在數學上,高斯噪聲是一種通過向輸入數據添加均值為零和標準差(σ)的正態分布隨機值而產生的噪聲。 正態分布,也稱為高斯分布,是一種連續概率分布,由其概率密度函數 (PDF) 定義:
pdf(x) = (1 / (σ * sqrt(2 * π))) * e^(- (x — μ)2 / (2 * σ2))
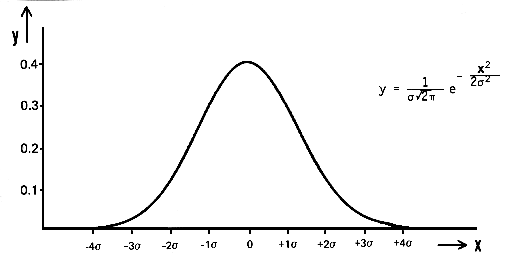
其中 x 是隨機變量,μ 是均值,σ 是標準差。
通過生成具有正態分布的隨機值并將它們添加到輸入數據。例如如果對圖像添加高斯噪聲,可以將圖像表示為像素值的二維矩陣,然后使用 numpy 庫 np.random.randn(rows,cols) 生成具有正態分布的隨機值, 并將它們添加到圖像的像素值中。 這就會得到添加了高斯噪聲的新圖像。
高斯噪聲也稱為白噪聲,是一種服從正態分布的隨機噪聲。 在深度學習中,訓練時往往會在輸入數據中加入高斯噪聲,以提高模型的魯棒性和泛化能力。 這稱為數據擴充。 通過向輸入數據添加噪聲,模型被迫學習對輸入中的微小變化具有魯棒性的特征,這可以幫助它在新的、看不見的數據上表現更好。 高斯噪聲也可以在訓練過程中添加到神經網絡的權重中以提高其性能,這種技術稱為 Dropout。
讓我們先從一個簡單的例子開始:
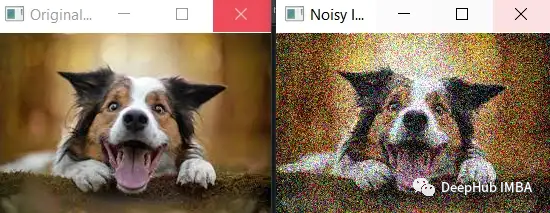
噪聲的標準偏差 (noise_std) 被設置為較大的值 50,這將導致更多的噪聲被添加到圖像中。 可以看到噪聲更加明顯,并且原始圖像的特征不太明顯。
值得注意的是,在添加更多噪聲時,需要確保噪聲不超過像素值的有效范圍(即 0 到 255 之間)。 在這個例子中,np.clip() 函數用于確保噪聲圖像的像素值落在有效范圍內。
雖然更多的噪聲可能更容易看出原始圖像和噪聲圖像之間的差異,但它也可能使模型更難以從數據中學習有用的特征,并可能導致過度擬合或欠擬合。 所以最好從少量噪聲開始,然后在監控模型性能的同時逐漸增加噪聲。
import cv2
import numpy as np
# Load the image
image = cv2.imread('dog.jpg')
# Add Gaussian noise to the image
noise_std = 50
noise = np.random.randn(*image.shape) * noise_std
noisy_image = np.clip(image + noise, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
# Display the original and noisy images
cv2.imshow('Original Image', image)
cv2.imshow('Noisy Image', noisy_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
高斯噪聲如何用于深度學習的一些示例。
- 數據增強:高斯噪聲在深度學習中的一種常見用途是在訓練期間將其添加到輸入數據中。 例如可以在每個圖像通過模型之前添加高斯噪聲。 這將迫使模型學習對輸入中的微小變化具有魯棒性的特征,這些噪聲可以代表圖像上的污跡或輕微的缺失。 因此即使圖像與訓練數據略有不同,模型也更有可能正確識別圖像。
- Dropout:高斯噪聲在深度學習中的另一個用途是在訓練期間將其添加到神經網絡的權重中。 這被稱為Dropout。 在訓練過程中,dropout 以一定的概率(例如 0.5)隨機將網絡中的一些權重設置為零。 這迫使網絡學習數據的多個冗余表示,使模型更健壯且不易過度擬合。
- 正則化:將高斯噪聲添加到模型的參數中也可以看作是一種正則化技術。 它迫使模型具有更小的權重值,這反過來又使模型更通用并且更不容易過度擬合。
- 對抗訓練:對抗性示例是專門為欺騙模型而設計的輸入,在對抗訓練中,模型是在用小的、有針對性的擾動增強的例子上訓練的,比如高斯噪聲。 這使得模型對對抗性示例更加穩健。
- 半監督學習:訓練時可以在輸入數據中加入高斯噪聲,提高半監督模型的性能。 這可以幫助模型更好地利用有限的標記數據并學習更多的一般特征。
- 遷移學習:微調時可以在輸入數據中加入高斯噪聲,以提高遷移學習模型的性能。 這可以幫助模型更好地適應新任務并更好地泛化到看不見的數據。
- 生成對抗網絡 (GAN):可以將高斯噪聲添加到生成器輸入中,以提高生成樣本的多樣性。
- 貝葉斯深度學習:訓練時可以在模型的權重中加入高斯噪聲,使其對過擬合具有更強的魯棒性,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 強化學習:在訓練過程中,可以在代理的輸入或動作空間中加入高斯噪聲,使其對環境變化具有更強的魯棒性,提高智能體的泛化能力。
在上述所有示例中,高斯噪聲通過特定的均值和標準差,以受控方式添加到輸入或權重。 目標是提高模型的性能和魯棒性,同時又不會讓模型很難從數據中學習。
下面我們介紹如何在使用 Python 和 Keras在訓練期間將高斯噪聲添加到輸入數據,說明如何在訓練期間將高斯噪聲添加到輸入數據,然后再將其傳遞給模型:
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# Define the data generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset
samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0
featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset
samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std
zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening
rotation_range=0, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180)
width_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width)
height_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images
vertical_flip=False, # randomly flip images
noise_std=0.5 # add gaussian noise to the data with std of 0.5
)
# Use the generator to transform the data during training
model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32),
steps_per_epoch=len(x_train) / 32, epochs=epochs)
Keras 的 ImageDataGenerator 類用于定義一個數據生成器,該數據生成器將指定的數據增強技術應用于輸入數據。 我們將 noise_std 設置為 0.5,這意味著標準偏差為 0.5 的高斯噪聲將添加到輸入數據中。 然后在調用 model.fit_generator 期間使用生成器在訓練期間將數據擴充應用于輸入數據。
至于Dropout,可以使用Keras中的Dropout層,設置dropout的rate,如果設置rate為0.5,那么dropout層會drop掉50%的權重。 以下是如何向模型添加 dropout 層的示例:
from keras.layers import Dropout
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
需要注意的是,標準差、Dropout的實際值將取決于具體問題和數據的特征。使用不同的值進行試驗并監視模型的性能通常是一個好主意。
下面我們介紹使用Keras 在訓練期間將高斯噪聲添加到輸入數據和權重。為了向輸入數據添加噪聲,我們可以使用 numpy 庫生成隨機噪聲并將其添加到輸入數據中。 這是如何執行此操作的示例:
import numpy as np
# Generate some random input data
x_train = np.random.rand(1000, 64)
y_train = np.random.rand(1000, 10)
# Add Gaussian noise to the input data
noise_std = 0.5
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape)
# Train the model
model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
我們輸入數據 x_train 是形狀為 (1000, 64) 的二維數組,噪聲是使用 np.random.randn(*x_train.shape) 生成的,它將返回具有相同形狀的正態分布均值為 0,標準差為 1的隨機值數組。然后將生成的噪聲與噪聲的標準差 (0.5) 相乘,并將其添加到輸入數據中,從而將其添加到輸入數據中。
為了給權重添加噪聲,我們可以使用 Keras 中的 Dropout 層,它會在訓練過程中隨機丟棄一些權重。 高斯噪聲是深度學習中廣泛使用的技術,在圖像分類訓練時可以在圖像中加入高斯噪聲,提高圖像分類模型的魯棒性。 這在訓練數據有限或具有很大可變性時特別有用,因為模型被迫學習對輸入中的小變化具有魯棒性的特征。
以下是如何在訓練期間向圖像添加高斯噪聲以提高圖像分類模型的魯棒性的示例:
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# Define the data generator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset
samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0
featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset
samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std
zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening
rotation_range=0, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180)
width_shift_range=0, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width)
height_shift_range=0, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images
vertical_flip=False, # randomly flip images
noise_std=0.5 # add gaussian noise to the data with std of 0.5
)
# Use the generator to transform the data during training
model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32),
steps_per_epoch=len(x_train) / 32, epochs=epochs)
目標檢測:在目標檢測模型的訓練過程中,可以將高斯噪聲添加到輸入數據中,以使其對圖像中的微小變化(例如光照條件、遮擋和攝像機角度)更加魯棒。
def add_noise(image, std):
"""Add Gaussian noise to an image."""
noise = np.random.randn(*image.shape) * std
return np.clip(image + noise, 0, 1)
# Add noise to the training images
x_train_noisy = np.array([add_noise(img, 0.1) for img in x_train])
# Train the model
model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
語音識別:在訓練過程中,可以在音頻數據中加入高斯噪聲,這可以幫助模型更好地處理音頻信號中的背景噪聲和其他干擾,提高語音識別模型的魯棒性。
def add_noise(audio, std):
"""Add Gaussian noise to an audio signal."""
noise = np.random.randn(*audio.shape) * std
return audio + noise
# Add noise to the training audio
x_train_noisy = np.array([add_noise(audio, 0.1) for audio in x_train])
# Train the model
model.fit(x_train_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
生成模型:在 GAN、Generative Pre-training Transformer (GPT) 和 VAE 等生成模型中,可以在訓練期間將高斯噪聲添加到輸入數據中,以提高模型生成新的、看不見的數據的能力。
# Generate random noise
noise = np.random.randn(batch_size, 100)
# Generate fake images
fake_images = generator.predict(noise)
# Add Gaussian noise to the fake images
fake_images_noisy = fake_images + 0.1 * np.random.randn(*fake_images.shape)
# Train the discriminator
discriminator.train_on_batch(fake_images_noisy, np.zeros((batch_size, 1)))
在這個例子中,生成器被訓練為基于隨機噪聲作為輸入生成新的圖像,并且在生成的圖像傳遞給鑒別器之前,將高斯噪聲添加到生成的圖像中。這提高了生成器生成新的、看不見的數據的能力。
對抗訓練:在對抗訓練時,可以在輸入數據中加入高斯噪聲,使模型對對抗樣本更加魯棒。
下面的對抗訓練使用快速梯度符號法(FGSM)生成對抗樣本,高斯噪聲為 在訓練期間將它們傳遞給模型之前添加到對抗性示例中。 這提高了模型對對抗性示例的魯棒性。
# Generate adversarial examples
x_adv = fgsm(model, x_train, y_train, eps=0.01)
# Add Gaussian noise to the adversarial examples
noise_std = 0.05
x_adv_noisy = x_adv + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_adv.shape)
# Train the model
model.fit(x_adv_noisy, y_train, epochs=10)
去噪:可以將高斯噪聲添加到圖像或信號中,模型的目標是學習去除噪聲并恢復原始信號。下面的例子中輸入圖像“x_train”首先用標準的高斯噪聲破壞 0.1 的偏差,然后將損壞的圖像通過去噪自動編碼器以重建原始圖像。 自動編碼器學習去除噪聲并恢復原始信號。
# Add Gaussian noise to the images
noise_std = 0.1
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape)
# Define the denoising autoencoder
input_img = Input(shape=(28, 28, 1))
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
# at this point the representation is (7, 7, 32)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(encoded)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
decoded = Conv2D(1, (3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')(x)
autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded)
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary
異常檢測:高斯噪聲可以添加到正常數據中,模型的目標是學習將添加的噪聲作為異常檢測。
# Add Gaussian noise to the normal data
noise_std = 0.1
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_std * np.random.randn(*x_train.shape)
# Concatenate the normal and the noisy data
x_train_concat = np.concatenate((x_train, x_train_noisy))
y_train_concat = np.concatenate((np.zeros(x_train.shape[0]), np.ones(x_train_noisy.shape[0])))
# Train the anomaly detection model
model.fit(x_train_concat, y_train_concat, epochs=10)
穩健優化:在優化過程中,可以將高斯噪聲添加到模型的參數中,使其對參數中的小擾動更加穩健。
Define the loss function
def loss_fn(params):
model.set_weights(params)
return model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=32)[0]
# Define the optimizer
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(1e-3)
# Define the step function
def step_fn(params):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
loss = loss_fn(params)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, params)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, params))
return params + noise_std * np.random.randn(*params.shape)
# Optimize the model
params = model.get_weights()
高斯噪聲是深度學習中用于為輸入數據或權重添加隨機性的一種技術。 它是一種通過將均值為零且標準差 (σ) 正態分布的隨機值添加到輸入數據中而生成的隨機噪聲。 向數據中添加噪聲的目的是使模型對輸入中的小變化更健壯,并且能夠更好地處理看不見的數據。 高斯噪聲可用于廣泛的應用,例如圖像分類、對象檢測、語音識別、生成模型和穩健優化。