徹底搞懂Vue響應式數據、依賴收集更新、Watch/Computed原理
響應式原理初始化
響應式數據設置代理
- 訪問props的item對應的key時,使用this.[key]會自動代理到vm._props.[key]
- 訪問data的item對應的key1時,使用this.[key1]會自動代理到vm._data.[key1]
function initProps(vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {
for (const key in propsOptions) {
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}
}
}function initData(vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {};
const keys = Object.keys(data)
const props = vm.$options.props
const methods = vm.$options.methods
let i = keys.length
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i]
// 監測props是否已經有這個key了,有的話彈出警告
proxy(vm, `_data`, key)
}
}export function proxy(target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = function proxyGetter() {
return this[sourceKey][key]
}
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = function proxySetter(val) {
this[sourceKey][key] = val
}
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}Vue.props響應式數據設置
在合并配置mergeOptions()中,會調用normalizeProps()對props的數據進行整理,最終確保initPros調用時props已經是一個對象,因此不需要Observer判斷是否是數組,直接對key進行defineReactive即可
function initProps(vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}
const props = vm._props = {}
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
for (const key in propsOptions) {
keys.push(key)
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)
defineReactive(props, key, value)
}
}Vue.data響應式數據設置
- 為data建立一個Observer,主要功能是根據value類型判斷,是數組則遞歸調用observe,為每一個item都創建一個Observer對象,如果是對象,則遍歷key,為每一個key都創建響應式監聽
function initData(vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function'
? getData(data, vm)
: data || {}
// observe data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */)
}
export function observe(value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return
}
// ... 判斷數據value是否已經設置響應式過
let ob = new Observer(value)
return ob
}export class Observer {
value: any;
dep: Dep;
vmCount: number; // number of vms that have this object as root $data
constructor(value: any) {
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
this.observeArray(value)
} else {
this.walk(value)
}
}
walk(obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}
observeArray(items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}Object.defineProperty響應式基礎方法
- get:返回對應key的數據 + 依賴收集
- set:設置對應key的數據+派發更新
export function defineReactive(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, ...args) {
const dep = new Dep()
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val) // 如果val也是object
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
// key對應的val是Object,當val里面的key發生改變時
// 即obj[key][key1]=xxx
// 也會通知目前obj[key]收集的Watcher的更新
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}Dep響應式依賴管理類
- 每一個key都有一個Dep管理類
- Dep具備addSub,即關聯Watcher(渲染Watcher或者其它)的能力
- Dep具備depend(),被Watcher顯式關聯,可以被Watcher觸發dep.notify()通知它關聯Watcher更新的能力
Dep.target = null
const targetStack = []
export default class Dep {
static target: ?Watcher;
id: number;
subs: Array<Watcher>;
constructor () {
this.id = uid++
this.subs = []
}
addSub (sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
removeSub (sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub)
}
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
notify () {
const subs = this.subs.slice()
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id)
}
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update()
}
}
}Watcher響應式依賴收集和派發更新執行類
- get()方法進行pushTarget(this),觸發對應的getter回調,開始收集,然后popTarget(this),停止收集,最后觸發cleanupDeps()進行依賴的更新
- update()將更新內容壓入隊列中,然后根據順序調用Watcher.run(),也就是回調constructor()傳進來的this.cb方法
export default class Watcher {
constructor(...args) {
this.vm = vm
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this
}
vm._watchers.push(this)
this.cb = cb; // 觸發更新時調用的方法
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
get() {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
return value
}
addDep(dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
cleanupDeps() {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this)
}
}
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
update() {
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
run() {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (value !== this.value || isObject(value) || this.deep) {
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info)
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}
depend() {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
}Object數據類型響應式
最外一層key的響應式設置
使用observe()對每一個Object的key都進行Object.defineProperty()劫持
function observe(value, asRootData) {
ob = new Observer(value);
return ob
}
var Observer = function Observer(value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
this.walk(value);
};
walk (obj: Object) {
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i])
}
}export function defineReactive(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, customSetter?: ?Function, shallow?: boolean) {
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
dep.notify()
}
})
}深度key的響應式設置
export function defineReactive(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, customSetter?: ?Function, shallow?: boolean) {
const dep = new Dep()
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}- 由上面對observe()方法的分析,它會遍歷Object的每一個key,進行Object.defineProperty聲明
- 對于Object每一個key對應的value,如果childOb = !shallow && observe(val)不為空,那么它會遍歷value對應的每一個key,如果value[key]也是一個Object,那么會再次走到childOb = !shallow && observe(val),直到所有Object都為響應式數據為止
- 對于obj[key]來說,會調用dep.depend(),如果obj[key]本身也是一個對象,即childOb不為空,那么它就會調用childOb.dep.depend(),因此當obj[key][key1]=xx時,也會觸發dep.depend()收集的Watcher發生更新,例如
data: {
parent: {
children: {test: "111"}
}
}
<div>{{parent.children}}</div>由上面的分析可以知道,當this.parent.children.test發生變化時,會觸發this.parent.children收集的渲染Watcher發生變化,從而觸發界面重新渲染
額外添加key
由于Object.defineProperty()的限制,無法實現對Object新增key的響應式監聽,因此當我們想要為Object設置新的key的時候,需要調用Vue.set方法
export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
if (key in target && !(key in Object.prototype)) {
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
const ob = (target: any).__ob__;
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val);
ob.dep.notify();
return val;
}Vue.set()的流程可以總結為:
- 為Object增加對應的key和value數據
- 將新增的key加入響應式監聽中,如果key對應的value也是Object,按照上面深度key的監聽設置分析,會遞歸調用observe進行深度key的響應式設置
- 手動觸發Object收集的Watcher的刷新操作
本質上,上面的三步流程除了第二步有略微差別之外,其它部分跟defineReactive中的set()方法流程一致
刪除key
刪除key也無法觸發響應式的變化,需要手動調用Vue.del()方法:
- 刪除Object指定的key
- 手動觸發Object收集的Watcher的刷新操作
function del(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) {
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.splice(key, 1)
return
}
const ob = (target: any).__ob__
if (!hasOwn(target, key)) {
return
}
delete target[key]
if (!ob) {
return
}
ob.dep.notify()
}Array數據類型響應式
前置說明
根據官方文檔[1]說明,Vue 不能檢測以下數組的變動
- 當你利用索引直接設置一個數組項時,例如:vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue
- 當你修改數組的長度時,例如:vm.items.length = newLength
舉個例子:
var vm = new Vue({
data: {
items: ['a', 'b', 'c']
}
})
vm.items[1] = 'x' // 不是響應性的
vm.items.length = 2 // 不是響應性的為了解決第一類問題,以下兩種方式都可以實現和 vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue 相同的效果,同時也將在響應式系統內觸發狀態更新
// Vue.set
Vue.set(vm.items, indexOfItem, newValue)
// Array.prototype.splice
vm.items.splice(indexOfItem, 1, newValue)為了解決第二類問題,你可以使用 splice:
vm.items.splice(newLength)對Array[index]數據的響應式監聽
如果item=Array[index]是Object數據,使用observe()對Array的每一個item都進行響應式的聲明
function observe(value, asRootData) {
ob = new Observer(value);
return ob
}
var Observer = function Observer(value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value)
}
};
observeArray(items: Array < any >) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}Vue.set更新Array-item
從下面代碼可以看出,Vue.set()更新數組的item本質上也是調用Array.splice()方法
export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key)
target.splice(key, 1, val)
return val
}
}Array.splice更新Array-item
從上面的分析可以知道,一開始會觸發new Observer(value)的初始化從下面代碼可以知道,大部分瀏覽器會觸發protoAugment()方法,也就是改變Array.__proto__
var Observer = function Observer(value) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
def(value, '__ob__', this);
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
if (hasProto) {
protoAugment(value, arrayMethods)
} else {
copyAugment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys)
}
this.observeArray(value)
}
};
function protoAugment (target, src: Object) {
target.__proto__ = src
}
// node_modules/vue/src/core/observer/array.js
const arrayProto = Array.prototype
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto)而改變了Array.__proto__多少方法呢?
const methodsToPatch = [
'push',
'pop',
'shift',
'unshift',
'splice',
'sort',
'reverse'
]methodsToPatch.forEach(function (method) {
const original = arrayProto[method]
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator(...args) {
const result = original.apply(this, args)
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
break
}
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted)
// notify change
ob.dep.notify()
return result
})
})
// node_modules/vue/src/core/util/lang.js
export function def(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, enumerable?: boolean) {
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
value: val,
enumerable: !!enumerable,
writable: true,
configurable: true
})
}從上面代碼分析可以知道,Vue劫持了Array的'push','pop','shift', 'unshift', 'splice', 'sort','reverse'方法,一旦運行了這些方法,會主動觸發:
- 調用Array原來的方法進行調用,然后返回Array原來的方法的返回值,如Array.push調用后的返回值
- 進行observeArray的響應式設置,更新新設置的item(可能為Object,需要設置響應式)
- 手動觸發ob.dep.notify(),觸發對應的Watcher更新,達到響應式自動更新的目的
渲染Watcher依賴收集流程分析
僅僅分析最簡單的渲染Watcher依賴收集的流程,實際上并不是只有渲染Watcher一種
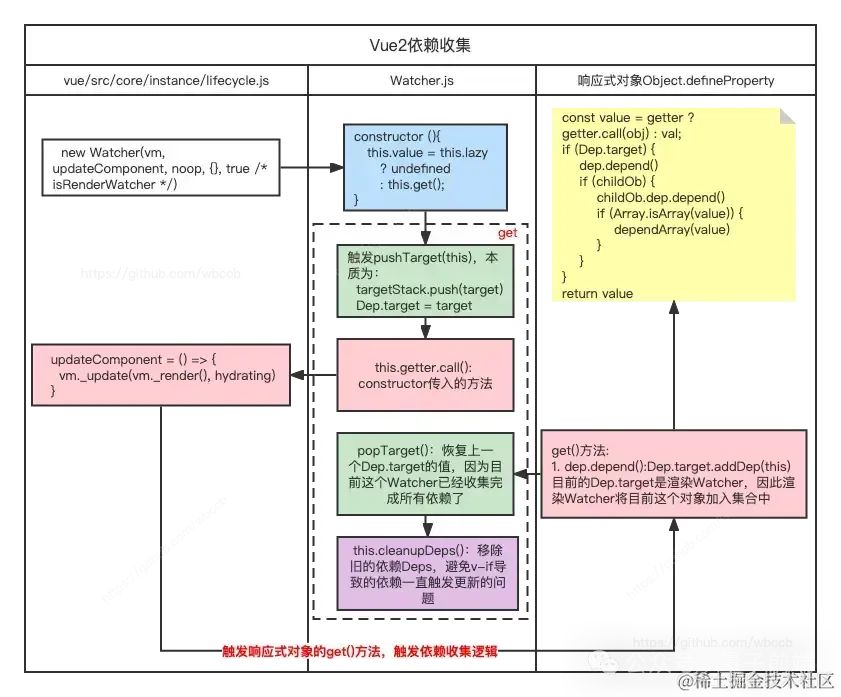 圖片
圖片
渲染Watcher派發更新流程分析
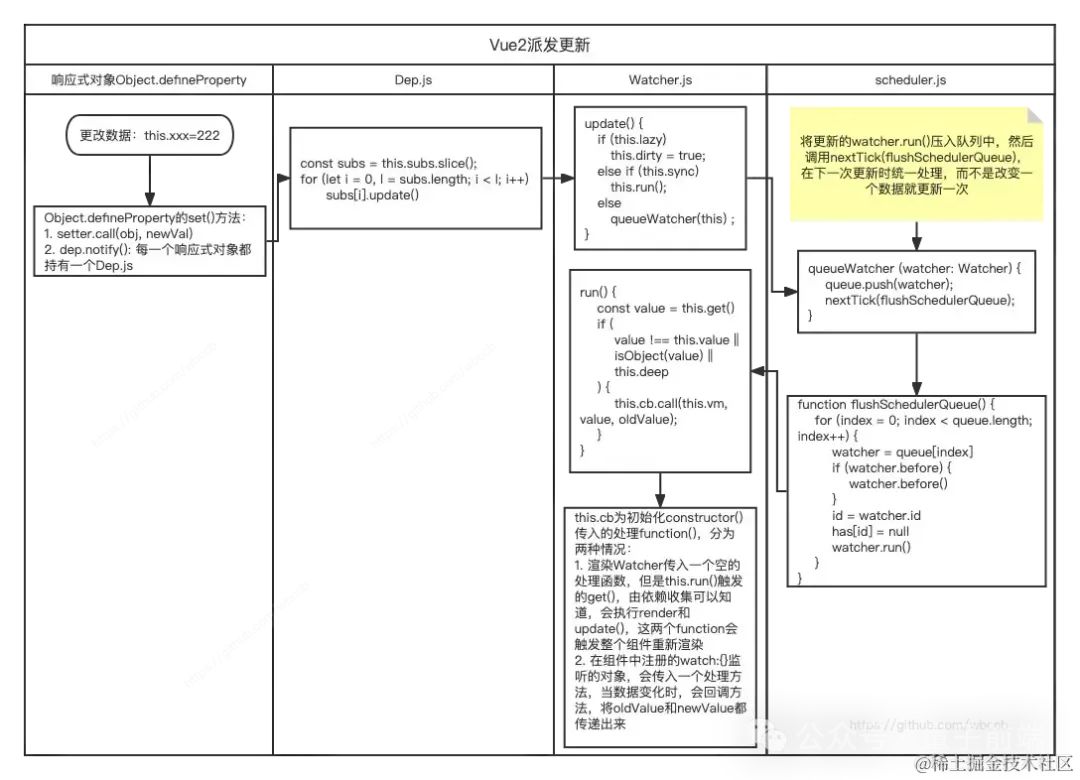 圖片
圖片
computed依賴收集和派發更新分析
測試代碼
<div>{{myName}}</div>
// { [key: string]: Function | { get: Function, set: Function } }
computed: {
myName: function() {
// 沒有set()方法,只有get()方法
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}依賴收集流程圖分析
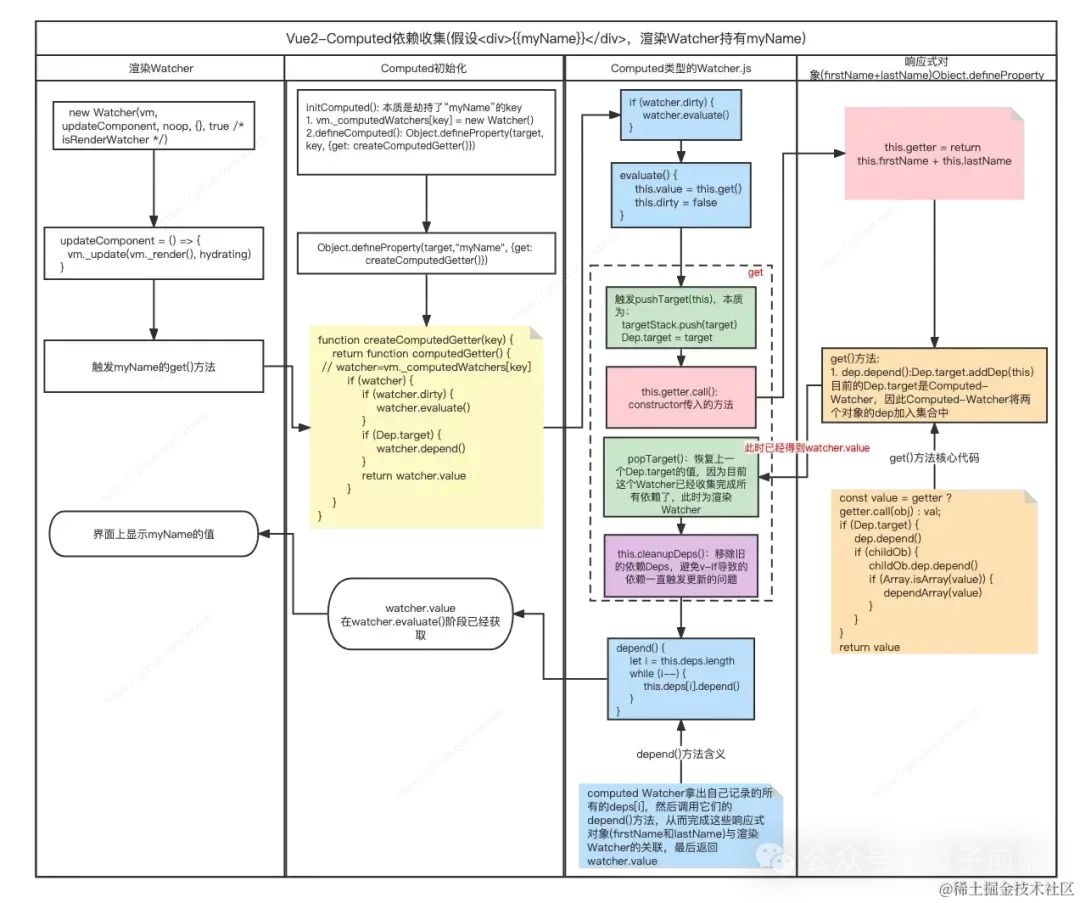 圖片
圖片
依賴收集代碼分析
computedWatcher初始化
Vue.prototype._init初始化時,會調用initState()->initComputed(),從而進行computed數據的初始化
// node_modules/vue/src/core/instance/state.js
function initComputed(vm: Component, computed: Object) {
const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)
for (const key in computed) {
const userDef = computed[key];
const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get;
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions //{ lazy: true }
)
defineComputed(vm, key, userDef);
}
}從上面代碼可以知道,最終為每一個computed監聽的數據建立一個Watcher,一個數據對應一個computed Watcher,傳入{ lazy: true },然后調用defineComputed()方法
export function defineComputed(target: any, key: string, userDef: Object | Function) {
// 為了減少分支判斷,方便理解,統一假設userDef傳入Function
sharedPropertyDefinition.get = createComputedGetter(key);
sharedPropertyDefinition.set = noop;
Object.defineProperty(target, key, sharedPropertyDefinition)
}
function createComputedGetter(key) {
return function computedGetter() {
const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) {
watcher.evaluate()
}
if (Dep.target) {
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}
}
}從上面代碼可以知道,最終defineComputed是進行了Object.defineProperty的數據劫持,一般在computed中都只寫get()方法,即
computed: {
myName: function() {
// 沒有set()方法,只有get()方法
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}而回到上面代碼的分析,defineComputed劫持了computed的get()方法,最終返回watcher.value
渲染Watcher觸發ComputedWatcher的get()方法執行
當界面上<template>{myName}</template>渲染myName的時候,會觸發myName的get()方法,由于Object.defineProperty的數據劫持,會先調用
- watcher.evaluate()->watcher.get()(從下面的代碼可以得出這樣的推導關系)
- watcher.depend()
const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) {
// evaluate () {
// this.value = this.get()
// this.dirty = false
// }
watcher.evaluate()
}
if (Dep.target) {
// depend() {
// let i = this.deps.length
// while (i--) {
// this.deps[i].depend()
// }
// }
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}// watcher.js
get() {
// function pushTarget (target: ?Watcher) {
// targetStack.push(target)
// Dep.target = target
// }
pushTarget(this);
let value;
const vm = this.vm;
try {
// this.getter = return this.firstName + this.lastName;
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm);
} catch (e) {}
finally {
if (this.deep) { // watch類型的watcher才能配置這個參數
traverse(value);
}
popTarget();
this.cleanupDeps();
}
return value;
}從上面的代碼可以知道,當調用watcher.evaluate()->watcher.get()的時候,會調用:
- pushTarget(this):將目前的Dep.target 切換到Computed Watcher
- this.getter.call(vm, vm):觸發this.firstName對應的get()方法和this.lastName對應的get()方法。由下面的依賴收集代碼可以知道,此時this.firstName和this.lastName持有的Dep會進行dep.addSub(this),收集該Computed Watcher
- popTarget():將目前的Dep.target恢復到上一個狀態
- cleanupDeps():更新Computed Watcher的所有依賴關系,將無效的依賴關系刪除(比如v-if造成的依賴關系不用再依賴)
- 最終返回myName= return this.firstName + this.lastName;
watcher.evaluate():求值 + 更新依賴 + 將涉及到的響應式對象firstName和lastName關聯到Computed Watcher
export function defineReactive(obj: Object, key: string, val: any, ...args) {
const dep = new Dep()
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
}
})
}
// Dep.js
depend () {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
// watcher.js
addDep(dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}回到myName的get()方法,即下面的代碼,我們剛剛分析了watcher.evaluate(),那么我們接下來還調用了myName中watcher.depend()我們從上面的代碼知道,這個方法主要是用來收集依賴的,此時的Dep.target是渲染Watcher,computed Watcher會進行自身的depend(),本質是拿出自己所有記錄的Dep(為了方便理解,我們理解Dep就是一個響應式對象的代理),computed Watcher拿出自己記錄的所有的deps[i],然后調用它們的depend()方法,從而完成這些響應式對象(firstName和lastName)與渲染Watcher的關聯,最后返回watcher.value
const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) {
// 上面分析觸發了watcher.get()方法
// 得到對應的watcher.value
// 收集了firstName+lastName和computerWatcher的綁定
watcher.evaluate();
// 將目前的Dep.target切換到渲染Watcher
}
if (Dep.target) {
// depend() {
// let i = this.deps.length
// while (i--) {
// this.deps[i].depend()
// }
// }
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}
// watcher.js
depend() {
// this.deps是從cleanupDeps()中
// this.deps = this.newDeps來的
// this.newDeps是通過addDep()來的
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
// Dep.js
depend() {
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}派發更新流程圖分析
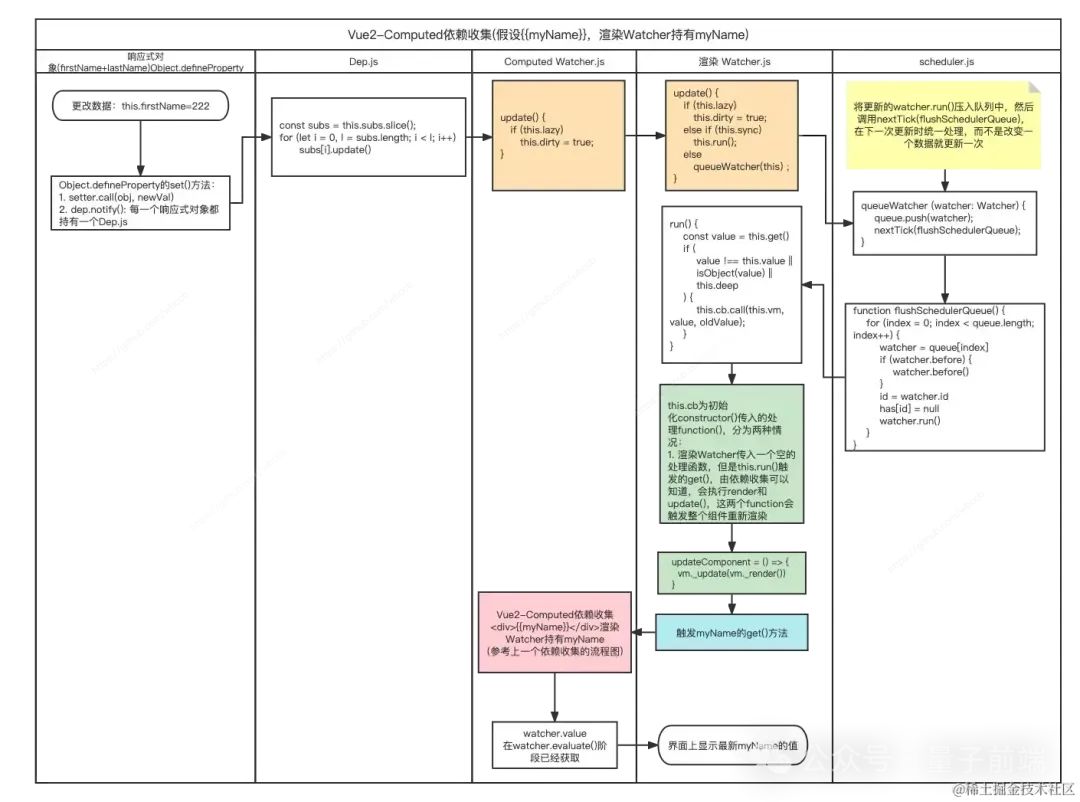 圖片
圖片
派發更新代碼分析
computed: {
myName: function() {
// 沒有set()方法,只有get()方法
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}當this.firstName發生改變時,會觸發this.firstName.dep.subs.notify()功能,也就是觸發剛剛注冊的兩個Watcher: 渲染Watcher和Computed Watcher,首先觸發的是Computed Watcher的notify()方法,由下面的代碼可以知道,只執行this.dirty=true
update () {
// Computed Watcher的this.lazy都為true
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}然后觸發渲染Watcher,觸發整個界面進行渲染,從而觸發該computed[key]的get()方法執行,也就是myName的get()方法執行,由依賴收集的代碼可以知道,最終執行為
const watcher = this._computedWatchers && this._computedWatchers[key]
if (watcher) {
if (watcher.dirty) {
// 上面分析觸發了watcher.get()方法
// 得到對應的watcher.value
watcher.evaluate();
}
if (Dep.target) {
// depend() {
// let i = this.deps.length
// while (i--) {
// this.deps[i].depend()
// }
// }
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}從上面的分析可以知道,computed[key]的get()先收集了一波依賴:
- watcher.evaluate():求值watcher.value + 更新依賴 + 將涉及到的響應式對象關聯到Computed Watcher
- watcher.depend():將涉及到的響應式對象關聯到當前的Dep.target,即渲染Watcher
然后返回了對應的值watcher.value
computedWatcher一般無set方法,因此觸發派發更新就是觸發渲染Watcher/其它Watcher持有computed進行重新渲染,從而觸發computed的get方法,收集最新依賴以及獲取最新值
watch依賴收集和派發更新分析
watch流程圖跟computed流程大同小異,因此watch只做源碼分析
測試代碼
watch支持多種模式的監聽方式,比如傳入一個回調函數,比如傳入一個方法名稱,比如傳入一個Object,配置參數
// { [key: string]: string | Function | Object | Array }
watch: {
a: function (val, oldVal) {},
b: 'someMethod', // 方法名
c: {
handler: function (val, oldVal) {}, // 值改變時的回調方法
deep: true, // 深度遍歷
immediate: true // 馬上回調一次
},
// 你可以傳入回調數組,它們會被逐一調用
e: [
'handle1', // 方式1
function handle2 (val, oldVal) {}, // 方式2
{ // 方式3
handler: function (val, oldVal) {},
deep: true,
immediate: true
},
],
// watch vm.e.f's value: {g: 5}
'e.f': function (val, oldVal) {}
}初始化watch
export function initState(vm: Component) {
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}
function initWatch(vm: Component, watch: Object) {
for (const key in watch) {
const handler = watch[key];
// 處理watch:{b: [三種形式都允許]}的形式
if (Array.isArray(handler)) {
for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler[i]);
}
} else {
createWatcher(vm, key, handler);
}
}
}
function createWatcher(vm: Component, expOrFn: string | Function, handler: any, options?: Object) {
if (isPlainObject(handler)) {
// 處理watch:{b: {handler: 處理函數, deep: true, immediate: true}}的形式
options = handler
handler = handler.handler
}
if (typeof handler === 'string') {
// 處理watch: {b: 'someMethod'}的形式
handler = vm[handler]
}
return vm.$watch(expOrFn, handler, options)
}從上面的代碼可以看出,初始化時,會進行watch中各種參數的處理,將3種不同類型的watch回調模式整理成為規范的模式,最終調用Vue.prototype.$watch進行new Watcher的構建
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (expOrFn: string | Function, cb: any, options?: Object): Function {
const vm: Component = this
// cb是回調方法,如果還是對象,則使用createWatcher拆出來里面的對象
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options.user = true
// 建立一個watch類型的Watcher
// expOrFn: getter
// cb: 注冊的回調
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
if (options.immediate) {
// optinotallow={immediate:true}的分支邏輯
pushTarget()
invokeWithErrorHandling(cb, vm, [watcher.value], vm, info)
popTarget()
}
return function unwatchFn() {
watcher.teardown()
}
}依賴收集代碼分析
新建Watcher的時候, 在constructor()中會觸發
class watcher {
constructor() {
// watch的key
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn);
this.value = this.lazy?undefined:this.get();
}
const bailRE = new RegExp(`[^${unicodeRegExp.source}.$_\d]`)
export function parsePath (path: string): any {
if (bailRE.test(path)) {
return
}
const segments = path.split('.')
return function (obj) {
for (let i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) {
if (!obj) return
obj = obj[segments[i]]
}
return obj
}
}從上面的代碼可以知道,最終this.getter調用的還是傳入的obj[key],從下面的get()方法可以知道,賦值this.getter后,會觸發get()方法,從而觸發this.getter.call(vm, vm),因此最終this.getter得到的就是vm[key]
get() {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value); // 深度遍歷數組/對象,實現
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
return value
}
// traverse.js
export function traverse (val: any) {
_traverse(val, seenObjects)
seenObjects.clear()
}
function _traverse (val: any, seen: SimpleSet) {
let i, keys
const isA = Array.isArray(val)
if ((!isA && !isObject(val)) || Object.isFrozen(val) || val instanceof VNode) {
return
}
if (val.__ob__) {
const depId = val.__ob__.dep.id
if (seen.has(depId)) {
return
}
seen.add(depId)
}
if (isA) {
i = val.length
while (i--) _traverse(val[i], seen)
} else {
keys = Object.keys(val)
i = keys.length
while (i--) _traverse(val[keys[i]], seen)
}
}上面代碼的步驟可以概括為
- pushTarget:修復當前的Dep.target為當前的watch類型的Watcher
- this.getter:返回當前的vm[key],同時觸發vm[key]的響應式劫持get()方法,從而觸發vm[key]持有的Dep對象啟動dep.depend()進行依賴收集(如下面代碼所示),vm[key]持有的Dep對象將當前的watch類型的Watcher收集到vm[key]中,下次vm[key]發生變化時,會觸發watch類型的Watcher進行callback的回調
- traverse(value):深度遍歷,會訪問每一個Object的key,由于每一個Object的key之前在initState()的時候已經使用Object.defineProperty()進行get方法的劫持,因此觸發它們對應的getter方法,進行dep.depend()收集當前的watch類型的Watcher,從而實現改變Object內部深層的某一個key的時候會回調watch類型的Watcher。沒有加deep=true的時候,watch類型的Watcher只能監聽Object的改變,比如watch:{curData: function(){}},只有this.curData=xxx,才會觸發watch,this.curData.children=xxx是不會觸發的
- popTarget:恢復Dep.target為上一個狀態
- cleanupDeps:更新依賴關系
- 返回值value,依賴收集結束,watch類型的Watcher初始化結束
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
}
})派發更新代碼分析
當watcher的值發生改變時,會觸發dep.subs.notify()方法,從上面的分析可以知道,最終會調用watcher.run()方法
run() {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info)
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}由于watch類型的Watcher傳入了this.user=true,因此會觸發invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info),將新值和舊值一起回調,比如
watch: {
myObject: function(value, oldValue) {//新值和舊值}
}watchOptions幾種模式分析
deep=true
// watcher.js
get() {
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (e) {
if (this.user) {
handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`)
} else {
throw e
}
} finally {
// "touch" every property so they are all tracked as
// dependencies for deep watching
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
}
return value
}在get()方法中進行對象的深度key的遍歷,觸發它們的getter()方法,進行依賴的收集,可以實現
watch: {
myObject: {
deep: true,
handler: function(value, oldValue) {//新值和舊值}
}
}
this.myObject.a = 2;雖然上面的例子只是監聽了myObject,但是由于加入deep=true,因此this.myObject.a也會觸發watcher.run(),如下面代碼所示,由于this.deep=true,因此會回調cb(value, oldValue)
run() {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
if (this.user) {
const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"`
invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info)
} else {
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
}
}
}
}immediate=true
從下面代碼可以知道,當聲明immediate=true的時候,初始化Watcher,會馬上調用invokeWithErrorHandling(cb, vm, [watcher.value], vm, info),即cb的回調
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
const vm: Component = this
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options = options || {}
options.user = true
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
if (options.immediate) {
const info = `callback for immediate watcher "${watcher.expression}"`
pushTarget()
invokeWithErrorHandling(cb, vm, [watcher.value], vm, info)
popTarget()
}
return function unwatchFn() {
watcher.teardown()
}
}
watch: {
myObject:
{
immediate: true,
handler: function() {...初始化馬上觸發一次}
}
}sync=true
如果聲明了sync=true,在dep.sub.notify()中,會馬上執行,如果沒有聲明sync=true,會推入隊列中,等到下一個nextTick周期才會執行
update() {
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
export function queueWatcher(watcher: Watcher) {
const id = watcher.id
if (has[id] == null) {
has[id] = true
if (!flushing) {
queue.push(watcher)
} else {
// if already flushing, splice the watcher based on its id
// if already past its id, it will be run next immediately.
let i = queue.length - 1
while (i > index && queue[i].id > watcher.id) {
i--
}
queue.splice(i + 1, 0, watcher)
}
// queue the flush
if (!waiting) {
waiting = true
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) {
flushSchedulerQueue()
return
}
nextTick(flushSchedulerQueue)
}
}
}





































