用 GroundingDINO 與 SAM 做分割
在計算機視覺領域,圖像分割是一項核心任務,廣泛應用于目標識別、追蹤和分析等多個場景。本文將介紹一種新穎的方法,利用兩個基于變換器模型的零樣本圖像分割技術:GroundingDINO負責目標檢測,而單任務注意力模型(SAM)負責語義分割。我們將詳細解讀代碼,并解釋涉及的關鍵概念。現在,讓我們先來了解一些重要的術語!

Grounding DINO與SAM的結合
1. 變換器模型
這類神經網絡架構在自然語言處理領域取得了革命性的進展,如翻譯、摘要和文本生成等任務。它們通過多層處理輸入序列(例如單詞或字符),并通過注意力機制關注輸入的不同部分。設想一個翻譯者使用變換器模型將英文句子翻譯成其他語言。在翻譯“the quick brown fox”時,模型可能會先關注“the”,然后是“quick”,逐步將信息整合進翻譯中。
變換器模型的設計使其能夠有效處理長距離依賴問題,并實現并行計算,這使得它們在處理序列數據時表現出色。在本文中,我們將應用GroundingDINO和SAM這兩個變換器模型。

2. 目標檢測與語義分割
這是計算機視覺中的兩個基礎任務。目標檢測通過邊界框定位圖像中的目標對象,而語義分割則為圖像中的每個像素分配類別標簽。目標檢測提供了對象的位置信息,語義分割則提供了對象與背景的詳細分割。

3. 零樣本學習
這是一種機器學習技術,允許模型在未針對特定任務進行訓練的情況下執行任務。模型通過利用其他相關任務的知識來執行新任務。在本文中,我們將利用零樣本學習技術,根據用戶提供的文本標簽描述來分割圖像中的對象,即使模型未曾針對這些標簽進行過訓練。
可以通過https://colab.research.google.com/訪問Google Colab編寫代碼:
#app.py
!pip install spaces
from transformers import AutoProcessor, AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection
import torch
from transformers import SamModel, SamProcessor
import spaces
import numpy as np
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
sam_model = SamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base").to("cuda")
sam_processor = SamProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
model_id = "IDEA-Research/grounding-dino-base"
dino_processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
dino_model = AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection.from_pretrained(model_id).to(device)
def infer_dino(img, text_queries, score_threshold):
queries=""
for query in text_queries:
queries += f"{query}. "
width, height = img.shape[:2]
target_sizes=[(width, height)]
inputs = dino_processor(text=queries, images=img, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = dino_model(**inputs)
outputs.logits = outputs.logits.cpu()
outputs.pred_boxes = outputs.pred_boxes.cpu()
results = dino_processor.post_process_grounded_object_detection(outputs=outputs, input_ids=inputs.input_ids,
box_threshold=score_threshold,
target_sizes=target_sizes)
return results
@spaces.GPU
def query_image(img, text_queries, dino_threshold):
text_queries = text_queries
text_queries = text_queries.split(",")
dino_output = infer_dino(img, text_queries, dino_threshold)
result_labels=[]
for pred in dino_output:
boxes = pred["boxes"].cpu()
scores = pred["scores"].cpu()
labels = pred["labels"]
box = [torch.round(pred["boxes"][0], decimals=2), torch.round(pred["boxes"][1], decimals=2),
torch.round(pred["boxes"][2], decimals=2), torch.round(pred["boxes"][3], decimals=2)]
for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels):
if label != "":
inputs = sam_processor(
img,
input_boxes=[[[box]]],
return_tensors="pt"
).to("cuda")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = sam_model(**inputs)
mask = sam_processor.image_processor.post_process_masks(
outputs.pred_masks.cpu(),
inputs["original_sizes"].cpu(),
inputs["reshaped_input_sizes"].cpu()
)[0][0][0].numpy()
mask = mask[np.newaxis, ...]
result_labels.append((mask, label))
return img, result_labels
import gradio as gr
description = "This Space combines [GroundingDINO](https://huggingface.co/IDEA-Research/grounding-dino-base), a bleeding-edge zero-shot object detection model with [SAM](https://huggingface.co/facebook/sam-vit-base), the state-of-the-art mask generation model. SAM normally doesn't accept text input. Combining SAM with OWLv2 makes SAM text promptable. Try the example or input an image and comma separated candidate labels to segment."
demo = gr.Interface(
query_image,
inputs=[gr.Image(label="Image Input"), gr.Textbox(label = "Candidate Labels"), gr.Slider(0, 1, value=0.05, label="Confidence Threshold for GroundingDINO")],
outputs="annotatedimage",
title="GroundingDINO ?? SAM for Zero-shot Segmentation",
description=description,
examples=[
["./cats.png", "cat, fishnet", 0.16],["./bee.jpg", "bee, flower", 0.16]
],
)
demo.launch(debug=True)代碼解析:
(1) 代碼首先通過pip安裝必要的包,并導入所需的庫,包括PyTorch、GroundingDINO、SAM和Gradio。
(2) GroundingDINO是一個基于變換器的目標檢測模型。它可以根據圖像和文本描述輸出與描述相對應的對象的邊界框。在本代碼中,我們利用GroundingDINO根據用戶指定的文本標簽來定位圖像中的對象。
(3) 單任務注意力模型(SAM)是另一個基于變換器的模型,用于圖像到圖像的翻譯任務,如語義分割。SAM模型可以根據圖像和文本描述生成與描述中對象相對應的分割掩碼。在本文中,我們將使用SAM根據GroundingDINO提供的邊界框進行對象的語義分割。
(4) 代碼根據可用性設置運行代碼的設備(GPU或CPU)。
(5) 加載SAM模型和GroundingDINO模型,并將它們的處理器轉移到GPU以加快計算速度。
(6) infer_dino()函數接受圖像、文本查詢(候選標簽)和置信度閾值作為輸入,并使用GroundingDINO模型處理輸入,識別具有邊界框的對象檢測。
(7) query_image()函數用@spaces.GPU裝飾器裝飾,表示它將在GPU上運行。這個函數接受圖像、文本查詢和置信度閾值作為輸入。
(8) query_image()首先將文本查詢分割成單獨的標簽,并將其傳遞給infer_dino()函數以獲取對象檢測和邊界框。
(9) 對于每個對象檢測,它使用SAM模型生成掩碼,即將對象的邊界框傳遞給SAM模型,并為每個對象生成一個掩碼。
(10) 最后,函數返回帶有生成的掩碼和相應標簽的圖像。
(11) 代碼定義了一個Gradio演示,接受圖像、候選標簽和置信度閾值作為輸入,并返回帶有生成的掩碼和標簽的注釋圖像,同時提供示例輸入以供演示。
(12) 啟動Gradio演示,并顯示用戶界面。
運行代碼后,我們將獲得Gradio空間鏈接:
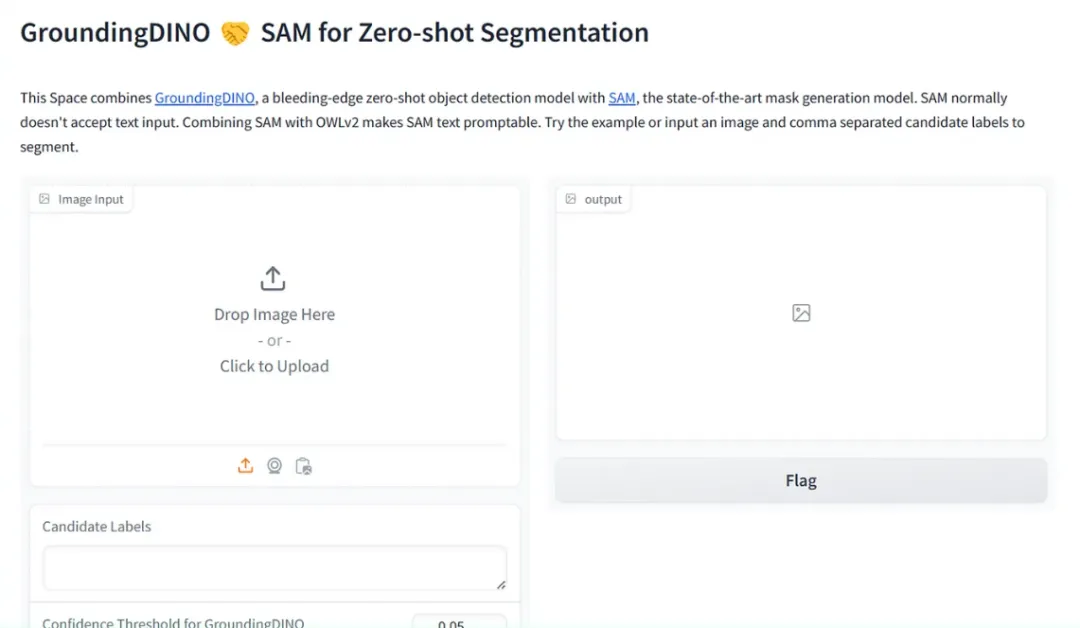
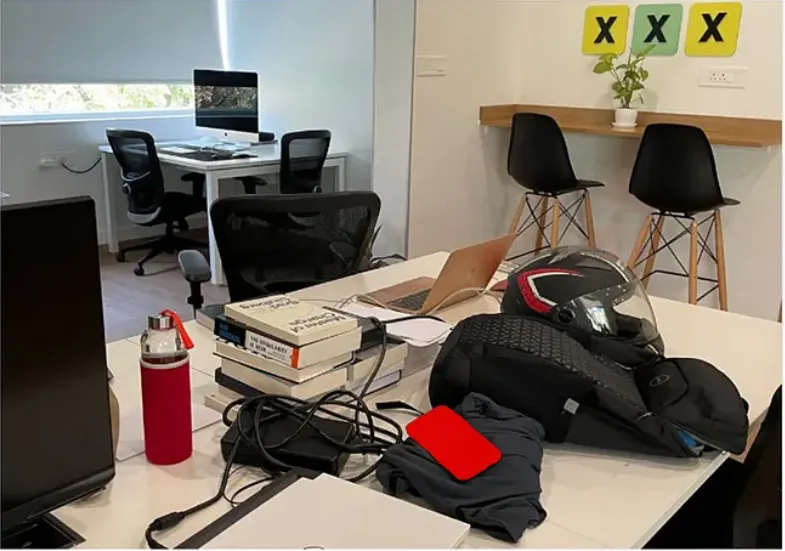
結果展示(紅色涂抹)

完整代碼:https://github.com/jyotidabass/GroundingSAM-Gradio-App/blob/main/GroundingSAM.ipynb








































