Java Nio FileChannel堆內堆外數據讀寫全流程分析及使用
背景
java nio中文件讀寫不管是普通文件讀寫,還是基于mmap實現零拷貝,都離不開FileChannel這個類。
隨便打開RocketMQ 源碼搜索FileChannel。
就可以看到使用頻率。
 圖片
圖片
kafka也是。
 圖片
圖片
所以在java中文件讀寫FileChannel尤為重用。
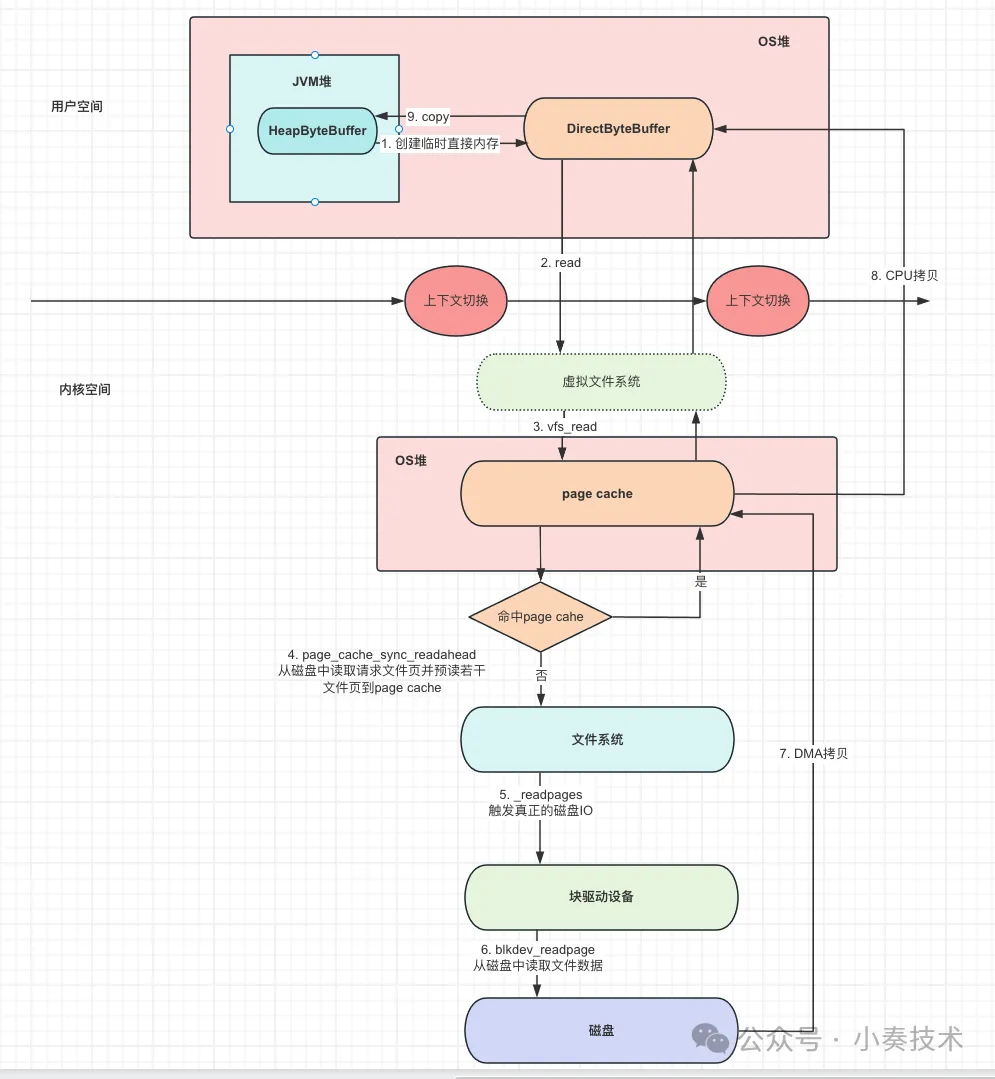
java文件讀寫全流程
 圖片
圖片
這里說的僅僅是FileChannel基于堆內存(HeapByteBuffer)的文件讀寫。
如果是mmap或者堆外內存,可能有些步驟會省略,相當于有一些優化。
- FileChannel調用read,將HeapByteBuffer拷貝到DirectByteBuffer。
- JVM在native層使用read系統調用進行文件讀取, 這里需要進行上下文切換,從用戶態進入內核態。
- JVM 進程進入虛擬文件系統層,查看文件數據再page cache是否緩存,如果有則直接從page cache讀取并返回到DirectByteBuffer。
- 如果請求文件數據不在page caceh,則進入文件系統。通過塊驅動設備進行真正的IO,并進行文件預讀,比如讀取的文件可能只有1-10,但是會將1-20都讀取。
- 磁盤控制器DMA將磁盤中的數據拷貝到page cache中。這里發生了一次數據拷貝(非CPU拷貝)。
- CPU將page cache數據拷貝到DirectByteBuffer,因為page cache屬于內核空間,JVM進程無法直接尋址。這里是發生第二次數據拷貝。
- JVM進程從內核態切換回用戶態,這里如果使用的是堆內存(HeapByteBuffer),實際還需要將堆外內存DirectByteBuffer拷貝到堆內存(HeapByteBuffer)。
FileChannel讀寫文件(非MMAP)
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filename = "小奏技術.txt";
String content = "Hello, 小奏技術.";
// 寫入文件
writeFile(filename, content);
// 讀取文件
System.out.println("Reading from file:");
readFile(filename);
}
public static void writeFile(String filename, String content) {
// 創建文件對象
File file = new File(filename);
// 確保文件存在
if (!file.exists()) {
try {
boolean created = file.createNewFile();
if (!created) {
System.err.println("Unable to create file: " + filename);
return;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("An error occurred while creating the file: " + e.getMessage());
return;
}
}
// 使用FileChannel寫入文件
try (RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(content.getBytes().length);
buffer.put(content.getBytes());
buffer.flip(); // 切換到讀模式
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
fileChannel.write(buffer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("An error occurred while writing to the file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void readFile(String filename) {
// 使用FileChannel讀取文件
try (RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(filename, "r");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) fileChannel.size());
while (fileChannel.read(buffer) > 0) {
// Do nothing, just read
}
// 切換到讀模式
buffer.flip();
/* while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) buffer.get());
}*/
Charset charset = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
String fileContent = charset.decode(buffer).toString();
System.out.print(fileContent);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("An error occurred while reading the file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}這里需要注意的一個細節 我們分配的內存的方式是:
ByteBuffer.allocate()這里我們可以進入看看源碼:
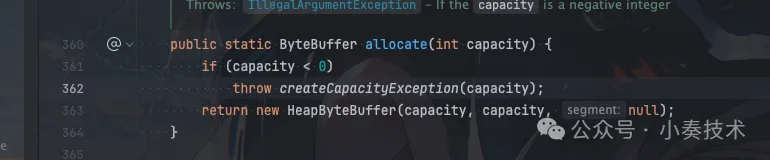 圖片
圖片
實際構造的是HeapByteBuffer,也就是JVM的堆內存。
如果我們使用:
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()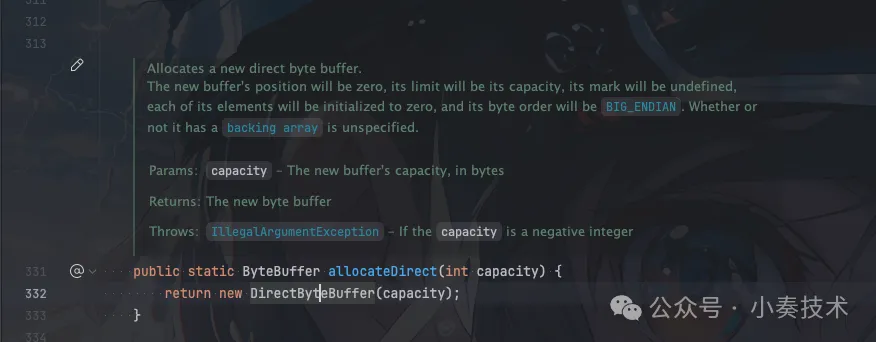 圖片
圖片
則構造的是堆外內存DirectByteBuffer。
HeapByteBuffer和DirectByteBuffer文件讀寫區別
我們看看FileChannel read方法:
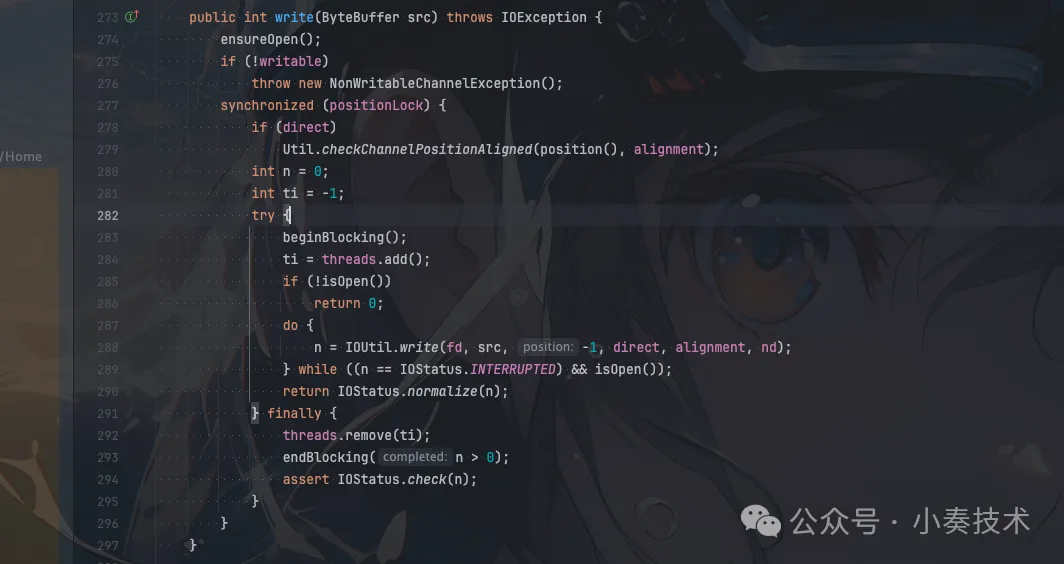 圖片
圖片
發現IO相關的處理被封裝在IOUtil,我們繼續看看IOUtil的write方法:
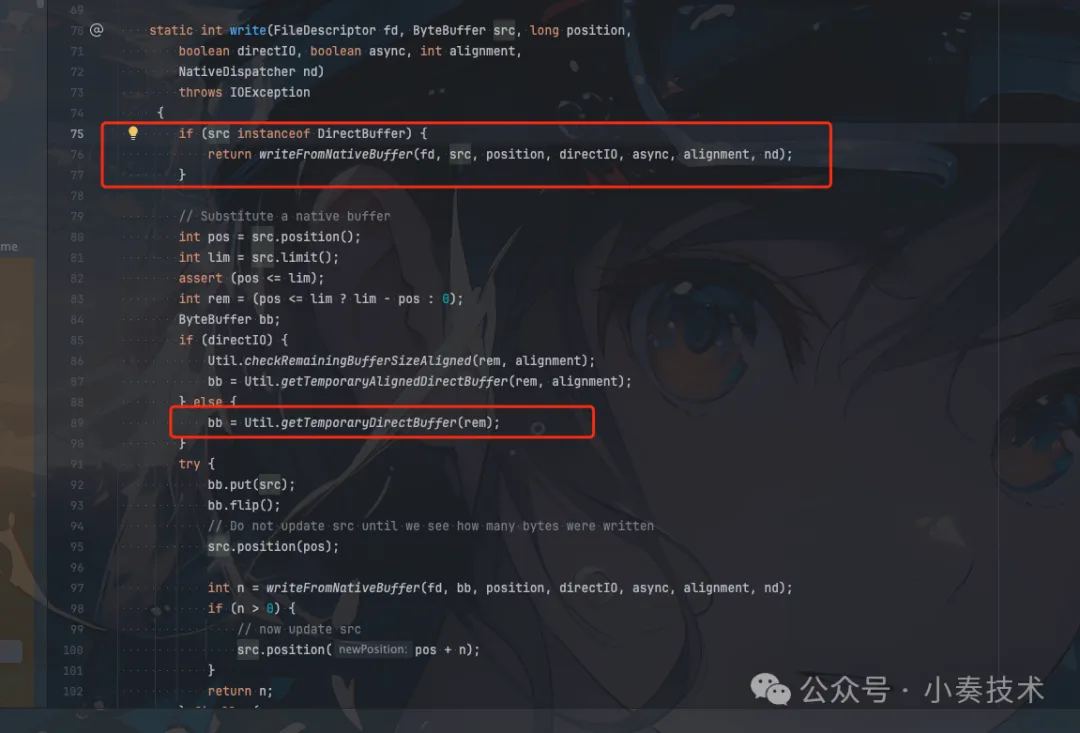 圖片
圖片
可以看到如果是DirectBuffer則可以直接寫。如果是HeapByteBuffer則需要轉換為DirectByteBuffer。
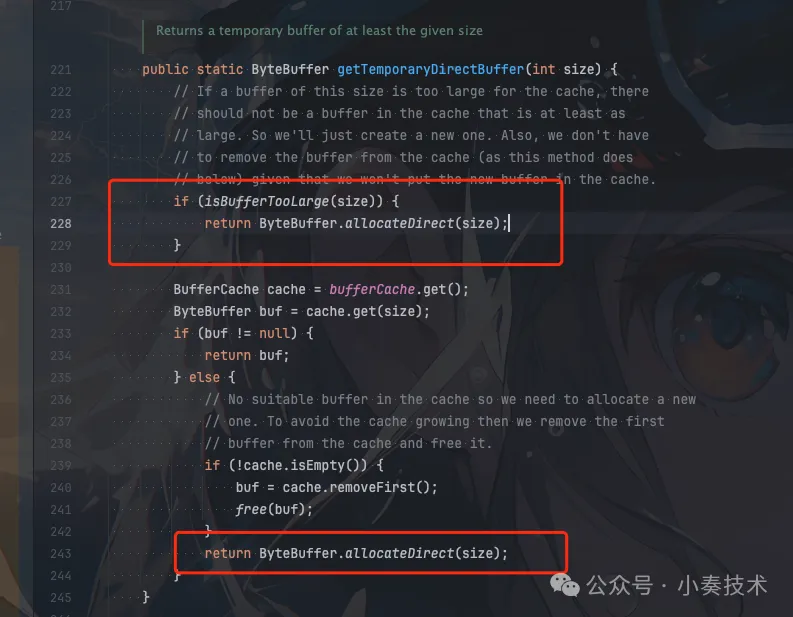 圖片
圖片
為什么要在DirectByteBuffer做一層轉換
主要是HeapByteBuffer受JVM管理,也就是會受到GC影響。如果在進行native調用的時候發生了GC,會導致HeapByteBuffer的內容出現錯誤。具體詳細的說明可以看看這篇MappedByteBuffer VS FileChannel:從內核層面對比兩者的性能差異。講解的非常清晰。
參考
- MappedByteBuffer VS FileChannel:從內核層面對比兩者的性能差異