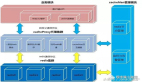
SpringBoot與ShardingSphere整合,重構高并發庫存扣減場景的分布式事務模型
作者:Java知識日歷
訂單創建和庫存扣減操作必須保證原子性,避免出現超賣或欠賣的情況,利用 ShardingSphere 的分布式事務管理功能,確保跨多個數據庫的操作具有一致性。
訂單創建和庫存扣減操作必須保證原子性,避免出現超賣或欠賣的情況,利用 ShardingSphere 的分布式事務管理功能,確保跨多個數據庫的操作具有一致性。
為什么選擇ShardingSphere?
- XA 事務支持:ShardingSphere 提供了 XA 協議的支持,確保跨多個數據庫的操作具有強一致性,即使在分布式環境下也能保持數據的一致性。
- 柔性事務:除了 XA 事務外,ShardingSphere 還支持柔性事務解決方案,如 Saga 和 BASE 模型,以適應不同的業務場景。
- 動態添加/刪除數據源:可以在運行時動態地添加或刪除數據源,而無需重啟應用程序,提高了系統的靈活性和可維護性。
- SQL 解析引擎:ShardingSphere 內置了強大的 SQL 解析引擎,能夠解析和改寫 SQL 語句,使其適用于分片后的數據庫結構。
- 透明化訪問:通過標準的 JDBC 接口訪問分片后的數據庫,無需關心底層的數據分布情況。
- 多種部署模式:ShardingSphere 支持多種部署模式,包括代理模式和嵌入式模式。
- 容器化支持:支持 Docker 和 Kubernetes 等容器化平臺,便于自動化部署和管理。
- 簡化開發:通過 Spring 的事務注解(如
@Transactional),開發者可以輕松地進行事務管理,無需手動編寫復雜的事務邏輯。 - 集成 Atomikos:Atomikos 是一個成熟的事務管理器,與 ShardingSphere 結合使用可以提供可靠的分布式事務管理能力。
- 靈活的分片策略:可以根據不同的業務需求選擇合適的分片算法(如
INLINE、RANGE等),確保數據均勻分布并優化查詢性能。 - 支持水平分片:ShardingSphere 支持將數據按一定的規則分散到多個數據庫實例中,從而實現水平擴展。這對于處理大規模訂單和產品數據非常有效。
代碼實操
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Data JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok (optional) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- ShardingSphere JDBC Core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Atomikos Transaction Manager -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atomikos</groupId>
<artifactId>transactions-jta</artifactId>
<version>5.0.13</version>
</dependency>application.yml
server:
port:8080
spring:
application:
name:sharding-demo
# 數據庫配置
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names:ds0,ds1
ds0:
type:com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db0?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username:root
password:root
ds1:
type:com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc-url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username:root
password:root
rules:
sharding:
tables:
t_product:
actual-data-nodes:ds$->{0..1}.t_product_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column:product_id
sharding-algorithm-name:t_product_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column:product_id
key-generator-name:snowflake
t_order:
actual-data-nodes:ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column:order_id
sharding-algorithm-name:t_order_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column:order_id
key-generator-name:snowflake
binding-tables:
-t_product,t_order
sharding-algorithms:
t_product_inline:
type:INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression:t_product_$->{product_id%2}
t_order_inline:
type:INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression:t_order_$->{order_id%2}
key-generators:
snowflake:
type:SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql-show:trueProduct
package com.example.demo.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Data
@Entity(name = "t_product")
publicclass Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long productId;
private String productName;
private Integer stock;
}Order
package com.example.demo.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Data
@Entity(name = "t_order")
publicclass Order {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long orderId;
private Long productId;
private Integer quantity;
}Repository
package com.example.demo.repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository<Product, Long> {
}OrderRepository
package com.example.demo.repository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Order;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface OrderRepository extends JpaRepository<Order, Long> {
}Service
package com.example.demo.service;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
import com.example.demo.repository.ProductRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
publicclass ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
public Product getProductById(Long productId) {
return productRepository.findById(productId).orElseThrow(() -> new RuntimeException("Product not found"));
}
public void updateStock(Long productId, int quantity) {
Product product = getProductById(productId);
product.setStock(product.getStock() - quantity);
productRepository.save(product);
}
}OrderService
package com.example.demo.service;
import com.example.demo.entity.Order;
import com.example.demo.repository.OrderRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service
publicclass OrderService {
@Autowired
private OrderRepository orderRepository;
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@Transactional
public void placeOrder(Long productId, int quantity) {
// 檢查庫存
if (!productService.getProductById(productId).getStock().equals(quantity)) {
thrownew RuntimeException("Insufficient stock");
}
// 創建訂單
Order order = new Order();
order.setProductId(productId);
order.setQuantity(quantity);
orderRepository.save(order);
// 扣減庫存
productService.updateStock(productId, quantity);
}
}Controller
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.entity.Product;
import com.example.demo.service.ProductService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/products")
publicclass ProductController {
@Autowired
private ProductService productService;
@GetMapping("/{productId}")
public Product getProduct(@PathVariable Long productId) {
return productService.getProductById(productId);
}
@PostMapping("/")
public Product createProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
return productService.createProduct(product);
}
}OrderController
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.OrderService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
publicclass OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@PostMapping("/place-order")
public String placeOrder(@RequestParam Long productId, @RequestParam int quantity) {
try {
orderService.placeOrder(productId, quantity);
return"Order placed successfully";
} catch (Exception e) {
return"Failed to place order: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}Application
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}測試
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/orders/place-order \
-d "productId=1&quantity=5"Respons
Order placed successfully責任編輯:武曉燕
來源:
Java知識日歷