借助HuggingFace輕松實施一個端到端項目 原創
本文介紹了使用FastAPI和Docker生成一個隨時可用的Hugging Face模型。
?想象一下,利用Hugging Face模型來確定評論的情緒。在過去,第一步是制作這樣一個模型,并確保它正常工作。
然而,今天的預訓練模型讓我們只需花很少的精力,就能準備好這樣的大語言模型(LLM)。
一旦我們準備好使用這個模型,主要目標是讓公司的同事能夠使用這個模型,而不需要下載或從頭開始實現它。
為此,我們將創建一個端點API,使用戶能夠獨立地調用和使用模型。這就是我們所說的從頭到尾構建的端到端項目。
今天,我們將使用Hugging Face、FastAPI和Docker部署一個簡單的模型,演示如何有效地實現這個目標。
第1步:選擇我們的Hugging Face模型
首先要做的是選擇一個適合我們需要的Hugging Face模型。我們可以使用以下命令在我們的環境中輕松安裝Hugging Face:
pip install transformers
# remember to work with transformers we need either tensorflow or pytorch
installed as well
pip install torch
pip install tensorflow現在,我們需要導入Transformer庫的管道命令。
from transformers import pipeline然后,使用pipeline命令,我們可以輕松生成一個模型來定義特定文本的情緒。我們可以使用兩種不同的方法來做到這一點:通過定義任務“情緒分析”或通過定義模型,如下面的代碼所示。
# Defining directly the task we want to implement.
pipe = pipeline(task="sentiment-analysis")
# Defining the model we choose.
pipe = pipeline(model="model-to-be-used")值得一提的是,不建議使用基于任務的方法,因為它限制了我們對所使用的特定模型的控制。
在本文例子中,我選擇了“distilbert-base-uncase-fine tuned-sst-2-english”,但你可以隨意瀏覽Hugging Face Hub,選擇適合需要的任何型號。你可以在下面的文章(https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/what-is-hugging-face)中找到Hugging Face的簡單指南。
pipe =
pipeline(model="distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english")我們已定義了管道模型,只需發送一個簡單的提示,就可以返回結果。比如說,輸入以下命令:
print(pipe("This tutorial is great!"))我們將得到[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998689889907837}]
想象一下,我們希望我們的用戶得到一個關于這個分類的自然語言句子。我們也可以實施簡單的Python代碼同樣實現這個目的:
def generate_response(prompt:str):
response = pipe("This is a great tutorial!")
label = response[0]["label"]
score = response[0]["score"]
return f"The '{prompt}' input is {label} with a score of {score}"
print(generate_response("This tutorial is great!"))重復同樣的試驗,我們會得到:
The 'This tutorial is great!' input is POSITIVE with a score of
0.9997909665107727現在我們有了一個切實可行的模型,可以繼續定義我們的API。
第2步:使用FastAPI為模型編寫API端點
為了定義API,我們將使用FastAPI。它是一個用于構建高性能Web API的Python框架。首先,使用pip命令安裝FastAPI庫,并將其導入到我們的環境中。此外,我們將利用pydantic庫來確保輸入是所需的類型。
下面的代碼將生成切實可行的API,我們的同事可以直接使用。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from transformers import pipeline
# You can check any other model in the Hugging Face Hub
pipe =
pipeline(model="distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english")
# We define the app
app = FastAPI()
# We define that we expect our input to be a string
class RequestModel(BaseModel):
input: str
# Now we define that we accept post requests
@app.post("/sentiment")
def get_response(request: RequestModel):
prompt = request.input
response = pipe(prompt)
label = response[0]["label"]
score = response[0]["score"]
return f"The '{prompt}' input is {label} with a score of {score}"下面是代碼中逐步發生的事情:
- 導入必要的庫:代碼先導入FastAPI和Pydantic,確保我們收發的數據結構正確。
- 加載模型:加載一個預訓練的情緒分析模型,正如我們在第一步中所做的那樣。
- 設置FastAPI應用程序:app = FastAPI()初始化FastAPI應用程序,使其準備好處理請求。
- 定義請求模型:使用Pydantic,定義RequestModel類。該類指定了我們期望輸入字符串,確保API只接受正確格式的數據。
- 創建端點:@app.post("/sentiment")裝飾器告訴FastAPI,當向/sentiment端點發出POST請求時,應該觸發該函數。get_response函數接受RequestModel對象作為輸入,輸入含有我們想要分析的文本。
- 處理請求:在get_response函數中,從請求中提取文本并傳遞給模型(pipe(prompt))。模型返回帶有情緒標簽(比如”POSITIVE”或“NEGATIVE”)的響應和表示預測置信度的分數。
- 返回響應:最后,函數返回格式化的字符串,其中包含輸入文本、情緒標簽和置信度分數,為用戶提供一個清晰而簡潔的結果。
如果我們執行代碼,API將在本地主機中可用,如下圖所示:
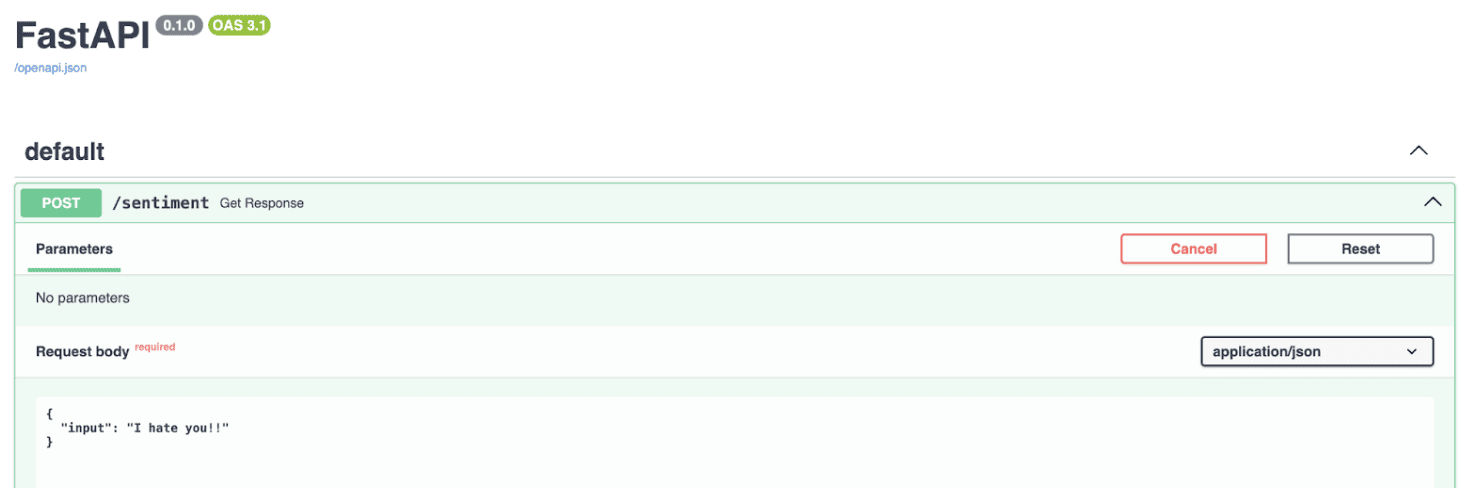
簡而言之,這段代碼設置簡單的Web服務,你可以往該服務發送一段文本,其給出的回復是分析該文本的情緒,通過FastAPI充分利用Hugging Face模型的強大功能。
接下來,我們應該將應用程序容器化,以便可以在任何地方執行,而不僅僅是在本地計算機上執行。這將確保更好的可移植性和易于部署。
第3步:使用Docker運行我們的模型
容器化需要將應用程序放入容器中。Docker容器運行Docker鏡像的實例,這包括它自己的操作系統和應用程序所需的所有依賴項。
比如說,你可以在容器中安裝Python和所有必需的包,這樣它可以在任何地方運行,不需要安裝這些庫。
為了在Docker容器中運行我們的情緒分析應用程序,我們先需要創建Docker鏡像。這個過程包括寫一個Dockerfile,指定Docker鏡像應該含有什么。
如果你的系統沒有安裝Docker,可以從Docker的網站上下載。這是我們將在這個項目中使用的Dockerfile,在存儲庫中名為Dockerfile。
# Use an official Python runtime as a parent image
FROM python:3.10-slim
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /sentiment
# Copy the requirements.txt file into the root
COPY requirements.txt .
# Copy the current directory contents into the container at /app as well
COPY ./app ./app
# Install any needed packages specified in requirements.txt
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
# Make port 8000 available to the world outside this container
EXPOSE 8000
# Run main.py when the container launches, as it is contained under the app
folder, we define app.main
CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8000"]然后,我們只需要在終端中運行以下命令來構建Docker鏡像。
docker build -t sentit-app然后為了執行,我們有兩個選項:
使用帶有命令的終端。
docker run -p 8000:8000 --name name_of_cointainer sentiment-hf使用docker hub。我們很容易進入docker hub,點擊鏡像的運行按鈕。
這就是全部細節!現在,我們有了一個切實可行的情緒分類模型,它可以在任何地方工作,并且可以使用API來執行。
結語
具體流程如下:
- 模型選擇和設置:選擇和配置一個Hugging Face預訓練模型進行情緒分析,確保它滿足你的要求。
- 使用FastAPI進行API開發:使用FastAPI創建API端點,實現與情緒分析模型的輕松交互。
- Docker容器化:使用Docker容器化應用程序,以確保可移植性和跨不同環境的無縫部署。
你可以在下面的GitHub代碼庫中查看我的全部代碼:https://github.com/rfeers/data-science-portfolio/tree/main/end-to-end-projects/simple-docker-hf-model。
原文標題:A Simple to Implement End-to-End Project with HuggingFace,作者:Josep Ferrer
鏈接:
https://www.kdnuggets.com/a-simple-to-implement-end-to-end-project-with-huggingface。

















