什么,你還不會用CompletableFuture?
上一篇我們講了Future機制,有興趣的可以參考談談Future、Callable、FutureTask關系
但Future機制,還不那么靈活,比如怎么去利用Future機制描述兩個任務串行執行,又或是兩個任務并行執行,又或是只關心最先執行結束的任務結果。
Future機制在一定程度上都無法快速地滿足以上需求,CompletableFuture便應運而生了。
本片會介紹CompletableFuture的api,并用一些示例演示如何去使用。
1. 創建一個異步任務
- public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
- public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor);
- public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
- public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor);
supplyAsync與runAsync的區別在于:supplyAsync有返回值,而runAsync沒有返回值
帶Executor參數的構造函數,則使用線程池中的線程執行異步任務(線程池可以參考說說線程池)
不帶Executor參數的構造函數,則使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()中的線程執行異步任務(Fork/Join框架可以參考談談并行流parallelStream)
1.1 示例:使用supplyAsync創建一個有返回值的異步任務
- public class Case1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
- try {
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return 1;
- });
- //該方法會一直阻塞
- Integer result = completableFuture.get();
- System.out.println(result);
- }
- }
2. 異步任務的回調
- public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
- public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
- public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor);
- public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
whenComplete開頭的方法在計算任務完成(包括正常完成與出現異常)之后會回調
而exceptionally則只會在計算任務出現異常時才會被回調
如何確定哪個線程去回調whenComplete,比較復雜,先略過。
而回調whenCompleteAsync的線程比較簡單,隨便拿一個空閑的線程即可,后綴是Async的方法同理。
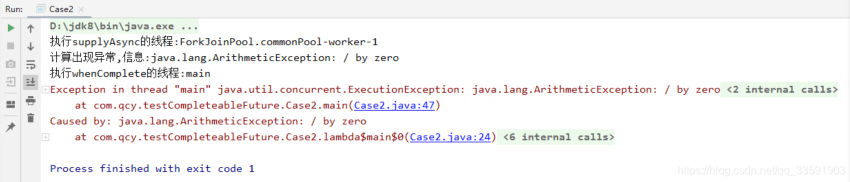
2.1 示例:計算出現異常,使用whenComplete與exceptionally進行處理
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
- import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
- import java.util.function.Function;
- import java.util.stream.IntStream;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- Thread.sleep(1000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("執行supplyAsync的線程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- int i = 1 / 0;
- return 1;
- });
- completableFuture.whenComplete(new BiConsumer<Integer, Throwable>() {
- @Override
- public void accept(Integer integer, Throwable throwable) {
- System.out.println("執行whenComplete的線程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- if (throwable == null) {
- System.out.println("計算未出現異常,結果:" + integer);
- }
- }
- });
- completableFuture.exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, Integer>() {
- @Override
- public Integer apply(Throwable throwable) {
- //出現異常時,則返回一個默認值
- System.out.println("計算出現異常,信息:" + throwable.getMessage());
- return -1;
- }
- });
- System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
- }
- }
輸出:
當然,CompletableFuture內的各種方法是支持鏈式調用與Lambda表達式的,我們進行如下改寫:
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- try {
- Thread.sleep(2000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("執行supplyAsync的線程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- int i = 1 / 0;
- return 1;
- }).whenComplete((integer, throwable) -> {
- System.out.println("執行whenComplete的線程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- if (throwable == null) {
- System.out.println("計算未出現異常,結果:" + integer);
- }
- }).exceptionally(throwable -> {
- //出現異常時,則返回一個默認值
- System.out.println("計算出現異常,信息:" + throwable.getMessage());
- return -1;
- });
- System.out.println("計算結果:" + completableFuture.get());
- }
3. 任務串行化執行
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
- public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
- public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
thenApply,依賴上一次任務執行的結果,參數中的Function<? super T,? extends U>,T代表上一次任務返回值的類型,U代表當前任務返回值的類型,當上一個任務沒有出現異常時,thenApply才會被調用
thenRun,不需要知道上一個任務的返回結果,只是在上一個任務執行完成之后開始執行Runnable
thenAccept,依賴上一次任務的執行結果,因為入參是Consumer,所以不返回任何值。
handle和thenApply相似,不過當上一個任務出現異常時,能夠執行handle,卻不會去執行thenApply
thenCompose,傳入一次任務執行的結果,返回一個新的CompleteableFuture對象
3.1 示例:使用串行化任務分解兩數相乘并輸出
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case4 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 2)
- .thenApply(num -> num * 3)
- .thenAccept(System.out::print);
- }
- }
很顯然,輸出為6
3.2 示例:使用串行化任務并且模擬出現異常
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- import java.util.function.BiFunction;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case4 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 2)
- .thenApply(num -> num / 0)
- .thenApply(result -> result * 3)
- .handle((integer, throwable) -> {
- if (throwable == null) {
- return integer;
- } else {
- throwable.printStackTrace();
- return -1;
- }
- }).thenAccept(System.out::print);
- }
- }
最終會輸出-1
4. 任務同時執行,且都需要執行完成
- public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
- Function<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
- public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
- Consumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
- public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
- public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
thenCombine,合并兩個任務,兩個任務可以同時執行,都執行成功后,執行最后的BiFunction操作。其中T代表第一個任務的執行結果類型,U代表第二個任務的執行結果類型,V代表合并的結果類型
thenAcceptBoth,和thenCombine特性用法都極其相似,唯一的區別在于thenAcceptBoth進行一個消費,沒有返回值
runAfterBoth,兩個任務都執行完成后,但不關心他們的返回結構,然后去執行一個Runnable。
allOf,當所有的任務都執行完成后,返回一個CompletableFuture
4.1 示例:使用thenCombine合并任務
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case5 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務1開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務1結束");
- return 2;
- });
- CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務2開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務2結束");
- return 3;
- });
- CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = cf1.thenCombine(cf2, (result1, result2) -> result1 * result2);
- System.out.println("計算結果:" + completableFuture.get());
- }
- }
輸出:
可以看到兩個任務確實是同時執行的
當然,熟練了之后,直接使用鏈式操作,代碼如下:
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case6 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務1開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務1結束");
- return 2;
- }).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務2開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(2000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務2結束");
- return 3;
- }), (result1, result2) -> result1 * result2);
- System.out.println("計算結果:" + completableFuture.get());
- }
- }
5. 任務同時執行,且只取最先完成的那個任務
- public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn);
- public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action);
- public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
- public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
applyToEither,最新執行完任務,將其結果執行Function操作,其中T是最先執行完的任務結果類型,U是最后輸出的類型
acceptEither,最新執行完的任務,將其結果執行消費操作
runAfterEither,任意一個任務執行完成之后,執行Runnable操作
anyOf,多個任務中,返回最先執行完成的CompletableFuture
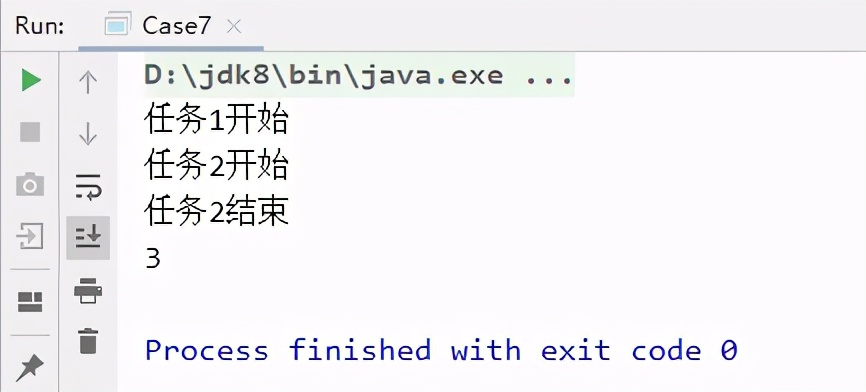
5.1 示例:兩個任務同時執行,打印最先完成的任務的結果
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case7 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務1開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務1結束");
- return 2;
- }).acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務2開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(2000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務2結束");
- return 3;
- }), result -> System.out.println(result));
- //等待CompletableFuture返回,防止主線程退出
- completableFuture.join();
- }
- }
輸出:
可以看得到,任務2結束后,直接不再執行任務1的剩余代碼
5.2 示例:多個任務同時執行,打印最先完成的任務的結果
- package com.qcy.testCompleteableFuture;
- import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
- /**
- * @author qcy
- * @create 2020/09/07 17:40:44
- */
- public class Case8 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- CompletableFuture<Integer> cf1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務1開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(3000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務1結束");
- return 2;
- });
- CompletableFuture<Integer> cf2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務2開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(2000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務2結束");
- return 3;
- });
- CompletableFuture<Integer> cf3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
- System.out.println("任務3開始");
- try {
- Thread.sleep(4000);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("任務3結束");
- return 4;
- });
- CompletableFuture<Object> firstCf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf1, cf2, cf3);
- System.out.println(firstCf.get());
- }
- }
輸出: