兩萬字 + 十張圖剖析Spring依賴注入和SpEL表達式

一、setter屬性注入
1、使用XML進行setter方法注入
我們在前面的文章中已經使用過XML進行setter方法的屬性注入了,下面讓我們再來回顧一下:
<bean id="userSetter" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">
<property name="username" value="example-username-setter"/>
<property name="age" value="25"/>
</bean>2、使用@Bean注解進行setter方法注入
我們在前面的文章中也學習過如何在bean創建時通過編程方式設置屬性:
@Bean
public User user() {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");
user.setAge(25);
return user;
}3、setter方法注入完整代碼示例
使用XML進行setter方法注入。
首先,我們需要創建一個User類,并在其中包含username和age兩個屬性,以及相應的getter、setter方法和構造器。
public class User {
private String username;
private Integer age;
public User() {}
// 為了節省篇幅,getter和setter方法省略......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{username='" + username + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}對于XML方式的setter注入和構造器注入,我們需要創建一個配置文件,比如叫applicationContext.xml。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- setter方法注入 -->
<bean id="userSetter" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">
<property name="username" value="example-username-setter"/>
<property name="age" value="25"/>
</bean>
</beans>然后,我們需要創建一個DemoApplication類,使用ApplicationContext來加載配置文件并獲取Bean:
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
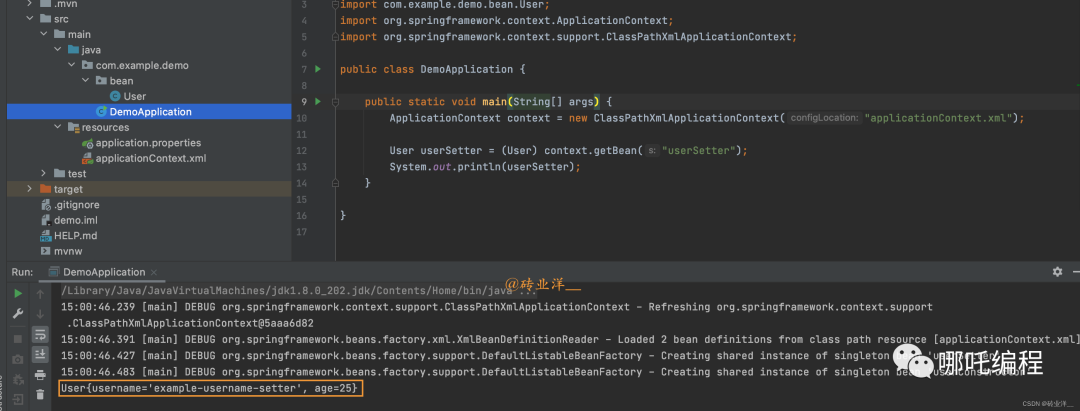
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");
System.out.println(userSetter);
}
}運行結果如下:
使用@Bean注解進行setter方法注入。
我們需要創建一個配置類,例如叫AppConfig.java:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public User userSetter() {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");
user.setAge(25);
return user;
}
}使用@Bean注解來定義Bean。每個@Bean方法對應于XML配置中的一個元素。這個方法的名稱就是Bean的id,方法的返回值就是Bean的類型。
然后修改主程序,這里使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext來創建Spring的應用上下文,并加載配置類。Spring會自動從配置類中獲取所有的Bean定義,并創建相應的Bean實例。
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import com.example.demo.configuration.AppConfig;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
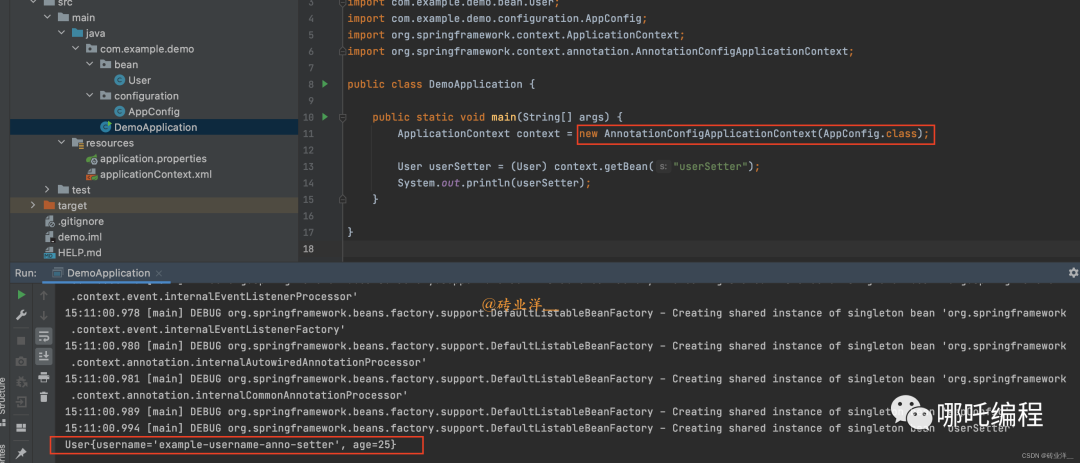
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");
System.out.println(userSetter);
}
}運行結果如下:
注意:XML配置方式已經相對陳舊,而且在Spring Boot項目中,主流的做法是使用注解和Java配置方式。對于setter注入,有時會引發循環依賴的問題。在Spring中,可以使用構造器注入來避免這種情況,這里了解即可。
二、構造器注入
setter注入是一種在對象被實例化之后(通過調用無參構造器創建實例)再通過setter方法注入依賴的方式。構造器注入則是在創建對象實例的時候就通過構造器參數來注入依賴。
為了演示構造器注入,我們需要給User添加一個全參數構造器:
public User(String username, Integer age) {
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
}添加這個構造器后,Java不再提供默認的無參構造器,這會導致我們之前的標簽創建時失敗,因為它找不到默認的構造器。
1、使用XML進行構造器注入
我們可以在標簽內部聲明一個子標簽:constructor-arg。它用于指定構造器的參數,來進行屬性注入。constructor-arg標簽的編寫規則如下:
<bean id="userConstructor" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="example-username-constructor"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="25"/>
</bean>index屬性表示構造函數參數的位置,它的值是一個非負整數,其中0表示第一個參數,1表示第二個參數,以此類推。雖然value屬性的值總是一個字符串,但是Spring會嘗試將它轉換為構造函數參數所需的類型。例如構造函數的第二個參數是int類型,那么Spring會嘗試將字符串"25"轉換為整數25。
使用index屬性來指定構造函數參數的位置在大多數情況下是可以的,但是如果構造函數的參數數量或者順序發生了改變,就可能會出錯。另外一種更為可靠的方式是使用name屬性來指定參數的名稱,如:
<bean id="userConstructor" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="username" value="example-username-constructor"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="25"/>
</bean>這樣無論參數的順序如何,只要參數名稱不變,就不會出錯。
2、使用@Bean注解進行構造器屬性注入
在注解驅動的bean注冊中,我們也可以直接使用編程方式賦值:
@Bean
public User user() {
return new User("example-username-anno-constructor", 25);
}3、構造器注入的完整代碼示例
使用XML進行構造器注入。
首先,我們需要創建一個User類,并在其中包含username和age兩個屬性,以及相應的getter、setter方法和構造器。
public class User {
private String username;
private Integer age;
public User() {}
public User(String username, Integer age) {
this.username = username;
this.age = age;
}
// 為了節省篇幅,getter和setter方法省略......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{username='" + username + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}對于XML方式的構造器注入,我們需要創建一個配置文件,比如叫applicationContext.xml,這里保留setter注入方便大家對比。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- setter方法注入 -->
<!-- setter方法注入 -->
<!-- <bean id="userSetter" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">-->
<!-- <property name="username" value="example-username-setter"/>-->
<!-- <property name="age" value="25"/>-->
<!-- </bean>-->
<!-- 構造器注入 -->
<bean id="userConstructor" class="com.example.demo.bean.User">
<constructor-arg name="username" value="example-username-constructor"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="25"/>
</bean>
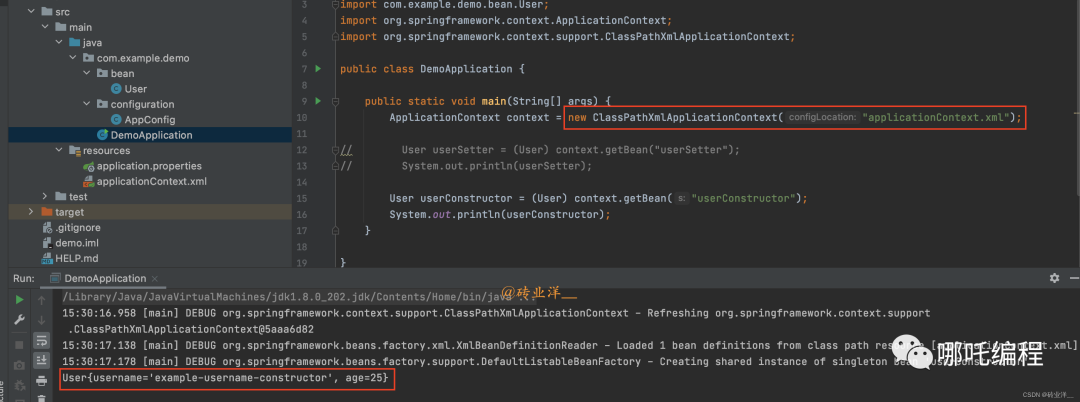
</beans>然后,我們需要創建一個DemoApplication類,使用ApplicationContext來加載配置文件并獲取Bean:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");
// System.out.println(userSetter);
User userConstructor = (User) context.getBean("userConstructor");
System.out.println(userConstructor);
}
}然后,我們需要創建一個DemoApplication類,使用ApplicationContext來加載配置文件并獲取Bean:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");
// System.out.println(userSetter);
User userConstructor = (User) context.getBean("userConstructor");
System.out.println(userConstructor);
}
}運行結果如下:
使用@Bean注解進行構造器屬性注入。
我們需要創建一個配置類,例如叫AppConfig.java:
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
// @Bean
// public User userSetter() {
// User user = new User();
// user.setUsername("example-username-anno-setter");
// user.setAge(25);
// return user;
// }
@Bean
public User userConstructor() {
return new User("example-username-anno-constructor", 25);
}
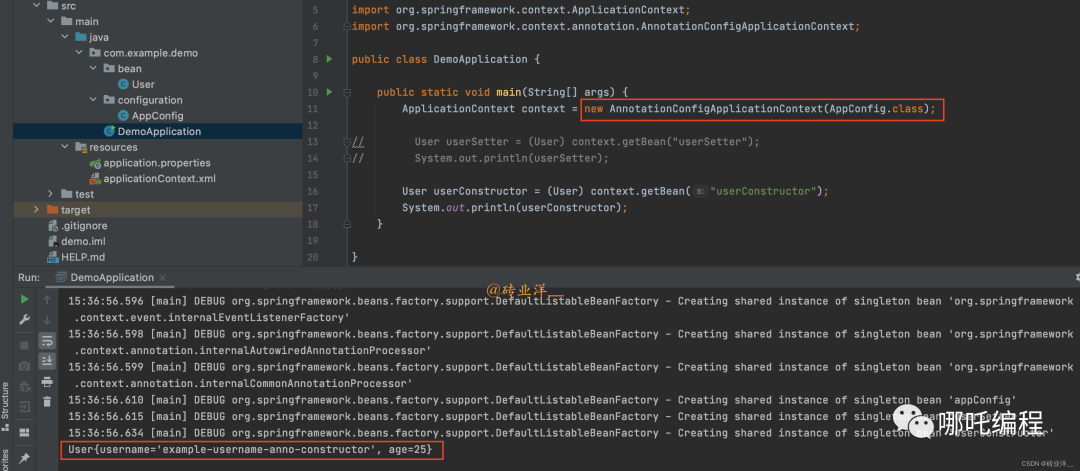
}同樣,我們需要創建一個DemoApplication類,使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext來加載配置類并獲取Bean:
import com.example.demo.bean.User;
import com.example.demo.configuration.AppConfig;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// User userSetter = (User) context.getBean("userSetter");
// System.out.println(userSetter);
User userConstructor = (User) context.getBean("userConstructor");
System.out.println(userConstructor);
}
}運行結果:
注意:如果在類中同時使用構造器注入和setter注入,需要注意它們注入的順序:先進行構造器注入,然后是setter注入。
三、注解式屬性注入
上面我們已經說過注解式的setter和構造器注入。我們又是如何處理那些通過@Component掃描而注冊的bean的屬性的呢?我們來仔細說說這個問題,同時展示如何在xml中進行相同的操作。
1、@Value注解式屬性注入的應用
首先,讓我們從最簡單的屬性注入方法:@Value開始。創建一個新的White類,并聲明一些字段,但是這次我們不會設置setter方法:
@Component
public class White {
@Value("white-value-annotation")
private String title;
@Value("1")
private Integer rank;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "White{" + "title='" + title + '\'' + ", rank=" + rank + '}';
}
}要實現注解式屬性注入,我們可以直接在需要注入的字段上添加@Value注解:
@Value("white-value-annotation")
private String title;
@Value("1")
private Integer rank;要注意的是,如果使用 @Value 注解來注入一個不存在的屬性,那么應用程序會在啟動時拋出異常。
然后,我們將通過組件掃描方式將這個White類掃描到IOC容器中,并將其取出并打印:
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(White.class);
White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);
System.out.println("Injected value : " + white);
}
}運行main方法會看到White的字段已經成功注入:
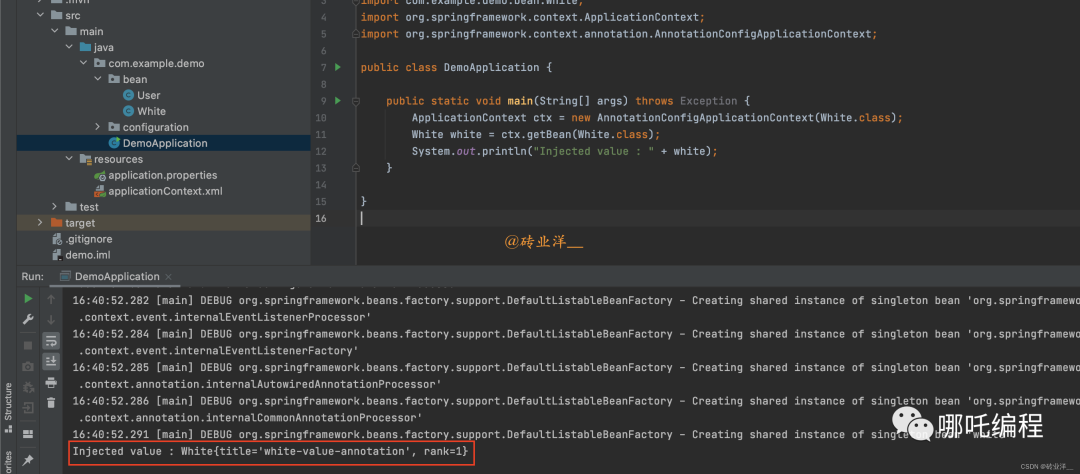
Injected value : White{title='white-value-annotation', rank=1}2、引入外部配置文件@PropertySource
如果我們需要在Spring中使用properties文件,我們應該怎么辦呢?Spring考慮到了這一點,并擴展了一個用于導入外部配置文件的注解:@PropertySource。
創建Bean和配置文件
創建一個新的Blue類,其結構與White類完全相同。然后在項目的resources目錄下創建一個新的blue.properties文件,用于存儲Blue類的屬性配置:
blue.title=blue-value-properties
blue.rank=2引入配置文件
使用@PropertySource注解將properties文件導入到配置類:
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example")
@PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties")
public class InjectValueConfiguration {
}這個blue.properties文件是一個鍵值對的列表,Spring 將這些鍵值對加載到 Environment 中,我們可以通過 @Value 注解或者 Environment 類的方法來獲取這些屬性值。
@Value 注解和 Environment 類都可以用于讀取 Spring 上下文中的屬性值。這些屬性值可能來自于多個不同的源,包括但不限于:
- Spring Boot 的默認配置文件(application.properties 或 application.yml)。
- 通過 @PropertySource 注解加載的屬性文件。
- 系統環境變量。
- Java 系統屬性(可以通過 -D 命令行參數設置)。
如果你想通過 @Value 注解來獲取屬性值,如下:
@Component
public class BlueConfig {
@Value("${blue.title}")
private String title;
@Value("${blue.rank}")
private int rank;
// getters and setters...
}在 Spring 應用中使用 @PropertySource 注解來加載一個 .properties 文件時,這個文件中的所有配置項都會被讀取,并存儲在一個內部的 Map 結構中。這個 Map 的鍵是配置項的名稱,值是配置項的值。Spring 中的一些內置配置項也會被添加到這個 Map 中。
當我們使用 {blue.title} 占位符來引用這個配置項的值。
如果想通過 Environment 類的方法來獲取屬性值,可以像下面這樣做:
@Component
public class SomeComponent {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public void someMethod() {
String title = env.getProperty("blue.title");
int rank = Integer.parseInt(env.getProperty("blue.rank"));
// ...
}
}在上述代碼中,Environment 類的 getProperty 方法用于獲取屬性值。注意,getProperty 方法返回的是 String,所以如果屬性是非字符串類型(如 int),則需要將獲取的屬性值轉換為適當的類型。
注意:@PropertySource 無法加載 YAML 格式的文件,只能加載 properties 格式的文件。如果需要加載 YAML 格式的文件,而且使用的是 Spring Boot框架,那么可以使用@ConfigurationProperties或@Value注解。例如以下的YAML文件:
application.yml:
appTest:
name: MyApp
version: 1.0.0可以使用@ConfigurationProperties來加載這些屬性:
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "appTest")
public class AppConfig {
private String name;
private String version;
// getters and setters...
}@ConfigurationProperties注解主要用于指定配置屬性的前綴,@ConfigurationProperties注解本身并不直接指定配置文件的位置, 而是由Spring Boot的自動配置機制處理的。
這樣,name字段就會被自動綁定到appTest.name配置屬性,version字段就會被自動綁定到appTest.version配置屬性。
默認情況下,Spring Boot會在啟動時自動加載src/main/resources目錄下的application.properties或application.yml文件。我們可以通過設置spring.config.name和spring.config.location屬性來改變默認的配置文件名或位置。
注意:@ConfigurationProperties注解需要配合@EnableConfigurationProperties注解或@Configuration注解使用,以確保Spring能夠發現并處理這些注解。
或者,你也可以使用@Value注解來加載這些屬性:
@Component
public class AppConfig {
@Value("${appTest.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${appTest.version}")
private String version;
// getters and setters...
}Blue類的屬性注入
對于properties類型的屬性,我們這里選擇@Value注解和占位符來注入屬性:
@Value("${blue.title}")
private String title;
@Value("${blue.rank}")
private Integer rank;如果你熟悉jsp的el表達式,會發現這和它非常相似!
測試啟動類
修改啟動類,將配置類引入,然后取出并打印Blue:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println("Properties value : " + blue);
}運行main方法會看到控制臺已經成功打印出了配置文件的屬性:
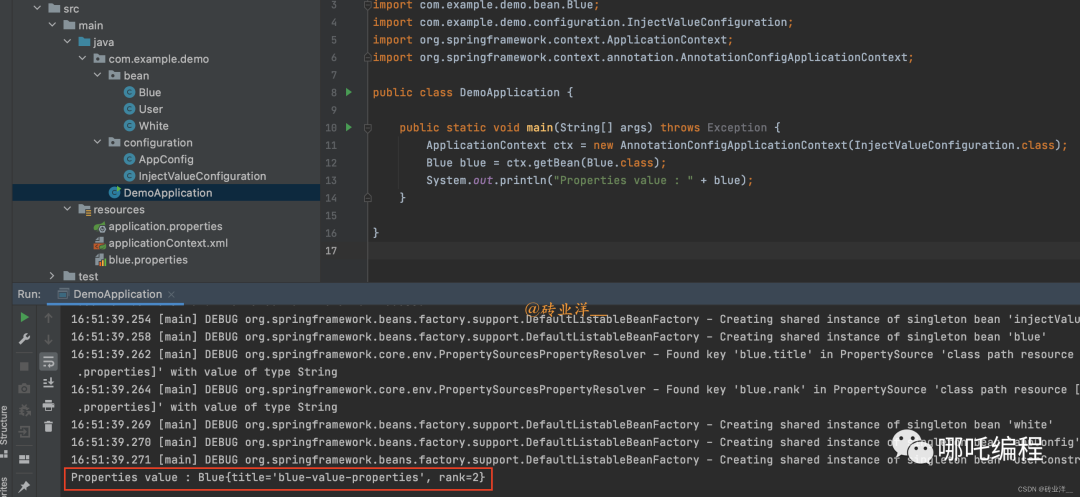
Properties value : Blue{title='blue-value-properties', rank=2}3、在XML中引入外部配置文件
在xml中,我們可以和@Value相同的方式使用占位符:
<?xml versinotallow="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context">
<!-- 相當于注解中的 @PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties") -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:blue.properties"/>
<bean class="com.example.demo.bean.Blue">
<property name="title" value="${blue.title}"/>
<property name="rank" value="${blue.rank}"/>
</bean>
</beans>4、注解式屬性注入完整代碼示例
@Value注解式屬性注入的應用。
創建White類:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class White {
@Value("white-value-annotation")
private String title;
@Value("1")
private Integer rank;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "White{" + "title='" + title + '\'' + ", rank=" + rank + '}';
}
}創建啟動類InjectValueAnnotationApplication:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.White;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(White.class);
White white = ctx.getBean(White.class);
System.out.println("Injected value : " + white);
}
}運行結果如下:
引入外部配置文件@PropertySource。
創建Blue類和配置文件,沒有setter和getter方法:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Blue {
@Value("${blue.title}")
private String title;
@Value("${blue.rank}")
private Integer rank;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blue{" + "title='" + title + '\'' + ", rank=" + rank + '}';
}
}resources目錄下的blue.properties文件:
blue.title=blue-value-properties
blue.rank=2創建配置類InjectValueConfiguration:
package com.example.demo.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example")
@PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties")
public class InjectValueConfiguration {
}修改啟動類,引入配置類:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.Blue;
import com.example.demo.configuration.InjectValueConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(InjectValueConfiguration.class);
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println("Properties value : " + blue);
}
}運行結果如下:
在xml中引入外部配置文件。
在使用XML配置的情況下,我們需要創建一個XML文件來替代InjectValueConfiguration類,我們可以先注釋掉InjectValueConfiguration類的所有內容。
下面是相應的XML文件內容:
<?xml versinotallow="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context">
<!-- 相當于注解中的 @PropertySource("classpath:blue.properties") -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:blue.properties"/>
<bean class="com.example.demo.bean.Blue">
<property name="title" value="${blue.title}"/>
<property name="rank" value="${blue.rank}"/>
</bean>
</beans>在這里我們使用了context:property-placeholder標簽來導入外部的properties文件,然后使用${...}占位符語法來引用配置文件中的屬性值。這樣無論是選擇用注解方式還是XML方式,都可以方便地在Spring中使用外部配置文件。
這里還需要修改下Blue類,因為通過XML方法注入屬性需要提供相應的setter方法,修改后的Blue類如下:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Blue {
@Value("${blue.title}")
private String title;
@Value("${blue.rank}")
private Integer rank;
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Integer getRank() {
return rank;
}
public void setRank(Integer rank) {
this.rank = rank;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Blue{" + "title='" + title + '\'' + ", rank=" + rank + '}';
}
}然后,我們需要修改啟動類,使用XmlApplicationContext代替AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.Blue;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
@ComponentScan("com.example")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
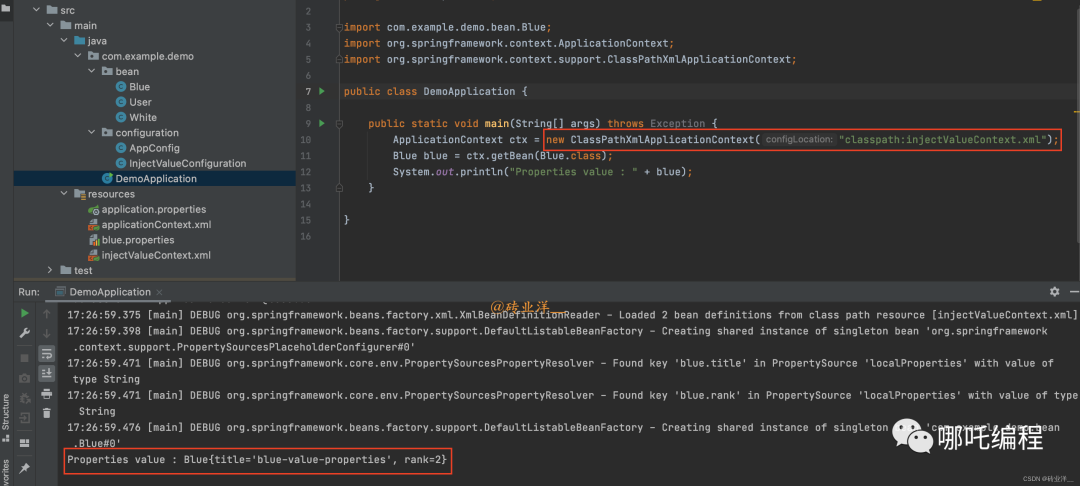
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:injectValueContext.xml");
Blue blue = ctx.getBean(Blue.class);
System.out.println("Properties value : " + blue);
}
}運行結果如下:
四、SpEL表達式
當我們談到屬性注入的時候,我們可能會遇到一些復雜的需求,例如我們需要引用另一個Bean的屬性,或者我們需要動態處理某個屬性值。這種需求無法通過使用${}的占位符方式實現,我們需要一個更強大的工具:SpEL表達式。
Spring Expression Language(SpEL)是從Spring框架 3.0開始支持的強大工具。SpEL不僅是Spring框架的重要組成部分,也可以獨立使用。它的功能豐富,包括調用屬性值、屬性參數、方法調用、數組存儲以及邏輯計算等。它與開源項目OGNL(Object-Graph Navigation Language)相似,但SpEL是Spring框架推出的,并默認內嵌在Spring框架中。
1、使用@Value注解和SpEL表達式實現屬性注入
SpEL的表達式用#{}表示,花括號中就是我們要編寫的表達式。
我們創建一個Bean,命名為Azure,同樣地,我們聲明屬性name和priority,并提供getter和setter方法以及toString()方法。然后我們使用@Component注解標注它。
使用@Value配合SpEL完成屬性注入,如下:
@Component
public class Azure {
@Value("#{'spel-for-azure'}")
private String name;
@Value("#{10}")
private Integer priority;
}我們修改啟動類,從IOC容器中獲取Azure并打印,可以看到屬性被成功注入:
Azure{name='spel-for-azure', priority=10}SpEL的功能遠不止這些,它還可以獲取IOC容器中其他Bean的屬性,讓我們來展示一下。
我們已經注冊了Azure Bean,現在我們再創建一個Bean,命名為Emerald。我們按照上述方法對字段和方法進行聲明,然后使用@Component注解標注。
我們希望name屬性直接復制Azure的name屬性,而priority屬性則希望比Azure的priority屬性大1,我們可以這樣編寫:
@Component
public class Emerald {
@Value("#{'copy of ' + azure.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{azure.priority + 1}")
private Integer priority;
}在Spring的SpEL中可以通過bean的名稱訪問到對應的bean,并通過.操作符訪問bean的屬性。在這個例子中,azure就是一個bean的名稱,它對應的bean就是Azure類的實例。所以,azure.name就是訪問Azure類實例的name屬性。
如果你在一個不涉及Spring的環境中使用SpEL,這個特性是不會生效的。這是因為這個特性依賴于Spring的IoC容器。
我們修改啟動類,測試運行,可以看到Azure的屬性已經成功被復制:
use spel bean property : Emerald{name='copy of spel-for-azure', priority=11}SpEL表達式不僅可以引用對象的屬性,還可以直接引用類的常量,以及調用對象的方法。下面我們通過示例進行演示。
我們新建一個Bean,命名為Ivory。我們按照上述方法初始化屬性、toString()方法、注解。
假設我們有一個需求,讓name取azure屬性的前3個字符,priority取Integer的最大值。那么我們可以使用SpEL這樣寫:
@Component
public class Ivory {
@Value("#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}")
private String name;
@Value("#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}")
private Integer priority;
}注意,直接引用類的屬性,需要在類的全限定名外面使用T()包圍。
我們修改啟動類,測試運行,可以看到Ivory的屬性已經是處理之后的值:
use spel methods : Ivory{name='spe', priority=2147483647}2、在XML中使用SpEL表達式實現屬性注入:
<bean id="ivory" class="com.example.demo.bean.Ivory">
<property name="name" value="#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}" />
<property name="priority" value="#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}" />
</bean>學習SpEL表達式不需要花費大量的精力,掌握基礎的使用方法即可。
3、SpEL表達式屬性注入完整代碼示例
使用@Value注解和SpEL表達式實現屬性注入。
創建三個SpEL表達式屬性注入的Bean:Azure.java、Emerald.java和Ivory.java。
Azure.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Azure {
@Value("#{'spel-for-azure'}")
private String name;
@Value("#{10}")
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Azure{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
}Emerald.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Emerald {
@Value("#{'copy of ' + azure.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{azure.priority + 1}")
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emerald{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
}Ivory.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Ivory {
@Value("#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}")
private String name;
@Value("#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}")
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Ivory{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
}MyBean.java:
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Autowired
private Azure azure;
@Autowired
private Emerald emerald;
@Autowired
private Ivory ivory;
public void init() {
System.out.println(azure);
System.out.println(emerald);
System.out.println(ivory);
}
}MyBean是一個用于展示如何在Spring中通過SpEL表達式來注入屬性的類,它聚合了三個對象Azure, Emerald和Ivory,并通過Spring的依賴注入機制將這三個對象注入到了MyBean類的實例中。
主程序DemoApplication:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
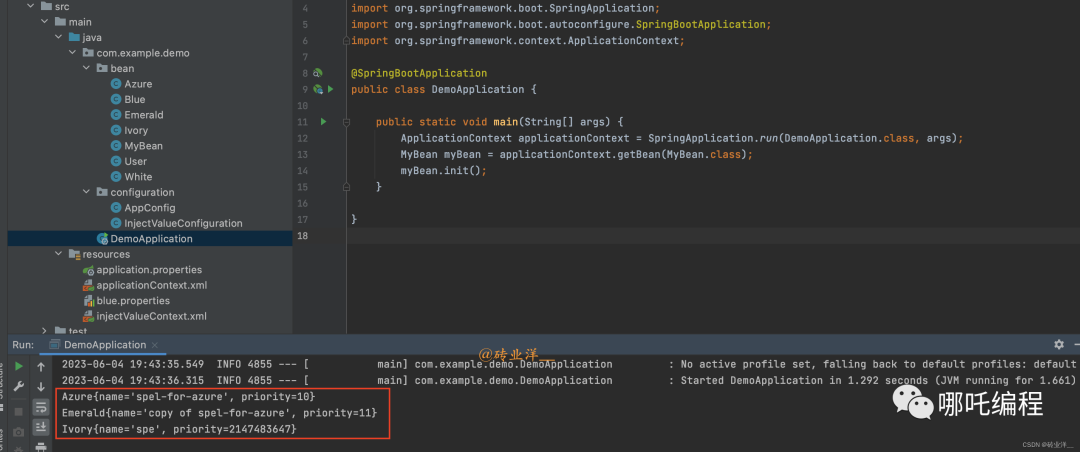
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
MyBean myBean = applicationContext.getBean(MyBean.class);
myBean.init();
}
}運行結果:
在XML中使用SpEL表達式實現屬性注入。
對于XML配置,Spring還支持在bean定義中使用SpEL。
首先,需要創建一個Spring XML配置文件,我們將其命名為app-config.xml:
<?xml versinotallow="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example" />
<bean id="azure" class="com.example.demo.bean.Azure">
<property name="name" value="#{'spel-for-azure'}" />
<property name="priority" value="#{10}" />
</bean>
<bean id="emerald" class="com.example.demo.bean.Emerald">
<property name="name" value="#{'copy of ' + azure.name}" />
<property name="priority" value="#{azure.priority + 1}" />
</bean>
<bean id="ivory" class="com.example.demo.bean.Ivory">
<property name="name" value="#{azure.name.substring(0, 3)}" />
<property name="priority" value="#{T(java.lang.Integer).MAX_VALUE}" />
</bean>
</beans>注意:在XML中使用SpEL需要使用#{},而不是${}。
然后修改這3個Bean,如果是使用XML來配置Spring的Bean的話,那么在Java類中就不需要使用@Component注解了。因為XML配置文件已經明確地告訴Spring這些類是Spring Bean。
同樣的,如果在XML文件中定義了Bean的屬性值,那么在Java類中就不需要使用@Value注解來注入這些值了。因為XML配置文件已經明確地為這些屬性賦了值。
Azure.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
public class Azure {
private String name;
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Azure{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
}Emerald.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
public class Emerald {
private String name;
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emerald{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
}Ivory.java:
package com.example.demo.bean;
public class Ivory {
private String name;
private Integer priority;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPriority() {
return priority;
}
public void setPriority(Integer priority) {
this.priority = priority;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Ivory{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", priority=" + priority +
'}';
}
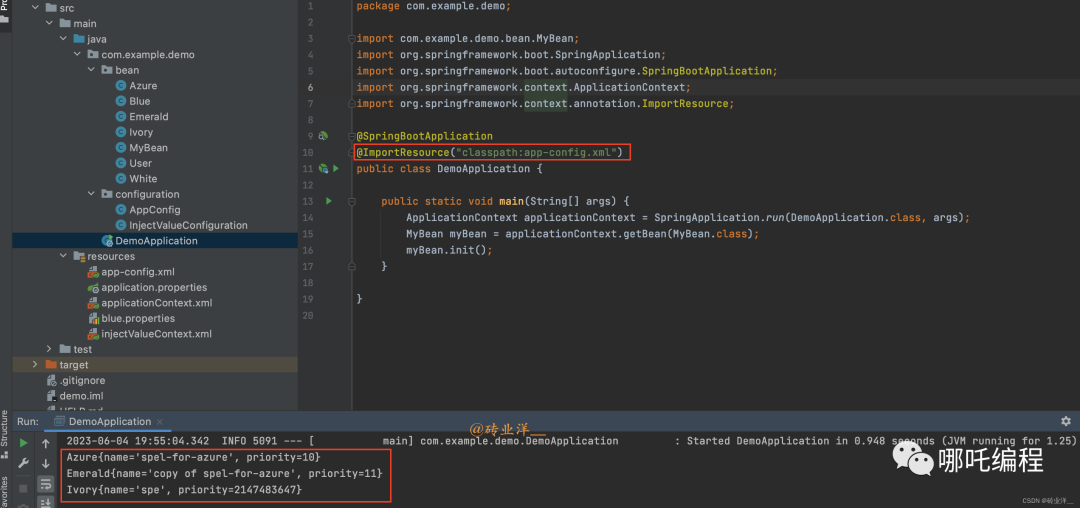
}然后需要在主程序中導入這個XML配置文件,這可以通過在主程序中添加@ImportResource注解實現:
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.bean.MyBean;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@SpringBootApplication
@ImportResource("classpath:app-config.xml")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
MyBean myBean = applicationContext.getBean(MyBean.class);
myBean.init();
}
}這樣就可以在Spring的XML配置文件中使用SpEL了。
運行結果如下: