數據結構與算法:圖形結構
圖
圖形結構是一種比樹形結構更復雜的非線性結構。在樹形結構中,結點間具有分支層次關系,每一層上的結點只能和上一層中的至多一個結點相關,但可能和下一層的多個結點相關。而在圖形結構中,任意兩個結點之間都可能相關,即結點之間的鄰接關系可以是任意的。
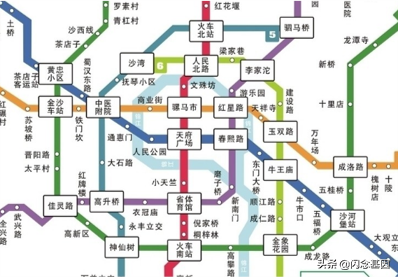
因此,圖形結構被用于描述各種復雜的數據對象,在自然科學、社會科學和人文科學等許多領域有著非常廣泛的應用 。圖形結構在計算機科學、人工智能、電子線路分析、最短路徑尋找、工程計劃、化學化合物分析統計力學、遺傳學、控制論語言學和社會科學等方面均有不同程度的應用可以這樣說,圖形結構在所有數據結構中應用最為廣泛。如在地鐵站中的線路圖:
圖的定義
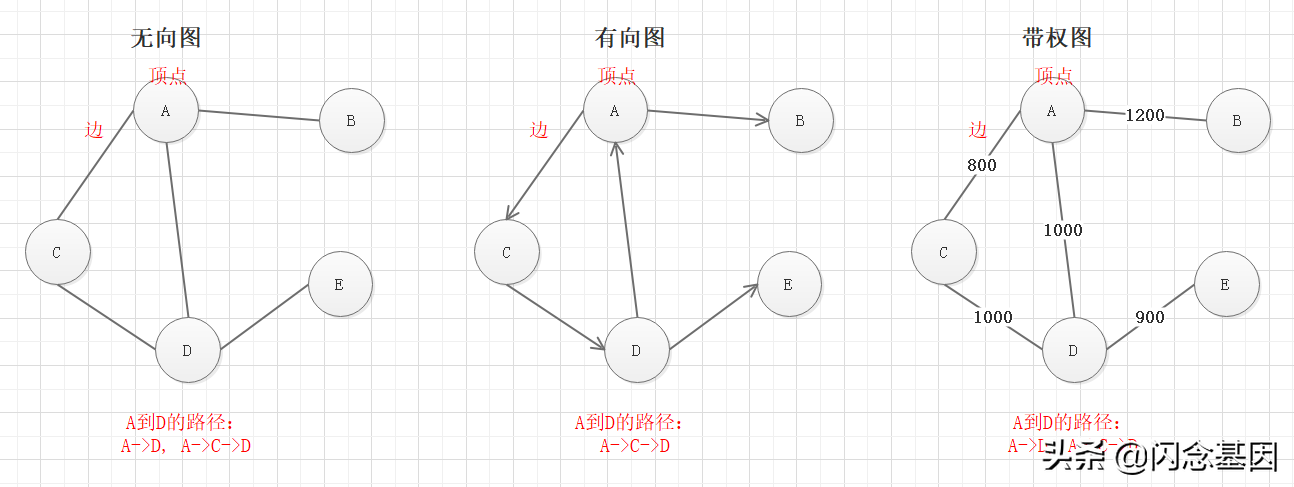
圖是一種數據結構,其中節點可以具有零個或多個相鄰元素,兩個節點的連接稱之為邊,節點在圖形結構中也被稱為頂點,一個頂點到另一個頂點的經過的的線路稱為路徑。
- 圖形結構有3種類型:無向圖、有向圖、帶權圖
- 無向圖:頂點A與頂點B之間的邊是無方向的,可以從A到B,也可以從B到A
- 有向圖:頂點A與頂點B之間的邊是有方向的,可以從A到B,但不可以從B到A
- 帶權圖:頂點A與頂點B之間的邊是帶有屬性的,如A到B的 距離。
圖的表達方式
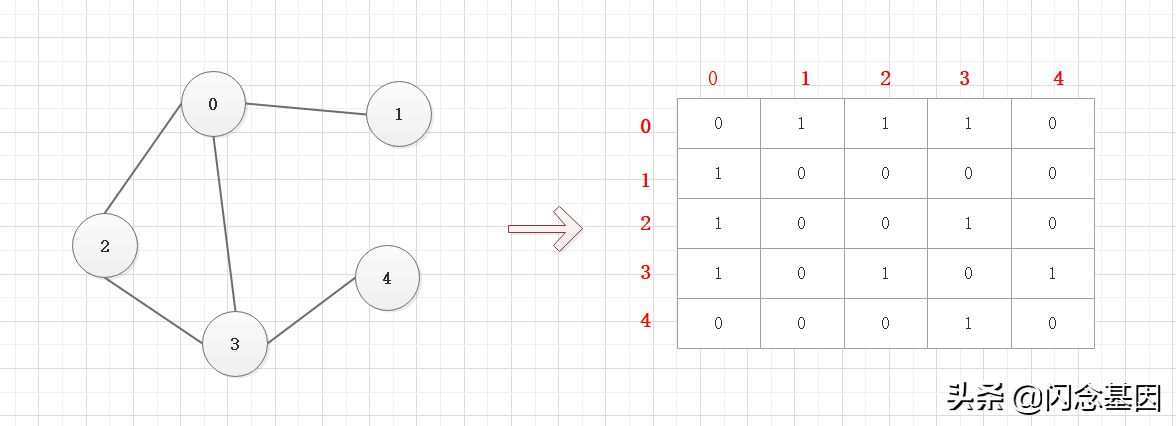
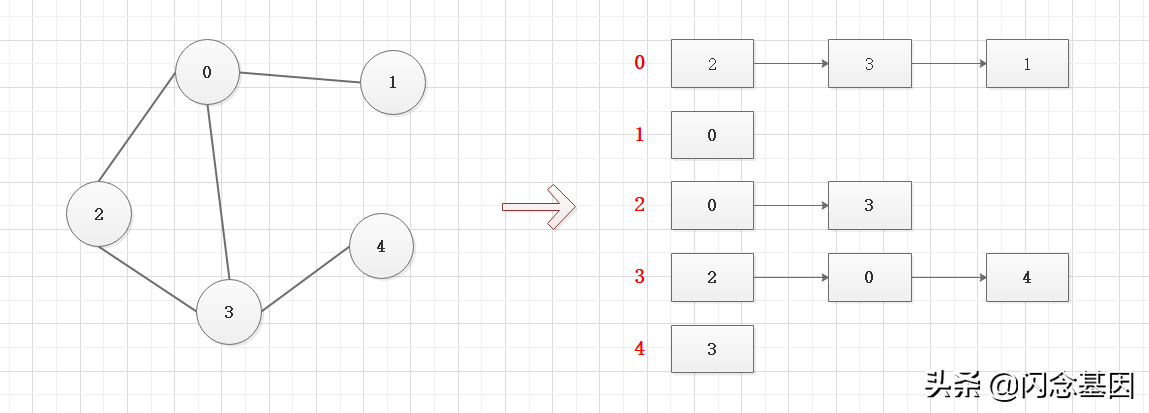
圖的表達方式有兩種:鄰接矩陣(使用二維數組)和鄰接表(使用數組+鏈表)
鄰接矩陣
鄰接矩陣是表示圖形中各頂點之間的關系,矩陣的行和列對應各頂點,坐標位置上的值對于它們之間的關系,1為連接, 0為沒有連接。在程序中用二維數組來實現。
鄰接表
鄰接表只關系存在的邊,不需要去為不存在的邊分配空間,因此比鄰接矩陣來說,避免了不必要的空間浪費。在程序中用數組+鏈表的形式實現,數組存儲對應的頂點,鏈表存儲該頂點連接的所有頂點。
圖的搜索算法
圖形結構基礎屬性和方法
以下的代碼演示都是以鄰接矩陣表達方式來實現的
- //圖形結構(鄰接矩陣)
- class Graph {
- //存儲圖中所有頂點
- private List<String> vertexes;
- //圖形結構的鄰接矩陣
- private int[][] matrix;
- //各頂點訪問情況,true為已訪問,false為未訪問
- private boolean[] visited;
- /**
- * 根據傳入的頂點信息生成矩陣
- * @param s
- */
- public Graph(String s[]) {
- vertexes = new ArrayList<>();
- for (String vertex : s){
- vertexes.add(vertex);
- }
- matrix = new int[s.length][s.length];
- }
- /**
- * 將倆個頂點連接,即生成邊
- * @param index1 頂點在集合中的索引
- * @param index2
- */
- public void connect(int index1, int index2){
- if (index1 < 0 || index1 > matrix.length || index2 < 0 || index2 > matrix.length){
- throw new RuntimeException("該頂點未存在");
- }
- //將新的鄰接添加的鄰接矩陣中
- matrix[index1][index2] = 1;
- matrix[index2][index1] = 1;
- }
- /**
- * 展示鄰接矩陣
- */
- public void showGraphMatrix(){
- for (int arr[] : matrix){
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- }
- }
- /**
- * 獲取頂點在鄰接矩陣對應行row中的第一個鄰接頂點下標
- * @param row
- * @return 當有鄰接頂點時返回鄰接頂點下標,沒有則返回-1
- */
- public int getFirstNeighbor(int row){
- for(int i =0; i<matrix.length; i++){
- if (matrix[row][i] != 0){
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- /**
- * 獲取頂點在鄰接矩陣對于行row中col列的下一個鄰接頂點
- * @param row
- * @param col
- * @return 當有鄰接頂點時返回鄰接頂點下標,沒有則返回-1
- */
- public int getNeighbor(int row, int col){
- for (int i=col+1; i<matrix.length; i++){
- if (matrix[row][i] != 0){
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- }
深度優先搜索
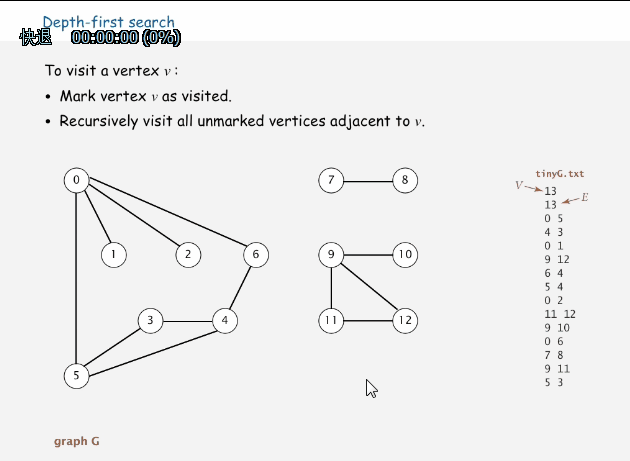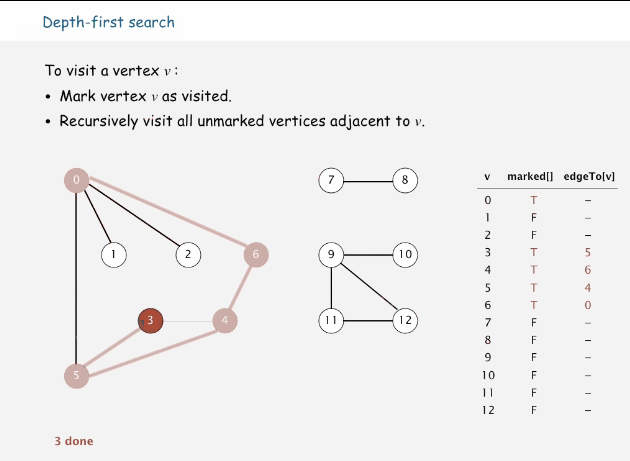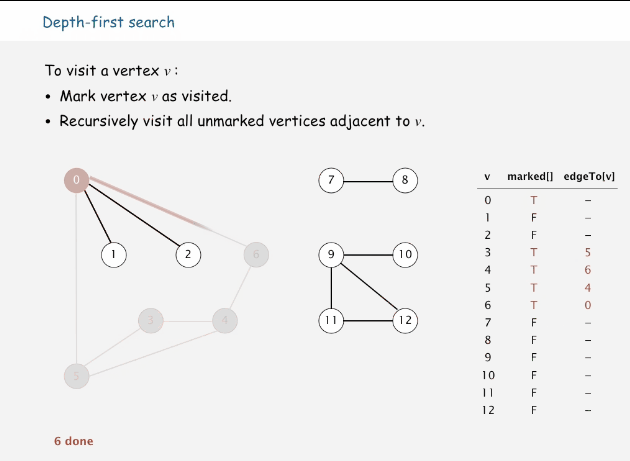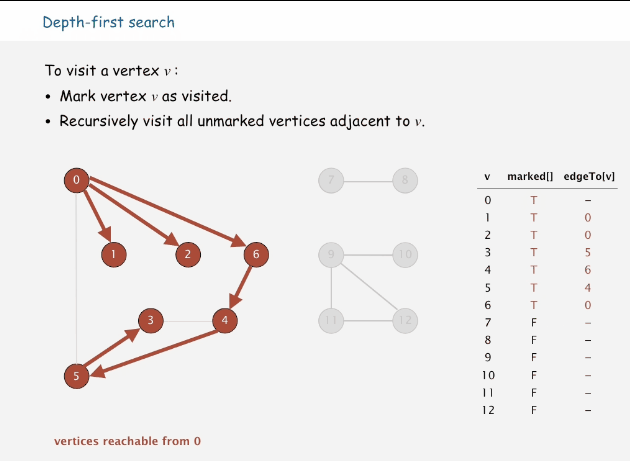
深度優先搜索屬于圖算法的一種,英文縮寫為DFS即Depth First Search.其過程簡要來說是對每一個可能的分支路徑深入到不能再深入為止,而且每個節點只能訪問一次。這樣的訪問策略是優先往縱向進行深入挖掘,而不是對一個頂點的所有鄰接頂點進行橫線訪問。簡單來說就是一條路走到死,不行再掉頭。
思路:從當前頂點選一個與之連接而未訪問過的頂點,將當前節點往該鄰接頂點移動,如果鄰接頂點沒有未訪問的,則回溯到上一個頂點位置,繼續該步驟。直到所有頂點都訪問過。
往鄰接但未訪問過的頂點移動
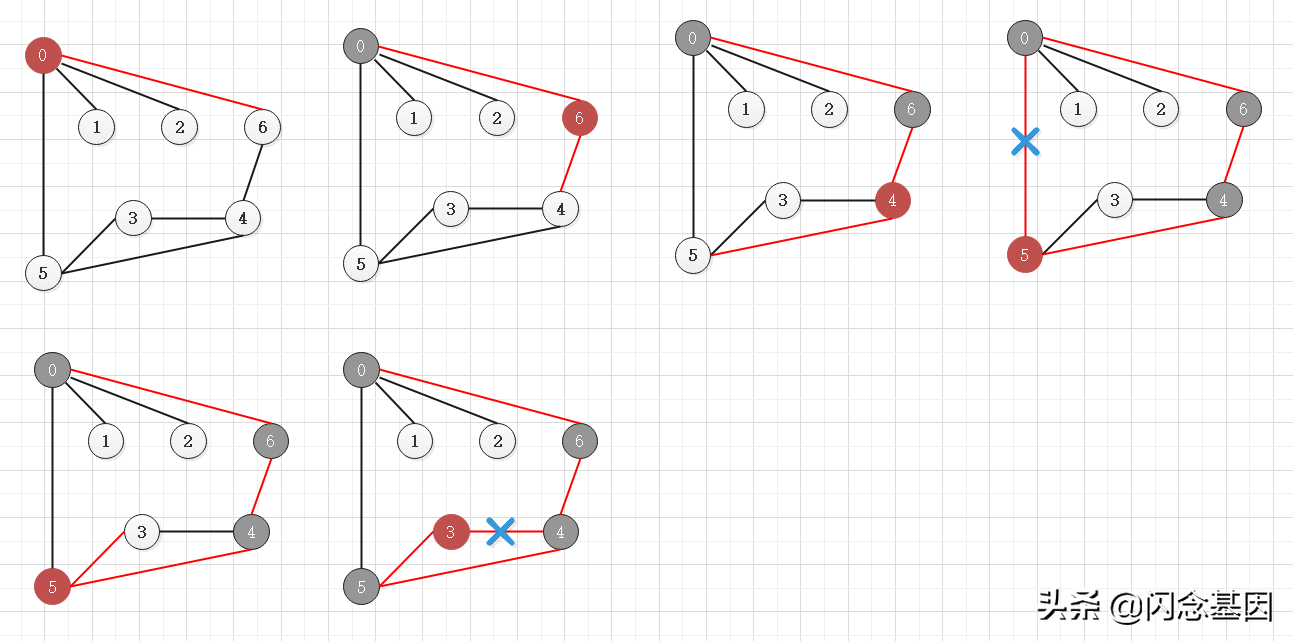
鄰接頂點沒有未訪問的,進行回溯,直到遇到未訪問的鄰接頂點
當所有頂點都被訪問過時,退出算法
下面是深度優先搜索的過程動畫
代碼演示
- public void dsf(){
- visited = new boolean[vertexes.size()];
- //以在集合中下標為0的頂點,進行深度搜索
- dsf(visited, 0);
- }
- /**
- * 深度優先搜索
- * @param visited
- * @param row
- */
- public void dsf(boolean[] visited, int row){
- //輸出當前頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(row) + " -> ");
- //將當前頂點設為已訪問
- visited[row] = true;
- //獲取當前頂點的鄰接頂點下標
- int index = getFirstNeighbor(row);
- //如果當前頂點有鄰接頂點則進行深度搜索
- while (index != -1){
- //當鄰接頂點未訪問時,則遞歸遍歷
- if (visited[index] != true){
- dsf(visited, index);
- }
- //當鄰接頂點已訪問時,則尋找另一個鄰接頂點
- index = getNeighbor(row, index);
- }
- }
寬度優先搜索
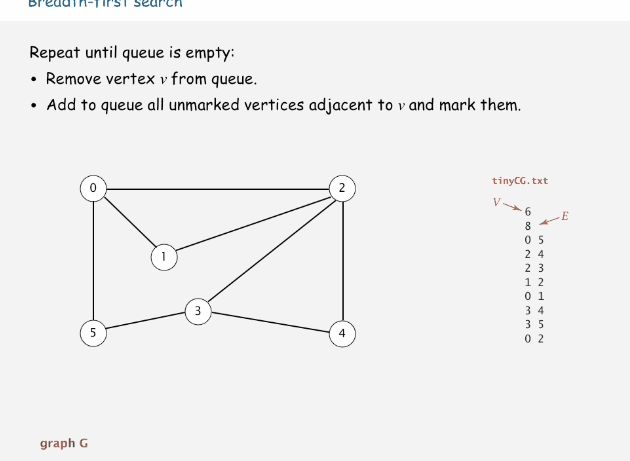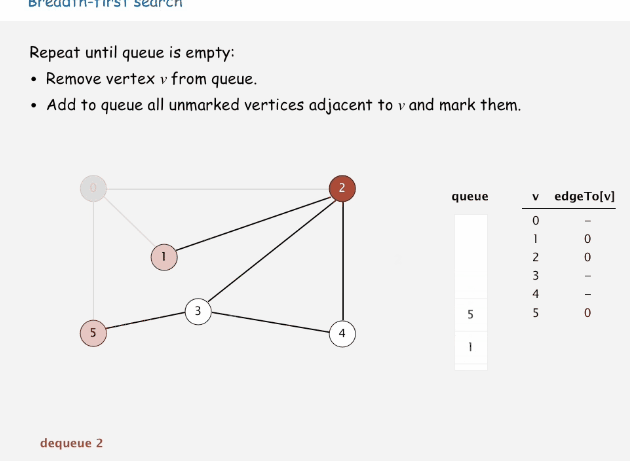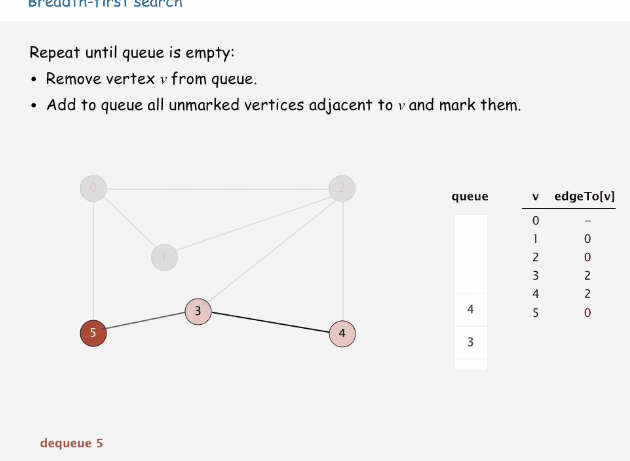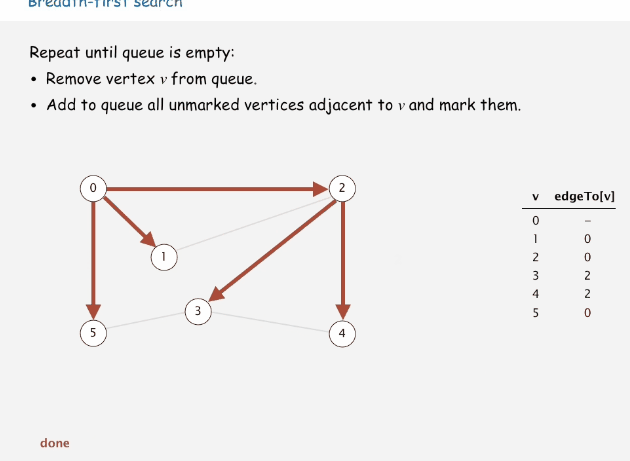
寬度優先搜索算法(又稱廣度優先搜索)是最簡便的圖的搜索算法之一,這一算法也是很多重要的圖的算法的原型。Dijkstra單源最短路徑算法和Prim最小生成樹算法都采用了和寬度優先搜索類似的思想。其別名又叫BFS,屬于一種盲目搜尋法,目的是系統地展開并檢查圖中的所有節點,以找尋結果。換句話說,它并不考慮結果的可能位置,徹底地搜索整張圖,直到找到結果為止。
寬度優先搜索算法類似于一個分層搜索的過程,寬度優先搜索算法需要一個隊列以保持訪問過頂點的順序,以便按這個順序來訪問這些頂點的鄰接頂點。
思路:依次訪問當前頂點的鄰接頂點,并按訪問順序將這些鄰接頂點存儲在隊列中,當當前頂點的所有鄰接頂點都被訪問后,從隊列中彈出一個頂點,以該頂點為當前頂點繼續該步驟,直到所有頂點都被訪問過。
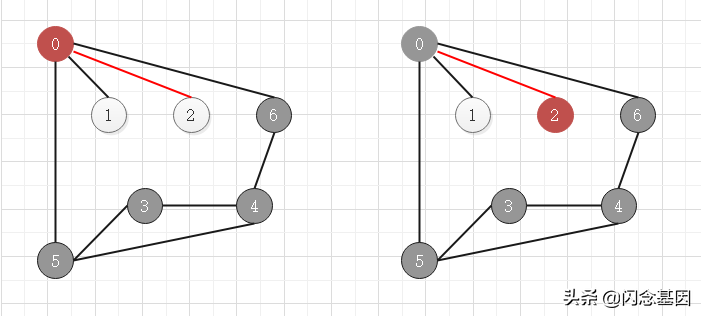
依次訪問當前頂點的所有鄰接頂點,并把這些鄰接頂點按訪問順序存儲在隊列中
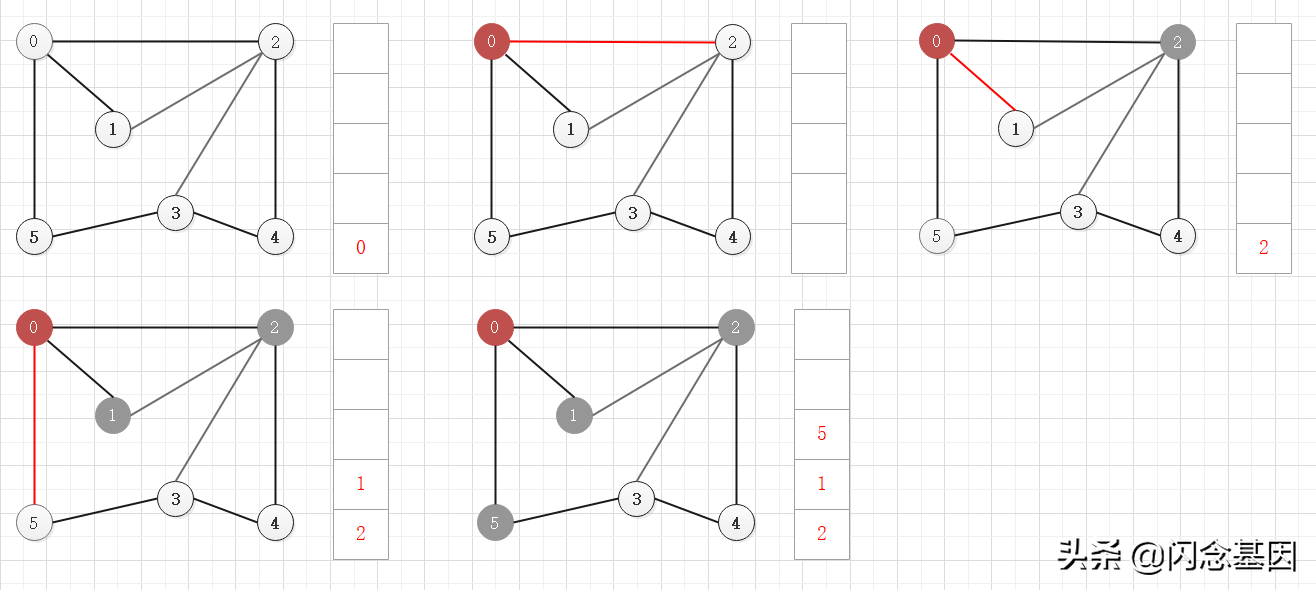
當前頂點沒有未訪問的鄰接頂點,從隊列中彈出一個頂點,以該彈出頂點繼續訪問未訪問的鄰接頂點
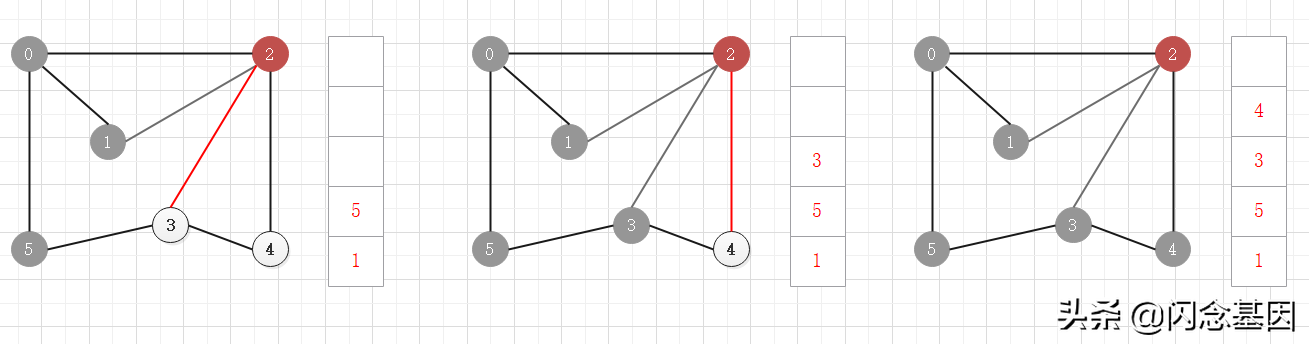
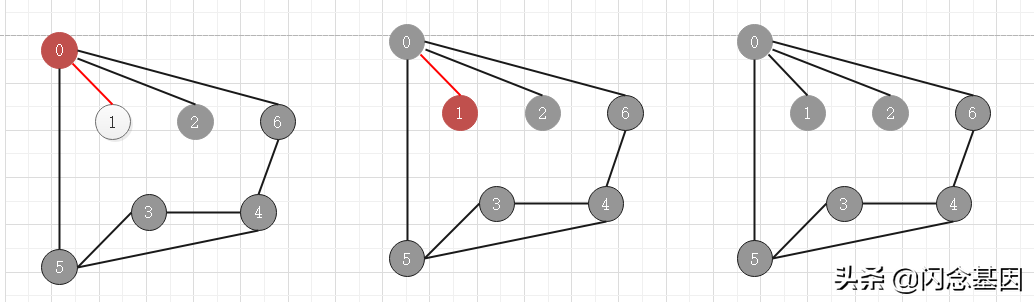
注意,雖然圖中的頂點都已經訪問過了,但還是要等隊列中的所有頂點彈出訪問后,算法才結束
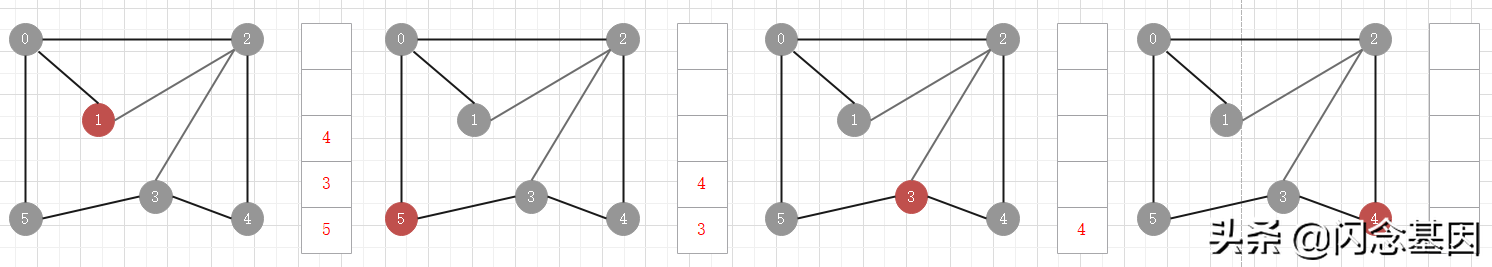
下面時寬度優先搜索的過程動畫
代碼演示
- public void bfs(){
- visited = new boolean[vertexes.size()];
- ////以在集合中下標為0的頂點,進行廣度優先搜索
- bfs(visited, 0);
- }
- /**
- * 廣度優先搜索
- * @param visited
- * @param row
- */
- public void bfs(boolean[] visited, int row){
- //創建隊列,存儲遍歷鄰接頂點的順序
- LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
- //輸出當前頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(row) + " -> ");
- //將當前頂點設為已訪問
- visited[row] = true;
- //將當前頂點加入隊列中
- queue.add(row);
- //當隊列不為空時,即有未搜索的鄰接頂點,進行搜索
- while (!queue.isEmpty()){
- //按順序從隊列中彈出鄰接頂點下標
- int last = (Integer)queue.removeFirst();
- //獲取該彈出頂點的鄰接頂點下標
- int index = getFirstNeighbor(last);
- //當彈出頂點有鄰接頂點時,進行廣度搜索
- while(index != -1){
- //當鄰接頂點未訪問時
- if(visited[index] != true){
- //輸出該鄰接頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(index) + " -> ");
- //把該鄰接頂點設為已訪問
- visited[index] = true;
- //將該鄰接頂點加入隊列
- queue.addLast(index);
- }
- //繼續尋找彈出頂點的另一個鄰接頂點
- index = getNeighbor(last, index);
- }
- }
- }
完整演示代碼
- public class GraphDemo {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String[] s = {"A","B","C","D","E","F","G"};
- Graph graph = new Graph(s);
- //A-B A-C A-G A-F F-D F-E D-E E-G
- graph.connect(0, 1);
- graph.connect(0, 2);
- graph.connect(0, 6);
- graph.connect(0, 5);
- graph.connect(5, 3);
- graph.connect(5, 4);
- graph.connect(3, 4);
- graph.connect(4, 6);
- graph.showGraphMatrix();
- graph.dsf();//A -> B -> C -> F -> D -> E -> G ->
- System.out.println();
- graph.bfs();//A -> B -> C -> F -> G -> D -> E ->
- }
- }
- //圖形結構
- class Graph {
- //存儲圖中所有頂點
- private List<String> vertexes;
- //圖形結構的鄰接矩陣
- private int[][] matrix;
- //各頂點訪問情況,true為已訪問,false為未訪問
- private boolean[] visited;
- /**
- * 根據傳入的頂點信息生成矩陣
- * @param s
- */
- public Graph(String s[]) {
- vertexes = new ArrayList<>();
- for (String vertex : s){
- vertexes.add(vertex);
- }
- matrix = new int[s.length][s.length];
- }
- /**
- * 將倆個頂點連接,即生成邊
- * @param index1 頂點在集合中的索引
- * @param index2
- */
- public void connect(int index1, int index2){
- if (index1 < 0 || index1 > matrix.length || index2 < 0 || index2 > matrix.length){
- throw new RuntimeException("該頂點未存在");
- }
- //將新的鄰接添加的鄰接矩陣中
- matrix[index1][index2] = 1;
- matrix[index2][index1] = 1;
- }
- /**
- * 展示鄰接矩陣
- */
- public void showGraphMatrix(){
- for (int arr[] : matrix){
- System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
- }
- }
- public void dsf(){
- visited = new boolean[vertexes.size()];
- //以在集合中下標為0的頂點,進行深度優先搜索
- dsf(visited, 0);
- }
- /**
- * 深度優先搜索
- * @param visited
- * @param row
- */
- public void dsf(boolean[] visited, int row){
- //輸出當前頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(row) + " -> ");
- //將當前頂點設為已訪問
- visited[row] = true;
- //獲取當前頂點的鄰接頂點下標
- int index = getFirstNeighbor(row);
- //如果當前頂點有鄰接頂點則進行深度搜索
- while (index != -1){
- //當鄰接頂點未訪問時,則遞歸遍歷
- if (visited[index] != true){
- dsf(visited, index);
- }
- //當鄰接頂點已訪問時,則尋找另一個鄰接頂點
- index = getNeighbor(row, index);
- }
- }
- public void bfs(){
- visited = new boolean[vertexes.size()];
- ////以在集合中下標為0的頂點,進行廣度優先搜索
- bfs(visited, 0);
- }
- /**
- * 廣度優先搜索
- * @param visited
- * @param row
- */
- public void bfs(boolean[] visited, int row){
- //創建隊列,存儲遍歷鄰接頂點的順序
- Queue queue = new ArrayDeque();
- //輸出當前頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(row) + " -> ");
- //將當前頂點設為已訪問
- visited[row] = true;
- //將當前頂點加入隊列中
- queue.add(row);
- //當隊列不為空時,即有未搜索的鄰接頂點,進行搜索
- while (!queue.isEmpty()){
- //按順序從隊列中彈出鄰接頂點下標
- int last = (Integer)queue.poll();
- //獲取該彈出頂點的鄰接頂點下標
- int index = getFirstNeighbor(last);
- //當彈出頂點有鄰接頂點時,進行廣度搜索
- while(index != -1){
- //當鄰接頂點未訪問時
- if(visited[index] != true){
- //輸出該鄰接頂點
- System.out.print(vertexes.get(index) + " -> ");
- //把該鄰接頂點設為已訪問
- visited[index] = true;
- //將該鄰接頂點加入隊列
- queue.add(index);
- }
- //繼續尋找彈出頂點的另一個鄰接頂點
- index = getNeighbor(last, index);
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 獲取頂點在鄰接矩陣對應行row中的第一個鄰接頂點下標
- * @param row
- * @return 當有鄰接頂點時返回鄰接頂點下標,沒有則返回-1
- */
- public int getFirstNeighbor(int row){
- for(int i =0; i<matrix.length; i++){
- if (matrix[row][i] != 0){
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- /**
- * 獲取頂點在鄰接矩陣對于行row中col列的下一個鄰接頂點
- * @param row
- * @param col
- * @return 當有鄰接頂點時返回鄰接頂點下標,沒有則返回-1
- */
- public int getNeighbor(int row, int col){
- for (int i=col+1; i<matrix.length; i++){
- if (matrix[row][i] != 0){
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
- }







































