Spring Security權限控制系列(六)

環境:Springboot2.4.12 + Spring Security 5.4.9
本篇主要內容:
- 業務接口權限認證
上一篇:《??Spring Security權限控制系列(五)??》
演示案例
有如下接口:
("/business")
public class BussinessController {
("/{id}")
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
}
安全配置:
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable() ;
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/resources/**", "/cache/**", "/process/login").permitAll() ;
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/demos/**").hasRole("USERS") ;
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/api/**").hasRole("ADMIN") ;
// 上面的配置都是基于之前的文章,這里我們不需要關心,僅僅看下面這個接口配置接口
// 這里我們會要求所有以/business開始的所有請求
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/business/**").authenticated() ;
}
}
有了上面的配置,啟動服務訪問http://localhost:8080/business/100接口時會要求登錄,只要登錄成功,接口就可以訪問。
這里我不希望通過如下方式進行的權限設置:
// hasRole("xxx") 或 hasAuthority("xxxx")
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/business/**").hasRole("xxx")
這種寫法限定了所有的/business開頭的請求都由于固定的權限,/business可能會有很多的子接口,每種子接口可能我們都需要定義不同的權限才可訪問,這時候如果在通過上面的方式配置就太繁瑣了。Spring Security還提供了基于訪問注解的方式細化接口權限的控制定義,接下來使用基于注解的方式控制Controller接口權限。
注意:并不是基于注解的權限控制只能應用到Controller上,只是我們一般都會加到Controller上;其實任何Service方法都是可以使用的。這些注解也可以直接加到接口方法上。
開啟方法認證
(jsr250Enabled = true, prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
屬性說明:
jsr250Enabled:啟用對JSR-250注釋的支持。@RolesAllowed。
prePostEnabled:啟用基于表達式的語法支持(jsr250Enabled和securedEnabled都是基于簡單角色的約束)。@PreAuthorize。
securedEnabled:啟用@Secured注解的支持。
示例:
("/{id}")
("ROLE_USERS") // ①
("ROLE_USERS1") // ②
("hasRole('USERS')") // ③
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
- 接收一個String[] 數組,可以定義多個角色。
- 接收一個String[] 數組,可以定義多個角色。
- 可以使用SpEL表達式。
本篇內容只演示基于@PreAuthorize注解的權限控制,其它兩個都非常簡單不做演示。
PreAuthorize注解使用
該注解用于指定方法訪問控制表達式的注釋,該表達式將被計算以確定是否允許方法調用。默認支持的如下表達式:
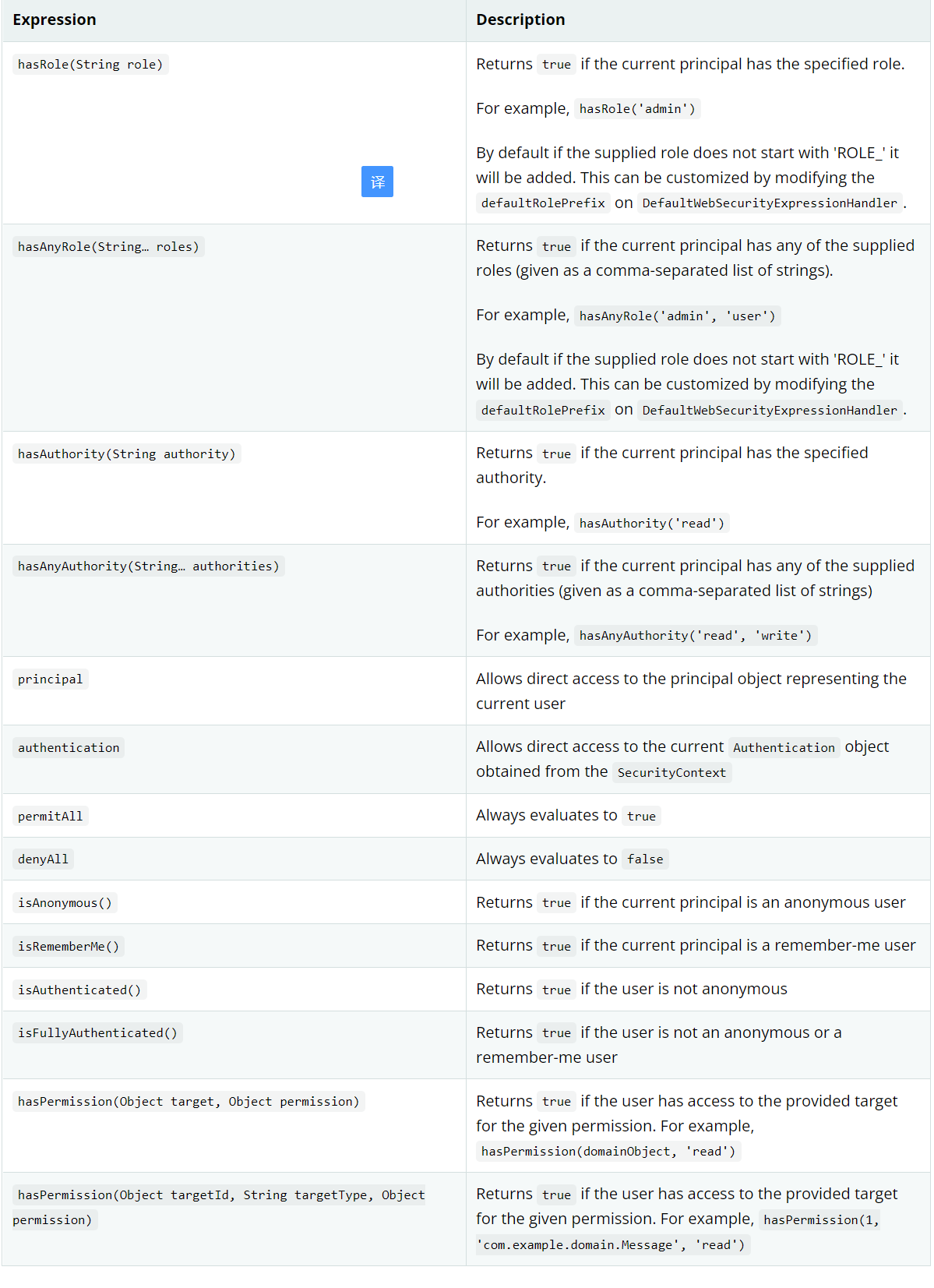
示例1:
訪問該接口必須具備USERS角色。
("hasRole('USERS')")
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
示例2:
訪問該接口只要具有其中任意一種角色即可。
("hasAnyRole('USERS', 'ADMIN')")
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
示例3:
訪問該接口必須擁有bus:news:see權限。
("hasAuthority('bus:news:see')")
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
實例4:
該接口只要擁有如下任意一個權限即可。
("hasAnyAuthority('bus:news:see', 'bus:news:write')")
public Object get(("id") Integer id) {
return "receive - " + id ;
}
注意:這里的hasRole和hasAuthority區別?
權限認證使用的 表達式根對象的基類是SecurityExpressionRoot。該基類中實現了相應方法的調用
public abstract class SecurityExpressionRoot implements SecurityExpressionOperations {
private String defaultRolePrefix = "ROLE_";
public final boolean hasRole(String role) {
return hasAnyRole(role);
}
public final boolean hasAnyRole(String... roles) {
return hasAnyAuthorityName(this.defaultRolePrefix, roles);
}
public final boolean hasAuthority(String authority) {
return hasAnyAuthority(authority);
}
public final boolean hasAnyAuthority(String... authorities) {
return hasAnyAuthorityName(null, authorities);
}
private boolean hasAnyAuthorityName(String prefix, String... roles) {
Set<String> roleSet = getAuthoritySet();
for (String role : roles) {
// 拼接ROLE_前綴
String defaultedRole = getRoleWithDefaultPrefix(prefix, role);
if (roleSet.contains(defaultedRole)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
通過上面的源碼知道,不管是hasRole還是hasAuthority最終都是調用的hasAnyAuthorityName方法,而hasRole方法拼接ROLE_前綴。
總結:
- 業務接口Controller權限控制個各種方式。