使用PyTorch實(shí)現(xiàn)混合專家(MoE)模型
Mixtral 8x7B 的推出在開放 AI 領(lǐng)域引發(fā)了廣泛關(guān)注,特別是混合專家(Mixture-of-Experts:MoEs)這一概念被大家所認(rèn)知。混合專家(MoE)概念是協(xié)作智能的象征,體現(xiàn)了“整體大于部分之和”的說法。MoE模型匯集了各種專家模型的優(yōu)勢(shì),以提供更好的預(yù)測。它是圍繞一個(gè)門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)和一組專家網(wǎng)絡(luò)構(gòu)建的,每個(gè)專家網(wǎng)絡(luò)都擅長特定任務(wù)的不同方面
在本文中,我將使用Pytorch來實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)MoE模型。在具體代碼之前,讓我們先簡單介紹一下混合專家的體系結(jié)構(gòu)。
MoE架構(gòu)
MoE由兩種類型的網(wǎng)絡(luò)組成:(1)專家網(wǎng)絡(luò)和(2)門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)。
專家網(wǎng)絡(luò):專家網(wǎng)絡(luò)是專有模型,每個(gè)模型都經(jīng)過訓(xùn)練,在數(shù)據(jù)的一個(gè)子集中表現(xiàn)出色。MoE的理念是擁有多名優(yōu)勢(shì)互補(bǔ)的專家,確保對(duì)問題空間的全面覆蓋。
門控網(wǎng)絡(luò):門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)充當(dāng)指揮,協(xié)調(diào)或管理個(gè)別專家的貢獻(xiàn)。它學(xué)習(xí)(或權(quán)衡)哪個(gè)網(wǎng)絡(luò)擅長處理哪種類型的輸入。經(jīng)過訓(xùn)練的門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)可以評(píng)估新的輸入向量,并根據(jù)專家的熟練程度將處理責(zé)任分配給最合適的專家或?qū)<医M合。門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)根據(jù)專家的輸出與當(dāng)前輸入的相關(guān)性動(dòng)態(tài)調(diào)整其權(quán)重,確保定制響應(yīng)。
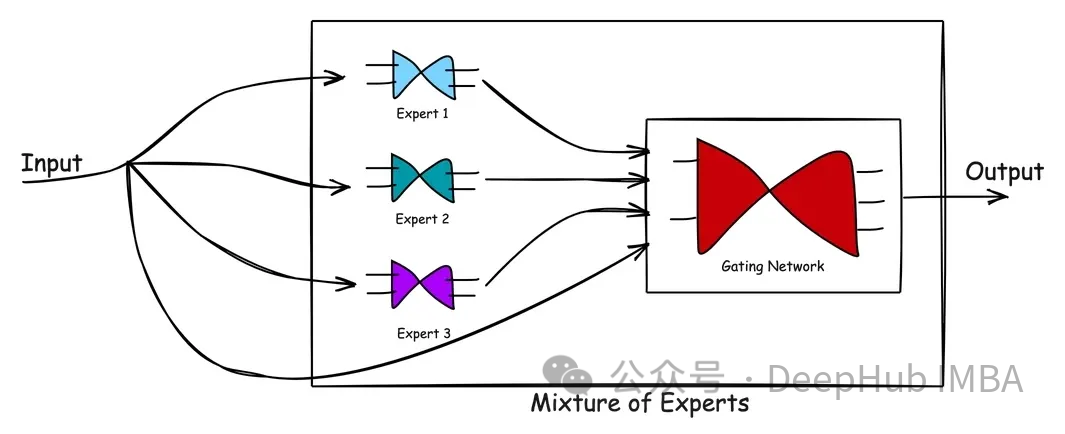
上圖顯示了MoE中的處理流程。混合專家模型的優(yōu)點(diǎn)在于它的簡單。通過學(xué)習(xí)復(fù)雜的問題空間以及專家在解決問題時(shí)的反應(yīng),MoE模型有助于產(chǎn)生比單個(gè)專家更好的解決方案。門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)作為一個(gè)有效的管理者,評(píng)估情景并將任務(wù)傳遞給最佳專家。當(dāng)新數(shù)據(jù)輸入時(shí),模型可以通過重新評(píng)估專家對(duì)新輸入的優(yōu)勢(shì)來適應(yīng),從而產(chǎn)生靈活的學(xué)習(xí)方法。
MoE為部署機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)模型提供了巨大的好處。以下是兩個(gè)顯著的好處。
MoE的核心優(yōu)勢(shì)在于其專家網(wǎng)絡(luò)的多元化和專業(yè)化。MoE的設(shè)置能夠以單一模型可能難以達(dá)到的精度處理多方面的問題。
MoE具有固有的可伸縮性。隨著任務(wù)復(fù)雜性的增加,可以在不改變其他專家模型的情況下將更多專家無縫地集成到系統(tǒng)中,擴(kuò)大專業(yè)知識(shí)的范圍。也就是說,MoE可以幫助將預(yù)先訓(xùn)練過的專家打包到機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)系統(tǒng)中。
混合專家模型在許多領(lǐng)域都有應(yīng)用,包括推薦系統(tǒng)、語言建模和各種復(fù)雜的預(yù)測任務(wù)。有傳言稱,GPT-4是由多個(gè)專家組成的。盡管我們無法確認(rèn),但類似gpt -4的模型將通過MoE方法利用多個(gè)模型的力量來提供最佳結(jié)果。
Pytorch代碼
我們這里不討論Mixtral 8x7B這種大模型中使用的MOE技術(shù),而是我們編寫一個(gè)簡單的、可以應(yīng)用在任何任務(wù)中的自定義MOE,通過代碼我們可以了解MOE的工作原理,這樣對(duì)理解MOE在大模型中的工作方式是非常有幫助的。
下面我們將一段一段地介紹PyTorch的代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)。
導(dǎo)入庫:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim定義專家模型:
class Expert(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
super(Expert, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.layer1(x))
return torch.softmax(self.layer2(x), dim=1)這里我們定義了一個(gè)簡單的專家模型,可以看到它是一個(gè)2層的mlp,使用了relu激活,最后使用softmax輸出分類概率。
定義門控模型:
# Define the gating model
class Gating(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim,
num_experts, dropout_rate=0.1):
super(Gating, self).__init__()
# Layers
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, 128)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(128, 256)
self.leaky_relu1 = nn.LeakyReLU()
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.layer3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.leaky_relu2 = nn.LeakyReLU()
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.layer4 = nn.Linear(128, num_experts)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.layer1(x))
x = self.dropout1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.leaky_relu1(x)
x = self.dropout2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.leaky_relu2(x)
x = self.dropout3(x)
return torch.softmax(self.layer4(x), dim=1)門控模型更復(fù)雜,有三個(gè)線性層和dropout層用于正則化以防止過擬合。它使用ReLU和LeakyReLU激活函數(shù)引入非線性。最后一層的輸出大小等于專家的數(shù)量,并對(duì)這些輸出應(yīng)用softmax函數(shù)。輸出權(quán)重,這樣可以將專家的輸出與之結(jié)合。
說明:其實(shí)門控網(wǎng)絡(luò),或者叫路由網(wǎng)絡(luò)是MOE中最復(fù)雜的部分,因?yàn)樗婕暗娇刂戚斎氲侥莻€(gè)專家模型,所以門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)也有很多個(gè)設(shè)計(jì)方案,例如(如果我沒記錯(cuò)的話)Mixtral 8x7B 只是取了8個(gè)專家中的top2。所以我們這里不詳細(xì)討論各種方案,只是介紹其基本原理和代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)。
完整的MOE模型:
class MoE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, trained_experts):
super(MoE, self).__init__()
self.experts = nn.ModuleList(trained_experts)
num_experts = len(trained_experts)
# Assuming all experts have the same input dimension
input_dim = trained_experts[0].layer1.in_features
self.gating = Gating(input_dim, num_experts)
def forward(self, x):
# Get the weights from the gating network
weights = self.gating(x)
# Calculate the expert outputs
outputs = torch.stack(
[expert(x) for expert in self.experts], dim=2)
# Adjust the weights tensor shape to match the expert outputs
weights = weights.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(outputs)
# Multiply the expert outputs with the weights and
# sum along the third dimension
return torch.sum(outputs * weights, dim=2)這里主要看前向傳播的代碼,通過輸入計(jì)算出權(quán)重和每個(gè)專家給出輸出的預(yù)測,最后使用權(quán)重將所有專家的結(jié)果求和最終得到模型的輸出。
這個(gè)是不是有點(diǎn)像“集成學(xué)習(xí)”。
測試
下面我們來對(duì)我們的實(shí)現(xiàn)做個(gè)簡單的測試,首先生成一個(gè)簡單的數(shù)據(jù)集:
# Generate the dataset
num_samples = 5000
input_dim = 4
hidden_dim = 32
# Generate equal numbers of labels 0, 1, and 2
y_data = torch.cat([
torch.zeros(num_samples // 3),
torch.ones(num_samples // 3),
torch.full((num_samples - 2 * (num_samples // 3),), 2) # Filling the remaining to ensure exact num_samples
]).long()
# Biasing the data based on the labels
x_data = torch.randn(num_samples, input_dim)
for i in range(num_samples):
if y_data[i] == 0:
x_data[i, 0] += 1 # Making x[0] more positive
elif y_data[i] == 1:
x_data[i, 1] -= 1 # Making x[1] more negative
elif y_data[i] == 2:
x_data[i, 0] -= 1 # Making x[0] more negative
# Shuffle the data to randomize the order
indices = torch.randperm(num_samples)
x_data = x_data[indices]
y_data = y_data[indices]
# Verify the label distribution
y_data.bincount()
# Shuffle the data to ensure x_data and y_data remain aligned
shuffled_indices = torch.randperm(num_samples)
x_data = x_data[shuffled_indices]
y_data = y_data[shuffled_indices]
# Splitting data for training individual experts
# Use the first half samples for training individual experts
x_train_experts = x_data[:int(num_samples/2)]
y_train_experts = y_data[:int(num_samples/2)]
mask_expert1 = (y_train_experts == 0) | (y_train_experts == 1)
mask_expert2 = (y_train_experts == 1) | (y_train_experts == 2)
mask_expert3 = (y_train_experts == 0) | (y_train_experts == 2)
# Select an almost equal number of samples for each expert
num_samples_per_expert = \
min(mask_expert1.sum(), mask_expert2.sum(), mask_expert3.sum())
x_expert1 = x_train_experts[mask_expert1][:num_samples_per_expert]
y_expert1 = y_train_experts[mask_expert1][:num_samples_per_expert]
x_expert2 = x_train_experts[mask_expert2][:num_samples_per_expert]
y_expert2 = y_train_experts[mask_expert2][:num_samples_per_expert]
x_expert3 = x_train_experts[mask_expert3][:num_samples_per_expert]
y_expert3 = y_train_experts[mask_expert3][:num_samples_per_expert]
# Splitting the next half samples for training MoE model and for testing
x_remaining = x_data[int(num_samples/2)+1:]
y_remaining = y_data[int(num_samples/2)+1:]
split = int(0.8 * len(x_remaining))
x_train_moe = x_remaining[:split]
y_train_moe = y_remaining[:split]
x_test = x_remaining[split:]
y_test = y_remaining[split:]
print(x_train_moe.shape,"\n", x_test.shape,"\n",
x_expert1.shape,"\n",
x_expert2.shape,"\n", x_expert3.shape)這段代碼創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)合成數(shù)據(jù)集,其中包含三個(gè)類標(biāo)簽——0、1和2。基于類標(biāo)簽對(duì)特征進(jìn)行操作,從而在數(shù)據(jù)中引入一些模型可以學(xué)習(xí)的結(jié)構(gòu)。
數(shù)據(jù)被分成針對(duì)個(gè)別專家的訓(xùn)練集、MoE模型和測試集。我們確保專家模型是在一個(gè)子集上訓(xùn)練的,這樣第一個(gè)專家在標(biāo)簽0和1上得到很好的訓(xùn)練,第二個(gè)專家在標(biāo)簽1和2上得到更好的訓(xùn)練,第三個(gè)專家看到更多的標(biāo)簽2和0。
我們期望的結(jié)果是:雖然每個(gè)專家對(duì)標(biāo)簽0、1和2的分類準(zhǔn)確率都不令人滿意,但通過結(jié)合三位專家的決策,MoE將表現(xiàn)出色。
模型初始化和訓(xùn)練設(shè)置:
# Define hidden dimension
output_dim = 3
hidden_dim = 32
epochs = 500
learning_rate = 0.001
# Instantiate the experts
expert1 = Expert(input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim)
expert2 = Expert(input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim)
expert3 = Expert(input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim)
# Set up loss
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Optimizers for experts
optimizer_expert1 = optim.Adam(expert1.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
optimizer_expert2 = optim.Adam(expert2.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
optimizer_expert3 = optim.Adam(expert3.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)實(shí)例化了專家模型和MoE模型。定義損失函數(shù)來計(jì)算訓(xùn)練損失,并為每個(gè)模型設(shè)置優(yōu)化器,在訓(xùn)練過程中執(zhí)行權(quán)重更新。
訓(xùn)練的步驟也非常簡單
# Training loop for expert 1
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer_expert1.zero_grad()
outputs_expert1 = expert1(x_expert1)
loss_expert1 = criterion(outputs_expert1, y_expert1)
loss_expert1.backward()
optimizer_expert1.step()
# Training loop for expert 2
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer_expert2.zero_grad()
outputs_expert2 = expert2(x_expert2)
loss_expert2 = criterion(outputs_expert2, y_expert2)
loss_expert2.backward()
optimizer_expert2.step()
# Training loop for expert 3
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer_expert3.zero_grad()
outputs_expert3 = expert3(x_expert3)
loss_expert3 = criterion(outputs_expert3, y_expert3)
loss_expert3.backward()每個(gè)專家使用基本的訓(xùn)練循環(huán)在不同的數(shù)據(jù)子集上進(jìn)行單獨(dú)的訓(xùn)練。循環(huán)迭代指定數(shù)量的epoch。
下面是我們MOE的訓(xùn)練
# Create the MoE model with the trained experts
moe_model = MoE([expert1, expert2, expert3])
# Train the MoE model
optimizer_moe = optim.Adam(moe_model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer_moe.zero_grad()
outputs_moe = moe_model(x_train_moe)
loss_moe = criterion(outputs_moe, y_train_moe)
loss_moe.backward()
optimizer_moe.step()MoE模型是由先前訓(xùn)練過的專家創(chuàng)建的,然后在單獨(dú)的數(shù)據(jù)集上進(jìn)行訓(xùn)練。訓(xùn)練過程類似于單個(gè)專家的訓(xùn)練,但現(xiàn)在門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)的權(quán)值在訓(xùn)練過程中更新。
最后我們的評(píng)估函數(shù):
# Evaluate all models
def evaluate(model, x, y):
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(x)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
correct = (predicted == y).sum().item()
accuracy = correct / len(y)
return accuracyevaluate函數(shù)計(jì)算模型在給定數(shù)據(jù)上的精度(x代表樣本,y代表預(yù)期標(biāo)簽)。準(zhǔn)確度計(jì)算為正確預(yù)測數(shù)與預(yù)測總數(shù)之比。
結(jié)果如下:
accuracy_expert1 = evaluate(expert1, x_test, y_test)
accuracy_expert2 = evaluate(expert2, x_test, y_test)
accuracy_expert3 = evaluate(expert3, x_test, y_test)
accuracy_moe = evaluate(moe_model, x_test, y_test)
print("Expert 1 Accuracy:", accuracy_expert1)
print("Expert 2 Accuracy:", accuracy_expert2)
print("Expert 3 Accuracy:", accuracy_expert3)
print("Mixture of Experts Accuracy:", accuracy_moe)
#Expert 1 Accuracy: 0.466
#Expert 2 Accuracy: 0.496
#Expert 3 Accuracy: 0.378
#Mixture of Experts Accuracy: 0.614可以看到
專家1正確預(yù)測了測試數(shù)據(jù)集中大約46.6%的樣本的類標(biāo)簽。
專家2表現(xiàn)稍好,正確預(yù)測率約為49.6%。
專家3在三位專家中準(zhǔn)確率最低,正確預(yù)測的樣本約為37.8%。
而MoE模型顯著優(yōu)于每個(gè)專家,總體準(zhǔn)確率約為61.4%。
總結(jié)
我們測試的輸出結(jié)果顯示了混合專家模型的強(qiáng)大功能。該模型通過門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)將各個(gè)專家模型的優(yōu)勢(shì)結(jié)合起來,取得了比單個(gè)專家模型更高的精度。門控網(wǎng)絡(luò)有效地學(xué)習(xí)了如何根據(jù)輸入數(shù)據(jù)權(quán)衡每個(gè)專家的貢獻(xiàn),以產(chǎn)生更準(zhǔn)確的預(yù)測。混合專家利用了各個(gè)模型的不同專業(yè)知識(shí),在測試數(shù)據(jù)集上提供了更好的性能。
同時(shí)也說明我們可以在現(xiàn)有的任務(wù)上嘗試使用MOE來進(jìn)行測試,也可以得到更好的結(jié)果。