使用遞歸圖 recurrence plot 表征時間序列
在本文中,我將展示如何使用遞歸圖 Recurrence Plots 來描述不同類型的時間序列。我們將查看具有500個數據點的各種模擬時間序列。我們可以通過可視化時間序列的遞歸圖并將其與其他已知的不同時間序列的遞歸圖進行比較,從而直觀地表征時間序列。

遞歸圖
Recurrence Plots(RP)是一種用于可視化和分析時間序列或動態系統的方法。它將時間序列轉化為圖形化的表示形式,以便分析時間序列中的重復模式和結構。Recurrence Plots 是非常有用的,尤其是在時間序列數據中存在周期性、重復事件或關聯結構時。
Recurrence Plots 的基本原理是測量時間序列中各點之間的相似性。如果兩個時間點之間的距離小于某個給定的閾值,就會在 Recurrence Plot 中繪制一個點,表示這兩個時間點之間存在重復性。這些點在二維平面上組成了一種圖像。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def recurrence_plot(data, threshold=0.1):
"""
Generate a recurrence plot from a time series.
:param data: Time series data
:param threshold: Threshold to determine recurrence
:return: Recurrence plot
"""
# Calculate the distance matrix
N = len(data)
distance_matrix = np.zeros((N, N))
for i in range(N):
for j in range(N):
distance_matrix[i, j] = np.abs(data[i] - data[j])
# Create the recurrence plot
recurrence_plot = np.where(distance_matrix <= threshold, 1, 0)
return recurrence_plot上面的代碼創建了一個二進制距離矩陣,如果時間序列i和j的值相差在0.1以內(閾值),則它們的值為1,否則為0。得到的矩陣可以看作是一幅圖像。
白噪聲
接下來我們將可視化白噪聲。首先,我們需要創建一系列模擬的白噪聲:
# Set a seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(0)
# Generate 500 data points of white noise
white_noise = np.random.normal(size=500)
# Plot the white noise time series
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(white_noise, label='White Noise')
plt.title('White Noise Time Series')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()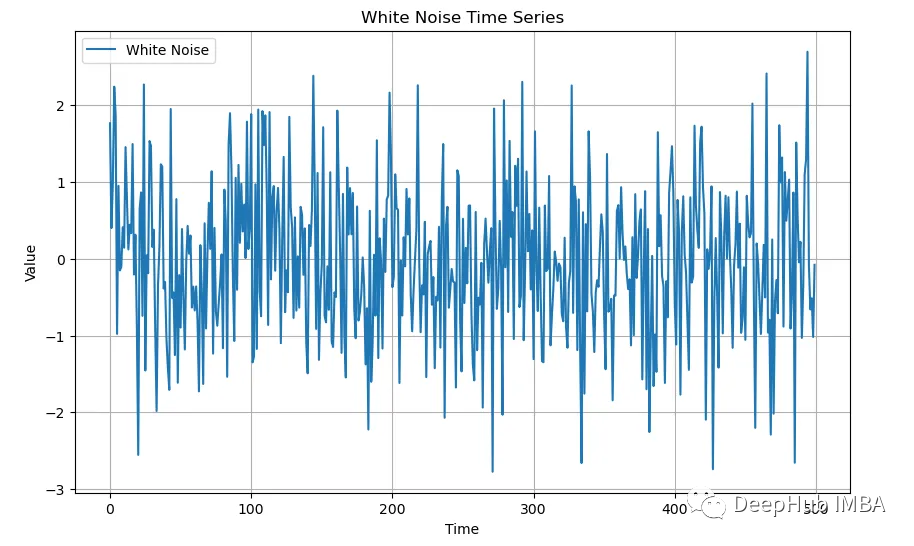
遞歸圖為這種白噪聲提供了有趣的可視化效果。對于任何一種白噪聲,圖看起來都是一樣的:
# Generate and plot the recurrence plot
recurrence = recurrence_plot(white_noise, threshold=0.1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(recurrence, cmap='binary', origin='lower')
plt.title('Recurrence Plot')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Time')
plt.colorbar(label='Recurrence')
plt.show()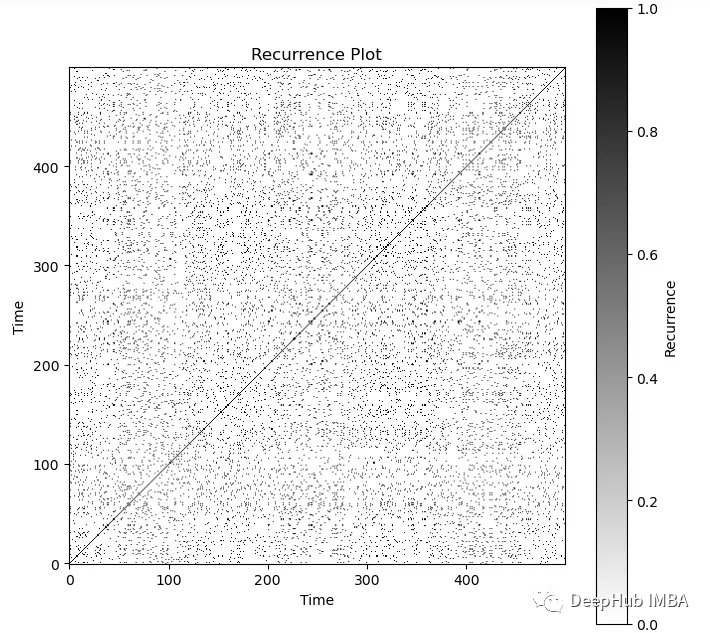
可以直觀地看到一個嘈雜的過程。可以看到圖中對角線總是黑色的。
隨機游走
接下來讓我們看看隨機游走(Random Walk)是什么樣子的:
# Generate 500 data points of a random walk
steps = np.random.choice([-1, 1], size=500) # Generate random steps: -1 or 1
random_walk = np.cumsum(steps) # Cumulative sum to generate the random walk
# Plot the random walk time series
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(random_walk, label='Random Walk')
plt.title('Random Walk Time Series')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()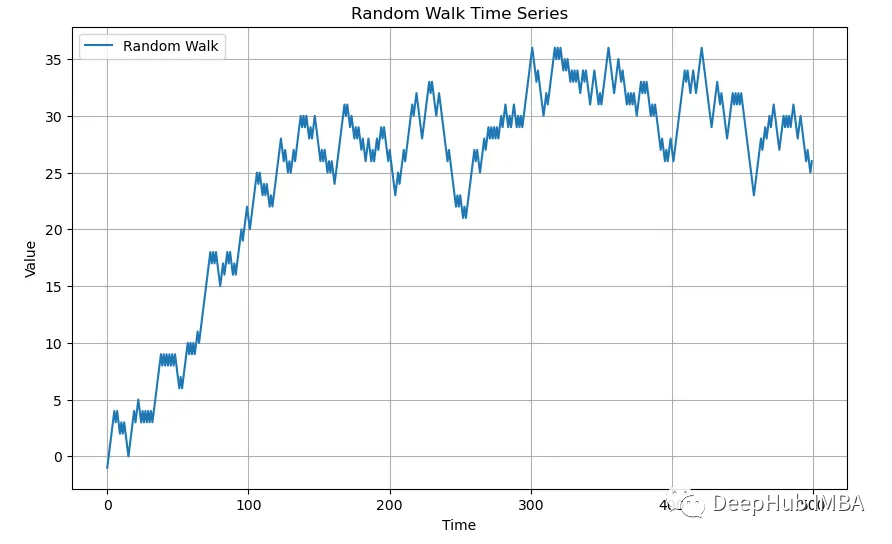
# Generate and plot the recurrence plot
recurrence = recurrence_plot(random_walk, threshold=0.1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(recurrence, cmap='binary', origin='lower')
plt.title('Recurrence Plot')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Time')
plt.colorbar(label='Recurrence')
plt.show()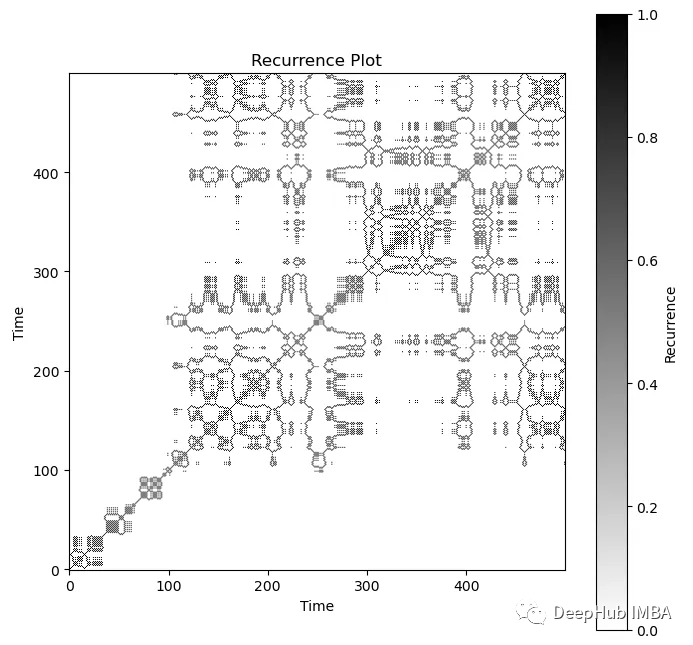
SARIMA
SARIMA(4,1,4)(1,0,0,12)的模擬數據
from statsmodels.tsa.statespace.sarimax import SARIMAX
# Define SARIMA parameters
p, d, q = 4, 1, 4 # Non-seasonal order
P, D, Q, s = 1, 0, 0, 12 # Seasonal order
# Simulate data
model = SARIMAX(np.random.randn(100), order=(p, d, q), seasonal_order=(P, D, Q, s), trend='ct')
fit = model.fit(disp=False) # Fit the model to random data to get parameters
simulated_data = fit.simulate(nsimulatinotallow=500)
# Plot the simulated time series
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(simulated_data, label=f'SARIMA({p},owocgsc,{q})({P},{D},{Q},{s})')
plt.title('Simulated Time Series from SARIMA Model')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()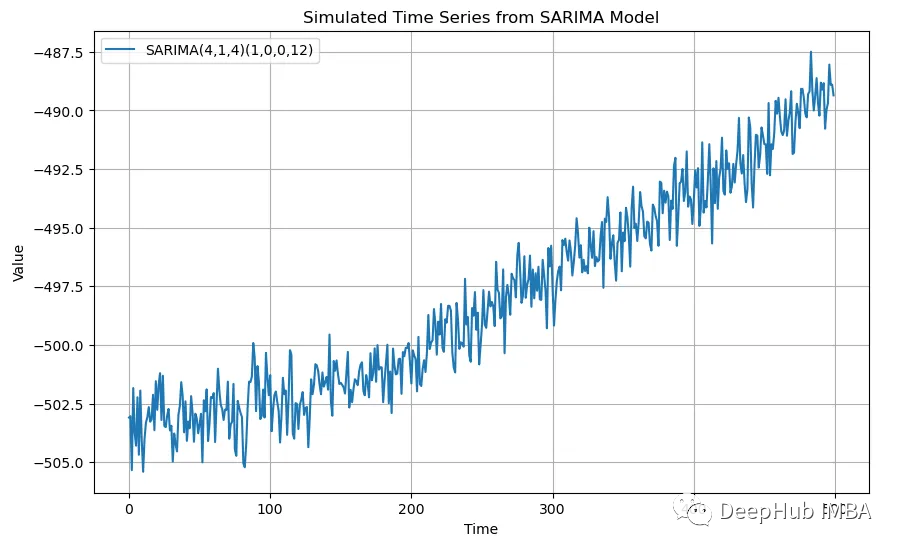
recurrence = recurrence_plot(simulated_data, threshold=0.1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(recurrence, cmap='binary', origin='lower')
plt.title('Recurrence Plot')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Time')
plt.colorbar(label='Recurrence')
plt.show()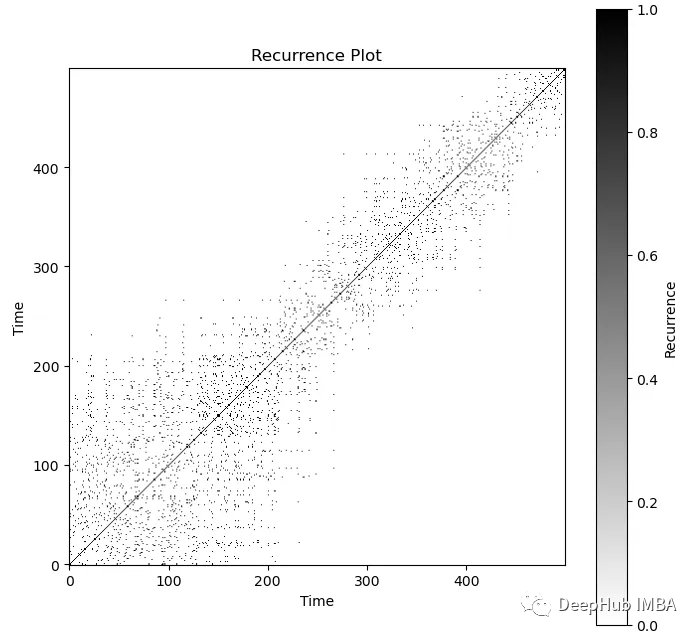
混沌的數據
def logistic_map(x, r):
"""Logistic map function."""
return r * x * (1 - x)
# Initialize parameters
N = 500 # Number of data points
r = 3.9 # Parameter r, set to a value that causes chaotic behavior
x0 = np.random.rand() # Initial value
# Generate chaotic time series data
chaotic_data = [x0]
for _ in range(1, N):
x_next = logistic_map(chaotic_data[-1], r)
chaotic_data.append(x_next)
# Plot the chaotic time series
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(chaotic_data, label=f'Logistic Map (r={r})')
plt.title('Chaotic Time Series')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Value')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()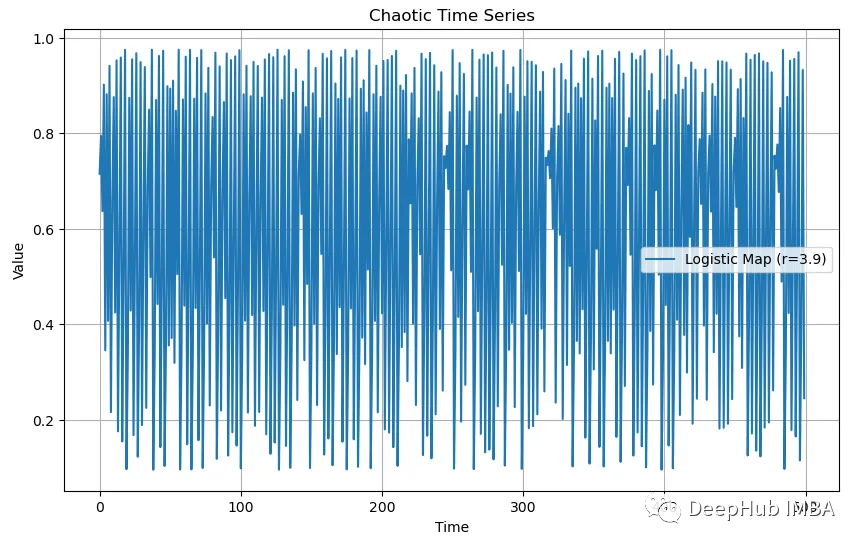
recurrence = recurrence_plot(chaotic_data, threshold=0.1)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(recurrence, cmap='binary', origin='lower')
plt.title('Recurrence Plot')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Time')
plt.colorbar(label='Recurrence')
plt.show()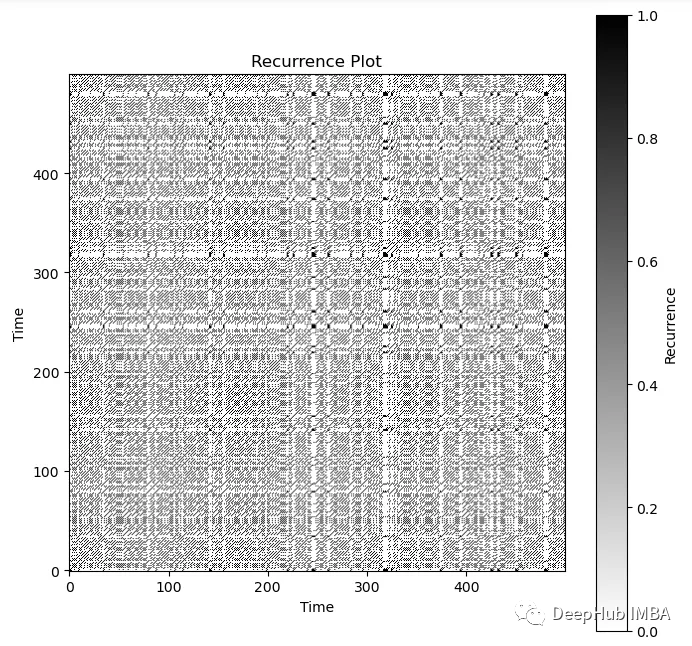
標準普爾500指數
作為最后一個例子,讓我們看看從2013年10月28日至2023年10月27日的標準普爾500指數真實數據:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('standard_and_poors_500_idx.csv', parse_dates=True)
df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'])
df.set_index('Date', inplace = True)
df.drop(columns = ['Open', 'High', 'Low'], inplace = True)
df.plot()
plt.title('S&P 500 Index - 10/28/2013 to 10/27/2023')
plt.ylabel('S&P 500 Index')
plt.xlabel('Date');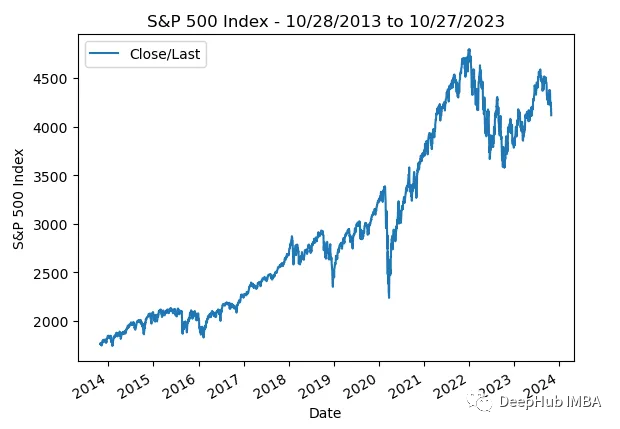
recurrence = recurrence_plot(df['Close/Last'], threshold=10)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(recurrence, cmap='binary', origin='lower')
plt.title('Recurrence Plot')
plt.xlabel('Time')
plt.ylabel('Time')
plt.colorbar(label='Recurrence')
plt.show()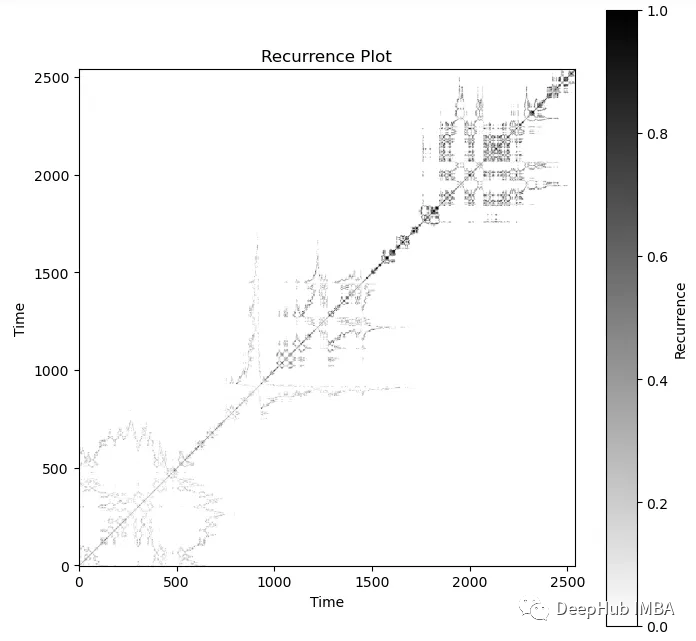
選擇合適的相似性閾值是 遞歸圖分析的一個關鍵步驟。較小的閾值會導致更多的重復模式,而較大的閾值會導致更少的重復模式。閾值的選擇通常需要根據數據的特性和分析目標進行調整。
這里我們不得不調整閾值,最終確得到的結果為10,這樣可以獲得更大的對比度。上面的遞歸圖看起來很像隨機游走遞歸圖和無規則的混沌數據的混合體。
總結
在本文中,我們介紹了遞歸圖以及如何使用Python創建遞歸圖。遞歸圖給了我們一種直觀表征時間序列圖的方法。遞歸圖是一種強大的工具,用于揭示時間序列中的結構和模式,特別適用于那些具有周期性、重復性或復雜結構的數據。通過可視化和特征提取,研究人員可以更好地理解時間序列數據并進行進一步的分析。
從遞歸圖中可以提取各種特征,以用于進一步的分析。這些特征可以包括重復點的分布、Lempel-Ziv復雜度、最長對角線長度等。
遞歸圖在多個領域中得到了廣泛應用,包括時間序列分析、振動分析、地震學、生態學、金融分析、生物醫學等。它可用于檢測周期性、異常事件、相位同步等。






































