifo的結構體示意如下:
type DeltaFIFO struct {
...
// We depend on the property that items in the s et are in
// the queue and vice versa, and that all Deltas in this
// map have at least one Delta.
items map[string]Deltas
queue []string
...
}主要分為兩部分,fifo 和 delta
(1)fifo:先進先出隊列
對應結構體中的 queue,結構體示例如下:
[default/centos-fd77b5886-pfrgn, xxx, xxx](2)delta:對應結構體中的items,存儲了資源對象并且攜帶了資源操作類型的一個 map,結構體示例如下:
map:{"default/centos-fd77b5886-pfrgn":[{Replaced &Pod{ObjectMeta: ${pod參數}], "xxx": [{},{}]}消費者從 queue 中 pop 出對象進行消費,并從 items 獲取具體的消費操作(執行動作 Update/Deleted/Sync,和執行的對象 object spec)
1.3、Indexer:
client-go 用來存儲資源對象并自帶索引功能的本地存儲,deltaFIFO 中 pop 出的對象將存儲到 Indexer。
indexer 與 etcd 集群中的數據保持一致,從而 client-go 可以直接從本地緩存獲取資源對象,減少 apiserver 和 etcd 集群的壓力。
2、一個基本例子
func main() {
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stopCh)
// (1)New a k8s clientset
masterUrl := "172.27.32.110:8080"
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags(masterUrl, "")
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("BuildConfigFromFlags err, err: %v", err)
}
clientset, err := k.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Get clientset err, err: %v", err)
}
// (2)New a sharedInformers factory
sharedInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, defaultResync)
// (3)Register a informer
// f.informers[informerType] = informer,
// the detail for informer is build in NewFilteredPodInformer()
podInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
// (4)Register event handler
podInformer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
mObj := obj.(v1.Object)
klog.Infof("Get new obj: %v", mObj)
klog.Infof("Get new obj name: %s", mObj.GetName())
},
})
// (5)Start all informers
sharedInformers.Start(stopCh)
// (6)A cronjob for cache sync
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, podInformer.HasSynced) {
klog.Infof("Cache sync fail!")
}
// (7)Use lister
podLister := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Pods().Lister()
pods, err := podLister.List(labels.Everything())
if err != nil {
klog.Infof("err: %v", err)
}
klog.Infof("len(pods), %d", len(pods))
for _, v := range pods {
klog.Infof("pod: %s", v.Name)
}
<- stopChan
}上面就是一個簡單的 informer 的使用例子,整個過程如上述幾個步驟,著重說一下(2)、(3)、(4)、(5)四個步驟
3、流程分析
3.1、New a sharedInformers factory
sharedInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, defaultResync)
factory := &sharedInformerFactory{
client: client,
namespace: v1.NamespaceAll,
defaultResync: defaultResync,
informers: make(map[reflect.Type]cache.SharedIndexInformer),
startedInformers: make(map[reflect.Type]bool),
customResync: make(map[reflect.Type]time.Duration),
}這個過程就是創建一個 informer 的工廠 sharedInformerFactory,sharedInformerFactory 中有一個 informers 對象,里面是一個 informer 的 map,sharedInformerFactory 是為了防止過多的重復 informer 監聽 apiserver,導致 apiserver 壓力過大,在同一個服務中,不同的 controller 使用同一個 informer
3.2、Register a informer
這個過程主要是生成和注冊 informer 到 sharedInformerFactory
podInformer := sharedInformers.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
func (f *podInformer) Informer() cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return f.factory.InformerFor(&corev1.Pod{}, f.defaultInformer)
}
### f.factory.InformerFor:
### 注冊 informer
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) InformerFor(obj runtime.Object, newFunc internalinterfaces.NewInformerFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
...
informer = newFunc(f.client, resyncPeriod)
f.informers[informerType] = informer
return informer
}
### f.defaultInformer:
### 生成 informer
func (f *podInformer) defaultInformer(client k.Interface, resyncPeriod time.Duration) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return NewFilteredPodInformer(client, f.namespace, resyncPeriod, cache.Indexers{cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc}, f.tweakListOptions)
}
func NewFilteredPodInformer(client k.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
},
},
&corev1.Pod{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
### cache.NewSharedIndexInformer:
func NewSharedIndexInformer(lw ListerWatcher, exampleObject runtime.Object, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers Indexers) SharedIndexInformer {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
sharedIndexInformer := &sharedIndexInformer{
processor: &sharedProcessor{clock: realClock},
indexer: NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers),
listerWatcher: lw,
objectType: exampleObject,
resyncCheckPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
cacheMutationDetector: NewCacheMutationDetector(fmt.Sprintf("%T", exampleObject)),
clock: realClock,
}
return sharedIndexInformer
}首先通過 f.defaultInformer 方法生成 informer,然后通過 f.factory.InformerFor 方法,將 informer 注冊到 sharedInformerFactory
3.3、Register event handler
這個過程展示如何注冊一個回調函數,以及如何觸發這個回調函數
### podInformer.AddEventHandler:
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandler(handler ResourceEventHandler) {
s.AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler, s.defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod)
}
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration) {
...
listener := newProcessListener(handler, resyncPeriod, determineResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod), s.clock.Now(), initialBufferSize)
if !s.started {
s.processor.addListener(listener)
return
}
...
}
### s.processor.addListener(listener):
func (p *sharedProcessor) addListener(listener *processorListener) {
p.addListenerLocked(listener)
if p.listenersStarted {
p.wg.Start(listener.run)
p.wg.Start(listener.pop)
}
}
### listener.run:
func (p *processorListener) run() {
// this call blocks until the channel is closed. When a panic happens during the notification
// we will catch it, **the offending item will be skipped!**, and after a short delay (one second)
// the next notification will be attempted. This is usually better than the alternative of never
// delivering again.
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
wait.Until(func() {
for next := range p.nextCh {
switch notification := next.(type) { // 通過next結構體本身的類型來判斷事件類型
case updateNotification:
p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj)
case addNotification:
p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj)
case deleteNotification:
p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj)
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))
}
}
// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closed
close(stopCh)
}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}
### listener.pop:
func (p *processorListener) pop() {
var nextCh chan<- interface{}
var notification interface{}
for {
select {
case nextCh <- notification:
// Notification dispatched
var ok bool
notification, ok = p.pendingNotifications.ReadOne()
if !ok { // Nothing to pop
nextCh = nil // Disable this select case
}
case notificationToAdd, ok := <-p.addCh:
if !ok {
return
}
if notification == nil { // No notification to pop (and pendingNotifications is empty)
// Optimize the case - skip adding to pendingNotifications
notification = notificationToAdd
nextCh = p.nextCh
} else { // There is already a notification waiting to be dispatched
p.pendingNotifications.WriteOne(notificationToAdd)
}
}
}
}這個過程總結就是:
(1)AddEventHandler 到 sharedProcessor,注冊事件回調函數到 sharedProcessor
(2)listener pop 方法里會監聽 p.addCh,通過 nextCh = p.nextCh 將 addCh 將事件傳遞給 p.nextCh
(3)listener run 方法里會監聽 p.nextCh,收到信號之后,判斷是屬于什么類型的方法,并且執行前面注冊的 Handler
所以后面需要關注當資源對象發生變更時,是如何將變更信號給 p.addCh,進一步觸發回調函數的
3.4、Start all informers
通過 sharedInformers.Start(stopCh)啟動所有的 informer,代碼如下:
// Start initializes all requested informers.
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) Start(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
for informerType, informer := range f.informers {
if !f.startedInformers[informerType] {
go informer.Run(stopCh)
f.startedInformers[informerType] = true
}
}
}我們的例子中其實就只啟動了 PodInformer,接下來看到 podInformer 的 Run 方法做了什么
### go informer.Run(stopCh):
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}){
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{ // Deltafifo
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo, // Deltafifo
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher, // listerWatcher
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
// HandleDeltas, added to process, and done in processloop
Process: s.HandleDeltas,
WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,
}
func() {
...
s.controller = New(cfg)
...
}
s.controller.Run(stopCh)
}
### s.controller.Run(stopCh)
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue,
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
c.reflector = r
// Run reflector
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
// Run processLoop, pop from deltafifo and do ProcessFunc,
// ProcessFunc is the s.HandleDeltas before
wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)
}可以看到上面的邏輯首先生成一個 DeltaFifo,然后接下來的邏輯分為兩塊,生產和消費:
(1)生產—r.Run:
主要的邏輯就是利用 list and watch 將資源對象包括操作類型壓入隊列 DeltaFifo
#### r.Run:
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// 執行listAndWatch
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh);
}
// 執行ListAndWatch流程
func (r *Reflector)ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error{
// 1、list:
// (1)、list pods, 實際調用的是podInformer里的ListFunc方法,
// client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options)
r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
// (2)、獲取資源版本號,用于watch
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
// (3)、數據轉換,轉換成列表
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
// (4)、將資源列表中的資源對象和版本號存儲到DeltaFifo中
r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion);
// 2、watch,無限循環去watch apiserver,當watch到事件的時候,執行watchHandler將event事件壓入fifo
for {
// (1)、watch pods, 實際調用的是podInformer里的WatchFunc方法,
// client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
// (2)、watchHandler
// watchHandler watches pod,更新DeltaFifo信息,并且更新resourceVersion
if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh);
}
}
### r.watchHandler
// watchHandler watches w and keeps *resourceVersion up to date.
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
...
loop:
for {
select {
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object) // Add event to srore, store的具體方法在fifo中
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
...
}
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
eventCount++
}
}
...
}
### r.store.Add:
## 即為deltaFifo的add方法:
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Add(obj interface{}) error {
...
return f.queueActionLocked(Added, obj)
...
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
newDeltas := append(f.items[id], Delta{actionType, obj})
newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas)
if len(newDeltas) > 0 {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
f.queue = append(f.queue, id)
}
f.items[id] = newDeltas
f.cond.Broadcast() // 通知所有阻塞住的消費者
}
...
return nil
}(2)消費—c.processLoop:
消費邏輯就是從 DeltaFifo pop 出對象,然后做兩件事情:(1)觸發前面注冊的 eventhandler (2)更新本地索引緩存 indexer,保持數據和 etcd 一致
func (c *controller) processLoop() {
for {
obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))
}
}
### Queue.Pop:
## Queue.Pop是一個帶有處理函數的pod方法,首先先看Pod邏輯,即為deltaFifo的pop方法:
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {
for { // 無限循環
for len(f.queue) == 0 {
f.cond.Wait() // 阻塞直到生產端broadcast方法通知
}
id := f.queue[0]
item, ok := f.items[id]
delete(f.items, id)
err := process(item) // 執行處理方法
if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {
f.addIfNotPresent(id, item) // 如果處理失敗的重新加入到fifo中重新處理
err = e.Err
}
return item, err
}
}
### c.config.Process:
## c.config.Process是在初始化controller的時候賦值的,即為前面的s.HandleDeltas
### s.HandleDeltas:
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
isSync := false
switch {
case d.Type == Sync:
// Sync events are only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = true
case d.Type == Replaced:
if accessor, err := meta.Accessor(d.Object); err == nil {
if oldAccessor, err := meta.Accessor(old); err == nil {
// Replaced events that didn't change resourceVersion are treated as resync events
// and only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = accessor.GetResourceVersion() == oldAccessor.GetResourceVersion()
}
}
}
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
}
case Deleted:
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}可以看到上面主要執行兩部分邏輯:
s.processor.distribute
#### s.processor.distribute:
### 例如新增通知:s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
### 其中addNotification就是add類型的通知,后面會通過notification結構體的類型來執行不同的eventHandler
func (p *sharedProcessor) distribute(obj interface{}, sync bool) {
p.listenersLock.RLock()
defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()
if sync {
for _, listener := range p.syncingListeners {
listener.add(obj)
}
} else {
for _, listener := range p.listeners {
listener.add(obj)
}
}
}
func (p *processorListener) add(notification interface{}) {
p.addCh <- notification // 新增notification到addCh
}這里 p.addCh 對應到前面說的關注對象 p.addCh,processorListener 收到 addCh 信號之后傳遞給 nextCh,然后通過 notification 結構體的類型來執行不同的 eventHandler
s.indexer 的增刪改:
這個就是本地數據的緩存和索引,自定義控制邏輯里面會通過 indexer 獲取操作對象的具體參數,這里就不展開細講了。
4、總結
至此一個 informer 的 client-go 部分的流程就走完了,可以看到啟動 informer 主要流程就是:
1、Reflector ListAndWatch:
(1)通過一個 reflector run 起來一個帶有 list 和 watch api 的 client
(2)list 到的 pod 列表通過 DeltaFifo 存儲,并更新最新的 ResourceVersion
(3)繼續監聽 pod,監聽到的 pod 操作事件繼續存儲到 DeltaFifo 中
2、DeltaFifo 生產和消費:
(1)生產:list and watch 到的事件生產壓入隊列 DeltaFifo
(2)消費:執行注冊的 eventHandler,并更新本地 indexer
所以 informer 本質其實就是一個通過 deltaFifo 建立生產消費機制,并且帶有本地緩存和索引,以及可以注冊回調事件的 apiServer 的客戶端庫。