Java基礎之I/O流詳解
總結一下Java I/O文件讀寫基本類相關知識和概念,對于程序設計者來說,創建一個好的輸入/輸出系統是一項艱難的任務,其中挑戰來源于所有的可能性,不僅存在各種源端 與接收端(文件,控制臺,網絡鏈接等),而且還需要以各種不同的方式與它們通信(順序,隨機存取,緩沖,二進制,按字符,按行,按字等)。
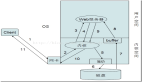
Java I/O主要包括如下幾個層次:
- File(文件特征與管理):用于文件或者目錄的描述信息,例如生成新目錄,修改文件名,刪除文件,判斷文件所在路徑等。
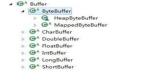
- InputStream(二進制格式操作):抽象類,基于字節的輸入操作,是所有輸入流的父類。定義了所有輸入流都具有的共同特征。
- OutputStream(二進制格式操作):抽象類。基于字節的輸出操作。是所有輸出流的父類。定義了所有輸出流都具有的共同特征。Java中字符是采用Unicode標準,一個字符是16位,即一個字符使用兩個字節來表示。為此,JAVA中引入了處理字符的流。
- Reader(文件格式操作):抽象類,基于字符的輸入操作。
- Writer(文件格式操作):抽象類,基于字符的輸出操作。
- RandomAccessFile(隨機文件操作):它的功能豐富,可以從文件的任意位置進行存取(輸入輸出)操作。
1. File
它是獨立于系統平臺的,利用其構造函數創建出相應的File 對象;再調用其中的方法實現對文件的各個屬性方面的操作。
構造函數:
- File( String path)
- File(String path, String FileName)
- File(File dir, String name)
用途:File類提供了一種與機器無關的方式來描述一個文件對象的屬性,通過類File所提供的方法,可以得到文件或目錄的描述信息,這主要包括名稱、所在路經、可讀性、可寫性、文件的長度等,還可以生成新的目錄、改變文件名、刪除文件、列出一個目錄中所有的文件等。
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- File f = new File("dir");
- f.createNewFile();// 創建一個.txt這個文件
- f.mkdir();// 創建一個名為.txt的目錄
- /*
- * 使用絕對路徑
- *
- * File f=new File("D:\\dir\\src\\A.java");
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- */
- /*
- * 跨平臺使用
- *
- * 根據不同操作系統獲得對應的分隔符 File fDir=new File(File.separator);
- *
- * String strFile="dir"+File.separator+"src"+File.separator +"A.java";
- *
- * File f=new File(fDir,strFile);
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- *
- * f.delete();//刪除文件或目錄
- *
- * //f.deleteOnExit();
- */
- /*
- * 在缺省的臨時文件目錄下創建臨時文件
- *
- * for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
- *
- * {
- *
- * File f=File.createTempFile("winTemp",".tmp");
- *
- * f.deleteOnExit();//退出時刪除
- *
- *
- *
- * }
- */
- /*
- * 列出指定目錄下所有子目錄及文件的名稱
- */
- File fDir = new File(File.separator);
- String strFile = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- File f = new File(fDir, strFile);
- String[] names = f.list();
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- // 有過濾器的情況FilenameFilter是個接口
- File dir = new File(File.separator);
- String filepath = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- /**
- * dir
- * 上級抽象路徑,如果dir為null,那么程序將自動調用單個參數的File構造方法,同時將filepath路徑應用到File但構造參數
- * 如果dir為//,則此路徑為本文件所在磁盤根目錄
- */
- File f = new File(dir, filepath);
- if (f.exists()) {
- } else {
- f.mkdirs();
- }
- String[] names = f.list(new FilenameFilter() { // 實現了FilenameFilter接口的匿名類,實現accept方法過濾文件
- @Override
- public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
- System.out.println(name.indexOf(".java"));
- return name.indexOf(".java") != -1;
- }
- });
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- }
#p#
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- File f = new File("dir");
- f.createNewFile();// 創建一個.txt這個文件
- f.mkdir();// 創建一個名為.txt的目錄
- /*
- * 使用絕對路徑
- *
- * File f=new File("D:\\dir\\src\\A.java");
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- */
- /*
- * 跨平臺使用
- *
- * 根據不同操作系統獲得對應的分隔符 File fDir=new File(File.separator);
- *
- * String strFile="dir"+File.separator+"src"+File.separator +"A.java";
- *
- * File f=new File(fDir,strFile);
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- *
- * f.delete();//刪除文件或目錄
- *
- * //f.deleteOnExit();
- */
- /*
- * 在缺省的臨時文件目錄下創建臨時文件
- *
- * for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
- *
- * {
- *
- * File f=File.createTempFile("winTemp",".tmp");
- *
- * f.deleteOnExit();//退出時刪除
- *
- *
- *
- * }
- */
- /*
- * 列出指定目錄下所有子目錄及文件的名稱
- */
- File fDir = new File(File.separator);
- String strFile = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- File f = new File(fDir, strFile);
- String[] names = f.list();
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- // 有過濾器的情況FilenameFilter是個接口
- File dir = new File(File.separator);
- String filepath = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- /**
- * dir
- * 上級抽象路徑,如果dir為null,那么程序將自動調用單個參數的File構造方法,同時將filepath路徑應用到File但構造參數
- * 如果dir為//,則此路徑為本文件所在磁盤根目錄
- */
- File f = new File(dir, filepath);
- if (f.exists()) {
- } else {
- f.mkdirs();
- }
- String[] names = f.list(new FilenameFilter() { // 實現了FilenameFilter接口的匿名類,實現accept方法過濾文件
- @Override
- public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
- System.out.println(name.indexOf(".java"));
- return name.indexOf(".java") != -1;
- }
- });
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
- File f = new File("dir");
- f.createNewFile();// 創建一個.txt這個文件
- f.mkdir();// 創建一個名為.txt的目錄
- /*
- * 使用絕對路徑
- *
- * File f=new File("D:\\dir\\src\\A.java");
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- */
- /*
- * 跨平臺使用
- *
- * 根據不同操作系統獲得對應的分隔符 File fDir=new File(File.separator);
- *
- * String strFile="dir"+File.separator+"src"+File.separator +"A.java";
- *
- * File f=new File(fDir,strFile);
- *
- * f.createNewFile();
- *
- * f.delete();//刪除文件或目錄
- *
- * //f.deleteOnExit();
- */
- /*
- * 在缺省的臨時文件目錄下創建臨時文件
- *
- * for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
- *
- * {
- *
- * File f=File.createTempFile("winTemp",".tmp");
- *
- * f.deleteOnExit();//退出時刪除
- *
- *
- *
- * }
- */
- /*
- * 列出指定目錄下所有子目錄及文件的名稱
- */
- File fDir = new File(File.separator);
- String strFile = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- File f = new File(fDir, strFile);
- String[] names = f.list();
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- // 有過濾器的情況FilenameFilter是個接口
- File dir = new File(File.separator);
- String filepath = "dir" + File.separator + "src";
- /**
- * dir
- * 上級抽象路徑,如果dir為null,那么程序將自動調用單個參數的File構造方法,同時將filepath路徑應用到File但構造參數
- * 如果dir為//,則此路徑為本文件所在磁盤根目錄
- */
- File f = new File(dir, filepath);
- if (f.exists()) {
- } else {
- f.mkdirs();
- }
- String[] names = f.list(new FilenameFilter() { // 實現了FilenameFilter接口的匿名類,實現accept方法過濾文件
- @Override
- public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
- System.out.println(name.indexOf(".java"));
- return name.indexOf(".java") != -1;
- }
- });
- for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(names[i]);
- }
- }
#p#
RandomAccessFile(隨機文件讀寫類):
(1)RandomAccessFile類:它直接繼承于Object類而非InputStream/OutputStream類,從而可以實現讀寫文件中任何位置中的數據(只需要改變文件的讀寫位置的指針)。
(2)由于RandomAccessFile類實現了DataOutput與DataInput接口,因而利用它可以讀寫Java中的不同類型的基本類型數據(比如采用readLong()方法讀取長整數,而利用 readInt()方法可以讀出整數值等)。
RandomFileRW.java
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
- public class RandomFileRW {
- public static void main(String args[]) {
- StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
- char ch;
- try {
- while ((ch = (char) System.in.read()) != '\n') {
- buf.append(ch);
- }
- // 讀寫方式可以為"r" or "rw"
- /**
- * @param mode 1. r 2. rw 3. rws 4. rwd
- * "r" Open for reading only. Invoking any of the write methods of the resulting object will
- * cause an IOException to be thrown.
- * "rw" Open for reading and writing. If the file does not already exist then an attempt will
- * be made to create it.
- * "rws" Open for reading and writing, as with "rw", and also require that every update to the
- * file's content or metadata be written synchronously to the underlying storage device.
- * "rwd" Open for reading and writing, as with "rw", and also require that every update to the
- * file's content be written synchronously to the underlying storage device.
- */
- RandomAccessFile myFileStream = new RandomAccessFile("c:\\UserInput.txt", "rw");
- myFileStream.seek(myFileStream.length());
- myFileStream.writeBytes(buf.toString());
- // 將用戶從鍵盤輸入的內容添加到文件的尾部
- myFileStream.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- }
- }
- }
原文鏈接http://blog.csdn.net/zhouzhiwengang/article/details/10427717: