Spring如何管理Bean的生命周期呢?
我們都知道,在面試的過程中,關于 Spring 的面試題,那是各種各樣,很多時候就會問到關于 Spring的相關問題,比如 AOP ,IOC 等等,還有就是關于 Spring 是如何管理 Bean 的生命周期的相關問題,今天了不起就來和大家一起看看 Spring 是如何管理 Bean 的生命周期的。
源碼分析
BeanFactory
其實我們對于這個 Spring 管理 Bean 的生命周期有時候并不需要我們去大篇幅的去背誦某塊的內容,我們需要的就是學會看源代碼,比如源代碼中的注釋部分,當我們看到這注釋部分的時候,很大程度上能夠幫助我們理解源碼的含義。
BeanFactory是Spring框架中的一個接口,它是一個工廠類,用來創建和管理Spring中的Bean對象。
我們看源碼中的注釋
* <p>Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces
* as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:這句話直接翻譯就是 Bean Factory 實現類應該盡可能的支持標準的生命周期接口。注釋的下半段內容,就是描述的 Bean 生命周期的相關內容了。所以源碼里面的注釋需要我們及時的去看一下,雖然都是純英文的,但是能讀出個大概得內容,再去看源碼的話,至少知道它是干嘛的方法。
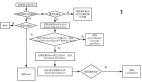
Bean 的生命周期
我們在了解他如何管理的時候,我們得先知道這個 Bean 的生命周期都有哪幾個階段,知道了階段,我們再來看它的實現。
我們先總結:
Bean 的生命周期可以總結為如下的幾個階段,
1. Bean的實例化階段
2. Bean的設置屬性階段
3. Bean的 初始化階段
4. Bean的銷毀階段
也有些人會細分實例化階段,就是把實例化拆分成兩部分,第一部分是注冊階段,第二部分是實例化階段,其實區別不大。
Bean實例化階段
在Spring框架中,Bean的實例化是一個核心過程,它涉及了多個步驟以確保Bean能夠正確地被創建并注入到應用上下文中。
Bean定義注冊:
- 首先,你需要在Spring的配置文件(如XML配置文件或Java配置類)中定義Bean。這包括指定Bean的類名、作用域、初始化方法、銷毀方法以及可能的依賴關系等。
- Spring容器會讀取這些配置,并將Bean定義信息存儲在其內部的數據結構中,通常是BeanDefinition對象。
實例化前的準備:
- 在實例化Bean之前,Spring會進行一些準備工作,如解析Bean定義中的屬性、檢查依賴關系等。
- 如果Bean定義中引用了其他Bean,Spring會嘗試先解析并實例化這些依賴Bean。
實例化:
- 實例化是創建Bean對象的過程。Spring提供了多種實例化Bean的方式:
構造器實例化:通過調用Bean的構造方法來創建實例。你可以在配置文件中指定要使用的構造方法,并提供相應的參數。
靜態工廠方法實例化:通過調用靜態工廠方法來創建Bean實例。你需要在配置文件中指定工廠類的類名和工廠方法的名稱。
實例工廠方法實例化:首先實例化一個工廠Bean,然后調用該工廠Bean的某個非靜態方法來創建目標Bean實例。
默認構造器實例化:如果Bean定義中沒有指定其他實例化方式,并且Bean類有一個無參構造器,那么Spring將使用默認構造器來實例化Bean。
- 實例化完成后,你得到的是一個原始的對象,它還沒有進行任何屬性注入或初始化。
屬性注入:
- 在Bean實例化之后,Spring會進行屬性注入(也稱為依賴注入)。這包括將Bean定義中指定的屬性值或對其他Bean的引用注入到Bean的相應屬性中。
- Spring支持多種屬性注入方式,如基于字段的注入、基于setter方法的注入和基于構造器的注入等。
BeanPostProcessor處理:
在Bean的屬性注入完成后,但Bean的初始化方法執行之前,Spring會調用已注冊的BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法。這是一個可選的步驟,你可以通過實現該接口并注冊相應的BeanPostProcessor來在Bean初始化前后執行自定義的邏輯。
初始化:
- 接下來,Spring會調用Bean定義中指定的初始化方法(如果有的話)。這通常是在Bean類中定義的某個方法,并用特定的注解(如@PostConstruct)或XML配置中的元素的init-method屬性來指定。
- 初始化方法是Bean在準備好接受請求之前進行必要設置或執行特定任務的地方。
BeanPostProcessor再處理:
在Bean初始化方法執行之后,Spring會再次調用已注冊的BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。這是另一個可選的步驟,你可以在這里執行一些清理或后處理操作。
Bean就緒:
經過上述步驟后,Bean就已經被完全創建并初始化了。現在它可以被應用上下文中的其他組件使用或注入到其他Bean中。
到這里,我們的實例化就說完了,記下來看第二階段。
Bean的設置屬性階段
Bean的設置屬性階段(也稱為屬性注入或依賴注入)是Bean生命周期中的一個重要環節。這個階段發生在Spring容器創建Bean的實例之后,但在Bean被實際使用之前。
- 當Spring容器創建一個Bean的實例后,它會檢查該Bean是否有需要注入的屬性。這些屬性可能是其他的Bean、基本數據類型、集合、Map等。
- Spring會查找與這些屬性對應的配置信息(可能是XML中的標簽、注解中的值或其他配置方式),并將它們注入到Bean的相應字段或setter方法中。
注入方式:
- 字段注入:通過直接在字段上使用@Autowired或其他相關注解來實現。但請注意,字段注入在某些情況下可能導致測試困難或難以遵循良好的封裝原則。
- 構造函數注入:在構造函數參數上使用@Autowired或其他相關注解。這是推薦的方式之一,因為它確保了Bean在創建時就已經擁有所有必需的依賴項,并且這些依賴項是不可變的。
- setter方法注入:在setter方法上使用@Autowired或其他相關注解。這種方式允許Bean在創建后的某個時間點接收其依賴項。
既然我們已經把這個屬性設置完畢了,那么就要開始后進行初始化階段了。
Bean 的初始化
- Bean Aware接口回調
- Bean初始化前操作
- Bean初始化操作
- Bean初始化后操作
- Bean初始化完成操作
BeanAware接口回調
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}Bean初始化前操作
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (result == null) {
return result;
}
}
return result;
}Bean初始化操作
調用InitializingBean接口的afterPropertiesSet方法 調用定義bean的時候指定的初始化方法。
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}Bean初始化后階段
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}Bean初始化完成操作
public interface SmartInitializingSingleton {
/**
* Invoked right at the end of the singleton pre-instantiation phase,
* with a guarantee that all regular singleton beans have been created
* already. {@link ListableBeanFactory#getBeansOfType} calls within
* this method won't trigger accidental side effects during bootstrap.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> This callback won't be triggered for singleton beans
* lazily initialized on demand after {@link BeanFactory} bootstrap,
* and not for any other bean scope either. Carefully use it for beans
* with the intended bootstrap semantics only.
*/
void afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}當我們完成了初始化之后,使用完成,最后 Bean 就要走到銷毀階段了。
Bean 的銷毀
@Override
public void destroyBean(Object existingBean) {
new DisposableBeanAdapter(
existingBean, getBeanPostProcessorCache().destructionAware, getAccessControlContext()).destroy();
}這里需要注意的是
- 當容器關閉時,或者當單例 Bean 的作用域結束時,Spring 會銷毀 Bean 的實例。
- 對于非單例 Bean(如 prototype 作用域的 Bean),它們會在每次請求時創建,并在不再需要時由 Java 的垃圾回收機制銷毀。
你知道 Spring是如何管理 Bean 的生命周期了么?