Kafka消費與心跳機制
1.概述
最近有同學咨詢Kafka的消費和心跳機制,今天筆者將通過這篇博客來逐一介紹這些內容。
2.內容
2.1 Kafka消費
首先,我們來看看消費。Kafka提供了非常簡單的消費API,使用者只需初始化Kafka的Broker Server地址,然后實例化KafkaConsumer類即可拿到Topic中的數據。一個簡單的Kafka消費實例代碼如下所示:
- public class JConsumerSubscribe extends Thread {
- public static void main(String[] args) { JConsumerSubscribe jconsumer = new JConsumerSubscribe(); jconsumer.start(); } /** 初始化Kafka集群信息. */ private Properties configure() { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("bootstrap.servers", "dn1:9092,dn2:9092,dn3:9092");// 指定Kafka集群地址
- props.put("group.id", "ke");// 指定消費者組
- props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true");// 開啟自動提交
- props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");// 自動提交的時間間隔
- // 反序列化消息主鍵 props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
- // 反序列化消費記錄 props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
- return props;
- } /** 實現一個單線程消費者. */ @Override public void run() { // 創建一個消費者實例對象 KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(configure()); // 訂閱消費主題集合 consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("test_kafka_topic"));
- // 實時消費標識 boolean flag = true;
- while (flag) {
- // 獲取主題消息數據 ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
- for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records)
- // 循環打印消息記錄 System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
- } // 出現異常關閉消費者對象 consumer.close();
- }}
上述代碼我們就可以非常便捷的拿到Topic中的數據。但是,當我們調用poll方法拉取數據的時候,Kafka Broker Server做了那些事情。接下來,我們可以去看看源代碼的實現細節。核心代碼如下:
org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer
- private ConsumerRecords<K, V> poll(final long timeoutMs, final boolean includeMetadataInTimeout) {
- acquireAndEnsureOpen(); try {
- if (timeoutMs < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Timeout must not be negative");
- if (this.subscriptions.hasNoSubscriptionOrUserAssignment()) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("Consumer is not subscribed to any topics or assigned any partitions");
- } // poll for new data until the timeout expires
- long elapsedTime = 0L;
- do {
- client.maybeTriggerWakeup(); final long metadataEnd; if (includeMetadataInTimeout) {
- final long metadataStart = time.milliseconds(); if (!updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded(remainingTimeAtLeastZero(timeoutMs, elapsedTime))) {
- return ConsumerRecords.empty();
- } metadataEnd = time.milliseconds(); elapsedTime += metadataEnd - metadataStart; } else {
- while (!updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded(Long.MAX_VALUE)) {
- log.warn("Still waiting for metadata");
- } metadataEnd = time.milliseconds(); } final Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records = pollForFetches(remainingTimeAtLeastZero(timeoutMs, elapsedTime)); if (!records.isEmpty()) {
- // before returning the fetched records, we can send off the next round of fetches
- // and avoid block waiting for their responses to enable pipelining while the user
- // is handling the fetched records.
- //
- // NOTE: since the consumed position has already been updated, we must not allow
- // wakeups or any other errors to be triggered prior to returning the fetched records.
- if (fetcher.sendFetches() > 0 || client.hasPendingRequests()) {
- client.pollNoWakeup(); } return this.interceptors.onConsume(new ConsumerRecords<>(records));
- } final long fetchEnd = time.milliseconds(); elapsedTime += fetchEnd - metadataEnd; } while (elapsedTime < timeoutMs);
- return ConsumerRecords.empty();
- } finally {
- release(); } }
上述代碼中有個方法pollForFetches,它的實現邏輯如下:
- private Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> pollForFetches(final long timeoutMs) {
- final long startMs = time.milliseconds();
- long pollTimeout = Math.min(coordinator.timeToNextPoll(startMs), timeoutMs);
- // if data is available already, return it immediately
- final Map<TopicPartition, List<ConsumerRecord<K, V>>> records = fetcher.fetchedRecords();
- if (!records.isEmpty()) {
- return records;
- }
- // send any new fetches (won't resend pending fetches)
- fetcher.sendFetches();
- // We do not want to be stuck blocking in poll if we are missing some positions
- // since the offset lookup may be backing off after a failure
- // NOTE: the use of cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions means we MUST call
- // updateAssignmentMetadataIfNeeded before this method.
- if (!cachedSubscriptionHashAllFetchPositions && pollTimeout > retryBackoffMs) {
- pollTimeout = retryBackoffMs;
- }
- client.poll(pollTimeout, startMs, () -> {
- // since a fetch might be completed by the background thread, we need this poll condition
- // to ensure that we do not block unnecessarily in poll()
- return !fetcher.hasCompletedFetches();
- });
- // after the long poll, we should check whether the group needs to rebalance
- // prior to returning data so that the group can stabilize faster
- if (coordinator.rejoinNeededOrPending()) {
- return Collections.emptyMap();
- }
- return fetcher.fetchedRecords();
- }
上述代碼中加粗的位置,我們可以看出每次消費者客戶端拉取數據時,通過poll方法,先調用fetcher中的fetchedRecords函數,如果獲取不到數據,就會發起一個新的sendFetches請求。而在消費數據的時候,每個批次從Kafka Broker Server中拉取數據是有最大數據量限制,默認是500條,由屬性(max.poll.records)控制,可以在客戶端中設置該屬性值來調整我們消費時每次拉取數據的量。
提示:這里需要注意的是,max.poll.records返回的是一個poll請求的數據總和,與多少個分區無關。因此,每次消費從所有分區中拉取Topic的數據的總條數不會超過max.poll.records所設置的值。
而在Fetcher的類中,在sendFetches方法中有限制拉取數據容量的限制,由屬性(max.partition.fetch.bytes),默認1MB。可能會有這樣一個場景,當滿足max.partition.fetch.bytes限制條件,如果需要Fetch出10000條記錄,每次默認500條,那么我們需要執行20次才能將這一次通過網絡發起的請求全部Fetch完畢。
這里,可能有同學有疑問,我們不能將默認的max.poll.records屬性值調到10000嗎?可以調,但是還有個屬性需要一起配合才可以,這個就是每次poll的超時時間(Duration.ofMillis(100)),這里需要根據你的實際每條數據的容量大小來確定設置超時時間,如果你將最大值調到10000,當你每條記錄的容量很大時,超時時間還是100ms,那么可能拉取的數據少于10000條。
而這里,還有另外一個需要注意的事情,就是會話超時的問題。session.timeout.ms默認是10s,group.min.session.timeout.ms默認是6s,group.max.session.timeout.ms默認是30min。當你在處理消費的業務邏輯的時候,如果在10s內沒有處理完,那么消費者客戶端就會與Kafka Broker Server斷開,消費掉的數據,產生的offset就沒法提交給Kafka,因為Kafka Broker Server此時認為該消費者程序已經斷開,而即使你設置了自動提交屬性,或者設置auto.offset.reset屬性,你消費的時候還是會出現重復消費的情況,這就是因為session.timeout.ms超時的原因導致的。
2.2 心跳機制
上面在末尾的時候,說到會話超時的情況導致消息重復消費,為什么會有超時?有同學會有這樣的疑問,我的消費者線程明明是啟動的,也沒有退出,為啥消費不到Kafka的消息呢?消費者組也查不到我的ConsumerGroupID呢?這就有可能是超時導致的,而Kafka是通過心跳機制來控制超時,心跳機制對于消費者客戶端來說是無感的,它是一個異步線程,當我們啟動一個消費者實例時,心跳線程就開始工作了。
在org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.AbstractCoordinator中會啟動一個HeartbeatThread線程來定時發送心跳和檢測消費者的狀態。每個消費者都有個org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.ConsumerCoordinator,而每個ConsumerCoordinator都會啟動一個HeartbeatThread線程來維護心跳,心跳信息存放在org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.Heartbeat中,聲明的Schema如下所示:
- private final int sessionTimeoutMs;
- private final int heartbeatIntervalMs;
- private final int maxPollIntervalMs;
- private final long retryBackoffMs;
- private volatile long lastHeartbeatSend;
- private long lastHeartbeatReceive;
- private long lastSessionReset;
- private long lastPoll;
- private boolean heartbeatFailed;
心跳線程中的run方法實現代碼如下:
- public void run() {
- try {
- log.debug("Heartbeat thread started");
- while (true) {
- synchronized (AbstractCoordinator.this) {
- if (closed)
- return;
- if (!enabled) {
- AbstractCoordinator.this.wait();
- continue;
- } if (state != MemberState.STABLE) {
- // the group is not stable (perhaps because we left the group or because the coordinator
- // kicked us out), so disable heartbeats and wait for the main thread to rejoin.
- disable();
- continue;
- }
- client.pollNoWakeup();
- long now = time.milliseconds();
- if (coordinatorUnknown()) {
- if (findCoordinatorFuture != null || lookupCoordinator().failed())
- // the immediate future check ensures that we backoff properly in the case that no
- // brokers are available to connect to.
- AbstractCoordinator.this.wait(retryBackoffMs);
- } else if (heartbeat.sessionTimeoutExpired(now)) {
- // the session timeout has expired without seeing a successful heartbeat, so we should
- // probably make sure the coordinator is still healthy.
- markCoordinatorUnknown();
- } else if (heartbeat.pollTimeoutExpired(now)) {
- // the poll timeout has expired, which means that the foreground thread has stalled
- // in between calls to poll(), so we explicitly leave the group.
- maybeLeaveGroup();
- } else if (!heartbeat.shouldHeartbeat(now)) {
- // poll again after waiting for the retry backoff in case the heartbeat failed or the
- // coordinator disconnected
- AbstractCoordinator.this.wait(retryBackoffMs);
- } else {
- heartbeat.sentHeartbeat(now);
- sendHeartbeatRequest().addListener(new RequestFutureListener<Void>() {
- @Override
- public void onSuccess(Void value) {
- synchronized (AbstractCoordinator.this) {
- heartbeat.receiveHeartbeat(time.milliseconds());
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) {
- synchronized (AbstractCoordinator.this) {
- if (e instanceof RebalanceInProgressException) {
- // it is valid to continue heartbeating while the group is rebalancing. This
- // ensures that the coordinator keeps the member in the group for as long
- // as the duration of the rebalance timeout. If we stop sending heartbeats,
- // however, then the session timeout may expire before we can rejoin.
- heartbeat.receiveHeartbeat(time.milliseconds());
- } else {
- heartbeat.failHeartbeat();
- // wake up the thread if it's sleeping to reschedule the heartbeat
- AbstractCoordinator.this.notify();
- }
- }
- }
- });
- }
- }
- }
- } catch (AuthenticationException e) {
- log.error("An authentication error occurred in the heartbeat thread", e);
- this.failed.set(e);
- } catch (GroupAuthorizationException e) {
- log.error("A group authorization error occurred in the heartbeat thread", e);
- this.failed.set(e);
- } catch (InterruptedException | InterruptException e) {
- Thread.interrupted();
- log.error("Unexpected interrupt received in heartbeat thread", e);
- this.failed.set(new RuntimeException(e));
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- log.error("Heartbeat thread failed due to unexpected error", e);
- if (e instanceof RuntimeException)
- this.failed.set((RuntimeException) e);
- else
- this.failed.set(new RuntimeException(e));
- } finally {
- log.debug("Heartbeat thread has closed");
- }
- }
- View Code
在心跳線程中這里面包含兩個最重要的超時函數,它們是sessionTimeoutExpired和pollTimeoutExpired。
- public boolean sessionTimeoutExpired(long now) {
- return now - Math.max(lastSessionReset, lastHeartbeatReceive) > sessionTimeoutMs;
- }public boolean pollTimeoutExpired(long now) {
- return now - lastPoll > maxPollIntervalMs;
- }
2.2.1 sessionTimeoutExpired
如果是sessionTimeout超時,則會被標記為當前協調器處理斷開,此時,會將消費者移除,重新分配分區和消費者的對應關系。在Kafka Broker Server中,Consumer Group定義了5中(如果算上Unknown,應該是6種狀態)狀態,org.apache.kafka.common.ConsumerGroupState,如下圖所示:
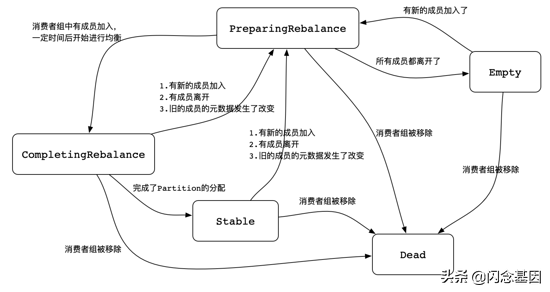
2.2.2 pollTimeoutExpired
如果觸發了poll超時,此時消費者客戶端會退出ConsumerGroup,當再次poll的時候,會重新加入到ConsumerGroup,觸發RebalanceGroup。而KafkaConsumer Client是不會幫我們重復poll的,需要我們自己在實現的消費邏輯中不停的調用poll方法。
3.分區與消費線程
關于消費分區與消費線程的對應關系,理論上消費線程數應該小于等于分區數。之前是有這樣一種觀點,一個消費線程對應一個分區,當消費線程等于分區數是最大化線程的利用率。直接使用KafkaConsumer Client實例,這樣使用確實沒有什么問題。但是,如果我們有富裕的CPU,其實還可以使用大于分區數的線程,來提升消費能力,這就需要我們對KafkaConsumer Client實例進行改造,實現消費策略預計算,利用額外的CPU開啟更多的線程,來實現消費任務分片。具體實現,留到下一篇博客,給大家分享《基于Kafka的分布式查詢SQL引擎》。
4.結束語
這篇博客就和大家分享到這里,如果大家在研究學習的過程當中有什么問題,可以加群進行討論或發送郵件給我,我會盡我所能為您解答,與君共勉!








































